
The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.
The United Nations General Assembly has granted observer status to international organizations, entities, and non-member states, to enable them to participate in the work of the United Nations General Assembly, though with limitations. The General Assembly determines the privileges it will grant to each observer, beyond those laid down in a 1986 Conference on treaties between states and international organizations. Exceptionally, the European Union (EU) was in 2011 granted the right to speak in debates, to submit proposals and amendments, the right of reply, to raise points of order and to circulate documents, etc. As of May 2011, the EU is the only international organization to hold these enhanced rights, which has been likened to the rights of full membership, short of the right to vote.

The United Nations Security Council veto power is the power of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council to veto any decision other than a "procedural" decision.

United Nations Security Council resolution 702, adopted without a vote on 8 August 1991, after examining separately the applications of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea and the Republic of Korea for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that North Korea and South Korea be admitted.

United Nations Security Council resolution 704, adopted without a vote on 9 August 1991, after examining the application of the Marshall Islands for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that the Marshall Islands be admitted.

United Nations Security Council resolution 763, adopted without a vote on 6 July 1992, after examining the application of the Republic of Georgia for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Georgia be admitted.
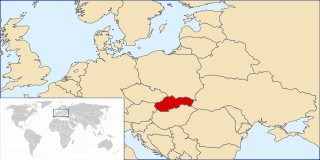
United Nations Security Council resolution 800, adopted without a vote on 8 January 1993, after examining the application of the Slovak Republic for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Slovakia be admitted.

United Nations Security Council resolution 801, adopted without a vote on 8 January 1993, after examining the application of the Czech Republic for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that the Czech Republic be admitted.

United Nations Security Council resolution 817, adopted unanimously on 7 April 1993, after examining the application of the Republic of Macedonia for membership in the United Nations, the council recommended to the General Assembly that Macedonia be admitted to membership in the United Nations, this State being provisionally referred to for all purposes within the United Nations as "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" pending settlement of the difference that has arisen over the name of the State.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 829, adopted without a vote on 26 May 1993, after examining the application of the Principality of Monaco for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Monaco be admitted.

United Nations Security Council resolution 848, adopted without a vote on 8 July 1993, after examining the application of the Principality of Andorra for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Andorra be admitted.
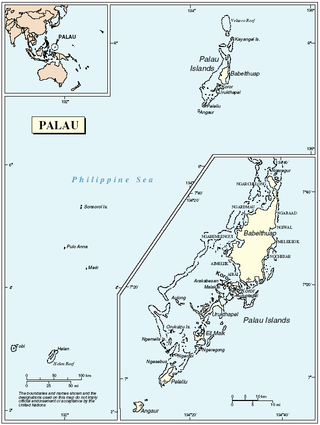
United Nations Security Council resolution 956, adopted unanimously on 10 November 1994, after recalling Chapter XII of the United Nations Charter which established the United Nations Trusteeship system and Resolution 21 (1947) which approved the Trusteeship Territory of the Japanese Mandated Islands, the Council determined that, in the light of entry into force of a new status agreement for the Republic of Palau, the objectives of the Trusteeship Agreement had been completed and therefore ended the status of Palau as a Trust Territory.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1426, adopted without a vote on 24 July 2002, after examining the application of the Swiss Confederation for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Switzerland be admitted.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1691, regarding the accession of Montenegro to the United Nations, was adopted without a vote on 22 June 2006. In the resolution, after examining the country's application for membership, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that it be admitted.
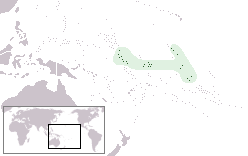
United Nations Security Council resolution 1248, adopted without a vote on 25 June 1999, after examining the application of the Republic of Kiribati for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Kiribati be admitted, bringing total membership of the United Nations to 186.
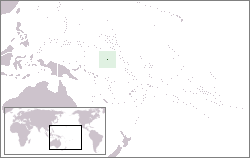
United Nations Security Council resolution 1249, adopted on 25 June 1999, after examining the application of the Republic of Nauru for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Nauru be admitted, bringing total membership of the United Nations to 187.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1414, adopted without a vote on 23 May 2002, after examining the application of the Democratic Republic of East Timor (Timor-Leste) for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that East Timor be admitted.

The Republic of Korea and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea were simultaneously admitted to the United Nations (UN) in 1991. On 8 August 1991, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 702, recommending both states to the General Assembly for membership. On 17 September 1991, the General Assembly admitted both countries under Resolution 46/1.

Democratic Federal Yugoslavia was a charter member of the United Nations from its establishment in 1945 as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia until 1992 during the Yugoslav Wars. During its existence the country played a prominent role in the promotion of multilateralism and narrowing of the Cold War divisions in which various UN bodies were perceived as important vehicles. Yugoslavia was elected a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council on multiple occasions in periods between 1950 and 1951, 1956, 1972–1973, and 1988–1989, which was in total 7 years of Yugoslav membership in the organization. The country was also one of 17 original members of the Special Committee on Decolonization.


















