
United Nations Security Council resolution 780 was adopted unanimously on 6 October 1992. After reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and subsequent resolutions on the topic, the Council expressed its concern at the continued "widespread violations of international humanitarian law" in Bosnia and Herzegovina and authorised the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to establish a Commission of Experts to examine and analyse the information submitted pursuant to Resolution 771 (1992) on violations of the Geneva Conventions in the region.
United Nations Security Council resolution 749, adopted unanimously on 7 April 1992, after reaffirming resolutions 713 (1991), 721 (1991), 724 (1991), 727 (1992), 740 (1992) and 743 (1992), the Council approved of a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali and decided to authorise the earliest possible deployment of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) in the former Yugoslavia.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 781 was adopted on 9 October 1992. After reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and all the subsequent resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, the Council decided to impose a ban on military flights in the airspace over Bosnia and Herzegovina, acting in accordance with the provisions set out in Resolution 770 (1992).
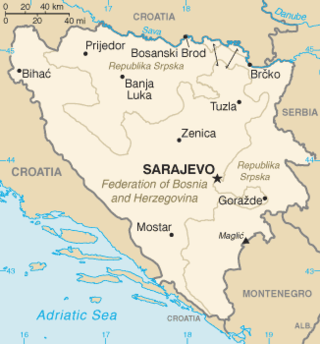
United Nations Security Council resolution 820, adopted on 17 April 1993, after reaffirming all previous resolutions on the topic for a lasting peace settlement in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the region, the council discussed the peace plan for Bosnia and Herzegovina and comprehensive steps to ensure its implementation.

United Nations Security Council resolution 842, adopted unanimously on 18 June 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 743 (1992) concerning the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) and Resolution 795 (1992) which authorised its presence in the Republic of Macedonia, the Council welcomed an increase in the number of peacekeeping personnel in the country.
United Nations Security Council resolution 871, adopted unanimously on 4 October 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 713 (1992) and 743 (1992) and subsequent resolutions relating to the situation in the former Yugoslavia and United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the Council expressed concern that United Nations peacekeeping plan for Croatia, in particular Resolution 769 (1992), had not been implemented and went on to discuss the peace plan and extend UNPROFOR's mandate until 31 March 1994.

United Nations Security Council resolution 942, adopted on 23 September 1994, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council reinforced measures relating to safe areas under control of Bosnian Serb forces.

United Nations Security Council resolution 958, adopted unanimously on 19 November 1994, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia including Resolution 836 (1993), the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, determined that the situation in the former Yugoslavia continued to constitute a threat to international peace and security and in its support of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), authorised the use of air strikes in Croatia in addition to Bosnia and Herzegovina by member states, in order for UNPROFOR to carry out its mandate. UNPROFOR was authorised to use air force independently, via direct member states support or via regional organizations. Subsequent air force interventions in Udbina airfield and other locations in Croatia and Bosnia, were conducted with NATO support.
United Nations Security Council resolution 970, adopted on 12 January 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina in particular Resolution 943 (1994) concerning the border closure between the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council decided that measures in that resolution would be suspended for a further period of 100 days.
United Nations Security Council resolution 982, adopted unanimously on 31 March 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia in particular Resolution 947 (1994) concerning the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR), the Council extended the mandate of UNPROFOR for additional period terminating 30 November 1995 and discussed operations in Croatia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 988, adopted on 21 April 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, in particular resolutions 943 (1994) and 970 (1995), the Council noted measures by the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia to continue the border closure with Bosnia and Herzegovina and therefore extended the partial suspension of sanctions against Serbia and Montenegro for a further 75 days until 5 July 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 990, adopted unanimously on 28 April 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, particularly resolutions 981 (1995) and 982 (1995), the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, authorised the deployment of the United Nations Confidence Restoration Operation in Croatia (UNCRO).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1031, adopted unanimously on 15 December 1995, after recalling all previous resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, discussed the transfer of authority from the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) to the multinational Implementation Force (IFOR).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1038, adopted unanimously on 15 January 1996, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995) and 1025 (1995), the Council authorised the United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1066, adopted unanimously on 15 July 1996, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995), 1025 (1995) and 1038 (1996), the Council authorised military observers to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia until 15 January 1997.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1093, adopted unanimously on 14 January 1997, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995), 1025 (1995), 1038 (1996) and 1066 (1996), the Council authorised the United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka (UNMOP) to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia until 15 July 1997.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1119, adopted unanimously on 14 July 1997, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995), 1025 (1995), 1038 (1996), 1066 (1996) and 1093 (1997), the Council authorised the United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka (UNMOP) to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia until 15 January 1998.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1147, adopted unanimously on 13 January 1998, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995), 1025 (1995), 1038 (1996), 1066 (1996), 1093 (1997) and 1119 (1997), the Council authorised the United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka (UNMOP) to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia until 15 July 1998.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1183, adopted unanimously on 15 July 1998, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995) and 1147 (1998), the Council authorised the United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka (UNMOP) to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia until 15 January 1999.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1222, adopted unanimously on 15 January 1999, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995), 1147 (1998) and 1183 (1998), the Council authorised the United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka (UNMOP) to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia until 15 July 1999.















