Related Research Articles

The organized environmental movement is represented by a wide range of non-governmental organizations or NGOs that seek to address environmental issues in the United States. They operate on local, national, and international scales. Environmental NGOs vary widely in political views and in the ways they seek to influence the environmental policy of the United States and other governments.

The environmental movement, is a social movement that aims to protect the natural world from harmful environmental practices in order to create sustainable living. Environmentalists advocate the just and sustainable management of resources and stewardship of the environment through changes in public policy and individual behavior. In its recognition of humanity as a participant in ecosystems, the movement is centered on ecology, health, as well as human rights.

Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physics, biology, and geography to the study of the environment, and the solution of environmental problems. Environmental science emerged from the fields of natural history and medicine during the Enlightenment. Today it provides an integrated, quantitative, and interdisciplinary approach to the study of environmental systems.

A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated due to their toxicity, flammability and the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and that of HFC refrigerants to climate change.

Joseph J. Romm is an American researcher, author, editor, physicist and climate expert, who advocates reducing greenhouse gas emissions to limit global warming and increasing energy security through energy efficiency and green energy technologies. Romm is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. In 2009, Rolling Stone magazine named Romm to its list of "100 People Who Are Changing America", and Time magazine named him one of its "Heroes of the Environment (2009)", calling him "The Web's most influential climate-change blogger".
The Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, or Assembly Bill (AB) 32, is a California State Law that fights global warming by establishing a comprehensive program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from all sources throughout the state. AB32 was co-authored by then-Assemblymember Fran Pavley and then-Speaker of the California Assembly Fabian Nunez and signed into law by Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger on September 27, 2006.
The U.S. Senate Environment and Public Works Subcommittee on Public Sector Solutions to Global Warming, Oversight, Children's Health Protection was one of the six subcommittees of the U.S. Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works. Created in 2007, the subcommittee has general oversight jurisdiction over the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency as well as diverse issues such as global warming, children's health protection, and the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA).
The U.S. Senate Environment and Public Works Subcommittee on Transportation and Infrastructure is a subcommittee of the U.S. Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works.
The United States Senate Environment and Public Works Subcommittee on Private Sector and Consumer Solutions to Global Warming and Wildlife Protection was one of six subcommittees of the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works during the 110th Congress. The subcommittee's jurisdiction included:
The U.S. Senate Environment and Public Works Subcommittee on Chemical Safety, Waste Management, Environmental Justice and Regulatory Oversight is one a subcommittee of the U.S. Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works.
The U.S. Senate Environment and Public Works Subcommittee on Subcommittee on Transportation Safety, Infrastructure Security, and Water Quality was one of six subcommittees of the U.S. Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works.

Frances J. "Fran" Pavley is an American politician who served two terms in the California State Senate and three terms in the California State Assembly. A Democrat, she last represented the 27th Senate District, which encompasses the Conejo Valley, and portions of the San Fernando and Santa Clarita Valleys. Due to term limits in California, Senator Pavley completed her legislative career in 2016. She is currently working as the Environmental Policy Director for the USC Schwarzenegger Institute.

A green-collar worker is a worker who is employed in an environmental sector of the economy. Environmental green-collar workers satisfy the demand for green development. Generally, they implement environmentally conscious design, policy, and technology to improve conservation and sustainability. Formal environmental regulations as well as informal social expectations are pushing many firms to seek professionals with expertise with environmental, energy efficiency, and clean renewable energy issues. They often seek to make their output more sustainable, and thus more favorable to public opinion, governmental regulation, and the Earth's ecology.

The Global Warming Pollution Reduction Act of 2007 (S. 309) was a bill proposed to amend the 1963 Clean Air Act, a bill that aimed to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2). U.S. Senator, Bernie Sanders (I-VT), introduced the resolution in the 110th United States Congress on January 16, 2007. The bill was referred to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works but was not enacted into law.
The America's Climate Security Act of 2007 was a global warming bill that was considered by the United States Senate to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases emitted in the United States. Also known as the Lieberman–Warner bill, bill number S. 2191, the legislation was introduced by Sens. Joseph Lieberman (I-CT) and John Warner (R-VA) on October 18, 2007. The bill was approved by the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works in December 2007, and was debated in the Senate during the week of June 2. The bill would create a national cap-and-trade scheme for greenhouse gas emissions, in which polluters would mostly be allocated right-to-emit credits based on how much greenhouse gas they currently emit. The cap would get tighter over time, until by 2050, emissions would be reduced to 63% below 2005 levels. Several environmental groups expressed their encouragement at the progress in legislation on the global warming issue while at the same time expressing disappointment that the bill did not reduce emissions enough. On June 6, 2008, the bill was killed by Senate Republicans over worries that it would damage the economy.
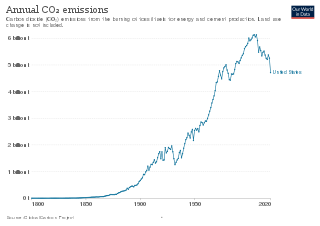
The environmental policy of the United States is a federal governmental action to regulate activities that have an environmental impact in the United States. The goal of environmental policy is to protect the environment for future generations while interfering as little as possible with the efficiency of commerce or the liberty of the people and to limit inequity in who is burdened with environmental costs. As his first official act bringing in the 1970s, President Richard Nixon signed the U.S. National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) into law on New Years Day, 1970. Also in the same year, America began celebrating Earth Day, which has been called "the big bang of U.S. environmental politics, launching the country on a sweeping social learning curve about ecological management never before experienced or attempted in any other nation." NEPA established a comprehensive US national environmental policy and created the requirement to prepare an environmental impact statement for “major federal actions significantly affecting the quality of the environment.” Author and consultant Charles H. Eccleston has called NEPA the world's “environmental Magna Carta”.
New Energy for America was a plan led by Barack Obama and Joe Biden beginning in 2008 to invest in renewable energy sources, reduce reliance on foreign oil, address global warming issues, and create jobs for Americans. The main objective of the New Energy for America plan was to implement clean energy sources in the United States to switch from nonrenewable resources to renewable resources. The plan led by the Obama Administration aimed to implement short-term solutions to provide immediate relief from pain at the pump, and mid- to- long-term solutions to provide a New Energy for America plan. The goals of the clean energy plan hoped to: invest in renewable technologies that will boost domestic manufacturing and increase homegrown energy, invest in training for workers of clean technologies, strengthen the middle class, and help the economy.

Mark Zachary Jacobson is a professor of civil and environmental engineering at Stanford University and director of its Atmosphere/Energy Program. He is also a co-founder of the non-profit, Solutions Project.
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. In total, the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gasses, more than any country in the world.

Energy Tax Prevention Act, also known as H.R. 910, was a 2011 bill in the United States House of Representatives to prohibit the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) from regulating greenhouse gases to address climate change. On April 7, 2011, the bill passed the House by a vote of 255 to 172. The bill died in January 2013 with the ending of the Congressional session.
References
- ↑ Bernie Sanders is an Independent, but caucuses with Democrats on the committee.