
Goniatids, informally goniatites, are ammonoid cephalopods that form the order Goniatitida, derived from the more primitive Agoniatitida during the Middle Devonian some 390 million years ago. Goniatites (goniatitids) survived the Late Devonian extinction to flourish during the Carboniferous and Permian only to become extinct at the end of the Permian some 139 million years later.
Agathiceras is a subglobose goniatitid from the family Agathiceratidae, widespread and locally abundant in Lower Pennsylvanian to Middle Permian sediments, e.g. the Urals, Sicily, and Texas.
Beyrichoceras is a genus belonging to the goniatitid family Muensteroceratidae, a group of ammonoids, extinct shelled cephalopods related to belemnites and recent coleoids and more distantly to the nautiloids

Beyrichoceras is a genus belonging to the goniatitid family Maxigoniatitidae that lived during the Mississippian Period
Ussuria is a genus of Lower Triassic ammonites with a smooth, involute discoidal shell with submonophyllic sutures, belonging to the ceratitid family Ussuriidae.
Prolobitidae is a family of middle and upper Devonian ammonoid cephalopods currently included in the goniatitid suborder Tornoceratina and superfamily Dimeroceratoidea, but previously included in the ancestral Anarcestida.
The Posttornoceratidae are Late Devonian goniatites (Ammonoidea) included in the superfamily Tornoceratoidea. The family, Posttornoceratidae, named by Bogoslovsky in 1962, is based on the genus Posttornoceras, named by Wedekind in 1910, originally included in the Tornoceratidae.

Gastrioceratoidea is one of 17 superfamilies in the suborder Goniatitina, ammonoid cephalopods from the Late Paleozoic.
Adrianitidae is a family in the Adrianitaceae, a superfamily of ammonites in the cephalopod order, Goniatitida, known from the Middle Pennsylvanian to the Middle Permian.
Thalassoceratidae a family of late Paleozoic ammonites included in the goniatitid superfamily Thalassoceratoidea along with the Bisatoceratidae. Some eight genera are included, although the specific number and exactly which depends on the particular classification.

Medlicottiidae is a family of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the Prolecanitida, known from the Upper Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) to the Early Triassic.

Prolecanitida is an order of extinct ammonoid cephalopods, the major Late Paleozoic group of ammonoids alongside the order Goniatitida. Prolecanitids had narrow shells, discoidal (disc-shaped) to thinly lenticular (lens-shaped). They retained a retrochoanitic siphuncle, a simple form with septal necks extending backwards. As is typical for ammonoids, the siphuncle sits along the ventral margin of the shell.

Prolecanitoidea is a taxonomic superfamily of ammonoids in the order Prolecanitida. Prolecanitoidea is one of two superfamilies in the order, along with the younger and more complex Medlicottioidea. The Prolecanitoidea were a low-diversity and morphologically conservative group. They lived from the Lower Carboniferous up to the Middle Permian. Their shells are generally smooth and discoidal, with a rounded lower edge, a moderate to large umbilicus, and goniatitic to ceratitic sutures. Suture complexity varies from 10 up to 22 total lobes ; new lobes are added from subdivision of saddles adjacent to the original main umbilical lobe.
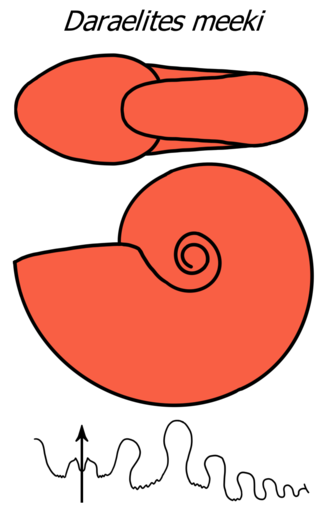
The Daraelitidae form a family in the ammonoid order Prolecanitida from the Upper Mississippian - Middle Permian characterized by discoidal shells with no prominent sculpture, moderately large umbilicus, and goniatitic or ceratitic sutures with a trifid ventral lobe and few auxiliary lobes.

Clyclolobus is a smooth, essentially involute subdiscoidal goniatitid ammonoid that has sutures with a bifurcate ventral lobe, flared outwardly at the end, in which the halves may be secondarily trifurcated, ending in sharp, narrow projections. Lateral sutural elements follow an acuate line that swings first to the front, then sharply to the rear before becoming hidden by the next whorl. Saddles are narrow, cumulous in appearance with short, irregular, rounded sub-endings. Ventro-lateal lobes are trifurcate with pointed, thorn-like projections.
Pachylyroceras is a large, generally subglobular, Upper Mississippian gonitite and included in the cephalopod subclass Ammonoidea.
Cravevoceras is an Upper Paleozoic ammonite in the goniatite family Cravenoceratidae, probably derived from Pachylyroceras and contemporary with other cravenoceratid genera like Caenolyroceras, Tympanoceras and later Alaoceras and Lyrogoniatites. It is also a member of the Neoglyphioceratoidea.

The Medlicottiinae is a subfamily of the Medlicottiidae, a family of ammonoid cephalopods included in the Prolecanitida, characterized by having discoidal to thinly lenticular shells with a retuse (grooved) venter and sutures with bifid auxiliary lobes.
Neoglaphyrites is a goniatitid ammonite that lived during the latest Pennsylvanian and early Permian. Its shell is ellipsoidal and moderately involute; the umbilicus deep and typically less than 15 per cent of the shell diameter but in some species closer to 20 per cent. Delicate growth lines forming ventral and lateral sinuses and ventrolateral and dorsolateral salients have been found on Canadian Arctic specimens. The suture is characterized by the ventral lobe split into two broad prongs that are separated by a high median ventral saddle; prongs closely approximate the width of the first lateral lobe. The first lateral saddle is evenly rounded and is nearly symmetrical. The umbilical lobe is V-shaped and internal lobes are deep and narrow.
Pronorites is a prolecanitid genus from the middle and upper Carboniferous, upper Mississippian and Pennsylvanian. Distribution is wide spread.






