
The Aouzou Strip is a strip of land in northern Chad that lies along the border with Libya, extending south to a depth of about 100 kilometers into Chad's Borkou, Ennedi Ouest, Ennedi Est, and Tibesti regions for an area of 114,000 km2. It is named after the small town and oasis of Aouzou. The strip played a significant role in the Chadian–Libyan War when it was claimed by Libya.

United Nations Security Council resolution 986, adopted unanimously on 14 April 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on Iraq and noting the serious humanitarian situation with the Iraqi civilian population, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, established a mechanism whereby Iraqi oil exports would finance humanitarian aid to the country, which later became known as the Oil-for-Food Programme.

The Case Concerning the Territorial Dispute [1994] is a public international law case decided by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) concerning the border between the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya and the Republic of Chad. The case was put forward to settle a territorial dispute between the two countries, particularly over a strip of land called the Aouzou Strip which Libya had occupied since the Chadian–Libyan War, and an area which Libya called the Libya–Chad Borderlands or simply the Borderlands. Libya's claim to the Borderlands included parts of the regions of Borkou, Ennedi and Tibesti, including parts of the localities of Erdi, Kanem and Ounianga. It also covered the Chadian region of B.E.T., excluding northern Kanem.
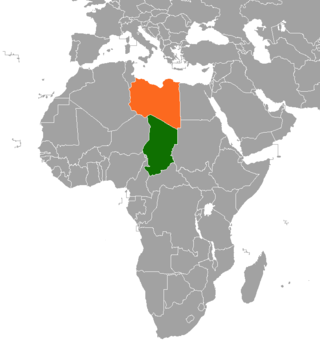
Chad–Libya relations have arisen out of centuries from ethnic, religious, and commercial ties.

United Nations Security Council resolution 850, adopted unanimously on 9 July 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 782 (1992), 797 (1992) and 818 (1993) on the situation in Mozambique, the Council discussed the implementation of the Rome General Peace Accords and the formation of a new armed forces in the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 867, adopted unanimously on 23 September 1993, after recalling resolutions 841 (1993), 861 (1993) and 862 (1993) on the situation in Haiti, the council reiterated its position of protecting international peace and stability and established the United Nations Mission in Haiti (UNMIH).

United Nations Security Council resolution 872, adopted unanimously on 5 October 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 812 (1993) and 846 (1993) on the situation in Rwanda and Resolution 868 (1993) on the security of United Nations operations, the council stressed the need for an international force in the country and therefore established the United Nations Assistance Mission for Rwanda (UNAMIR).

United Nations Security Council resolution 880, adopted unanimously on 4 November 1993, after recalling Resolution 745 (1992) and other relevant resolutions on Cambodia, the Council concerned itself with the withdrawal of the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) from the country.

UN Security Council Resolution 883, adopted on 11 November 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 731 (1992) and 748 (1992), the council noted that, twenty months later, Libya had not complied with previous Security Council resolutions and as a consequence imposed further international sanctions on the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 887, adopted unanimously on 29 November 1993, after considering a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali regarding the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF), the Council noted its efforts to establish a durable and just peace in the Middle East.

United Nations Security Council resolution 902, adopted unanimously on 11 March 1994, after receiving a report from the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali pursuant to Resolution 880 (1993), the council discussed confidence-building measures between the Republic of Cyprus and Northern Cyprus with the aim of resolving the Cyprus dispute.

United Nations Security Council resolution 910, adopted unanimously on 14 April 1994, after considering a letter by the UN Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali advising of his intention to send a reconnaissance team to the Aouzou Strip disputed between Chad and Libya, the Council decided to exempt the reconnaissance mission from a provision in Resolution 748 (1992) that imposed international sanctions on Libya.
United Nations Security Council resolution 920, adopted unanimously on 26 May 1994, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992), 784 (1992), 791 (1992), 832 (1993), 888 (1993), the council discussed the implementation of peace agreements in El Salvador and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) until 30 November 1994.

United Nations Security Council resolution 926, adopted unanimously on 13 June 1994, after reaffirming Resolution 915 (1994), the Council commended the work of the United Nations Aouzou Strip Observer Group (UNASOG) and the co-operation of Libya and Chad and decided, with immediate effect, to terminate the UNASOG mission in the Aouzou Strip.

United Nations Security Council resolution 945, adopted unanimously on 29 September 1994, after reaffirming Resolution 696 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on Angola, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 31 October 1994 and discussed the implementation of peace agreements.

United Nations Security Council resolution 962, adopted unanimously on 29 November 1994, after considering a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali regarding the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF), the Council noted its efforts to establish a durable and just peace in the Middle East.

United Nations Security Council resolution 968, adopted unanimously on 16 December 1994, after noting statements by the president of the security council and reports by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali on the situation in Tajikistan, the council established the United Nations Mission of Observers in Tajikistan (UNMOT) and addressed the process of national reconciliation in the country.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1021, adopted on November 22, 1995, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, particularly resolutions 713 (1991) and 727 (1992), the Council set a date of March 13, 1996, for the suspension of most aspects of the arms embargo on the former Yugoslavia. Resolution 1074 (1996) terminated the remaining measures of the embargo.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1031, adopted unanimously on 15 December 1995, after recalling all previous resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, discussed the transfer of authority from the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) to the multinational Implementation Force (IFOR).

The United Nations Aouzou Strip Observer Group (UNASOG) was a United Nations observation mission that was deployed to the Aouzou Strip, in the Republic of Chad. Established in the wake of the Aouzou Strip dispute under Security Council Resolution 915 of 4 April 1994, the mission's mandate was "to verify the withdrawal of the Libyan administration and forces from the Aouzou Strip in accordance with the decision of the International Court of Justice", rendered on 3 February 1994 in the Libya–Chad Territorial Dispute case.


















