Related Research Articles

Kidney stone disease, also known as renal calculus disease, nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material develops in the urinary tract. Renal calculi typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small calculus may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than 5 millimeters, it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A calculus may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a renal calculus are likely to have another within ten years.

Diabetes insipidus (DI), alternately called arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D) or arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R), is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. The amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. Reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. Complications may include dehydration or seizures.

Clinical chemistry is a division in medical laboratory sciences focusing on qualitative tests of important compounds, referred to as analytes or markers, in bodily fluids and tissues using analytical techniques and specialized instruments. This interdisciplinary field includes knowledge from medicine, biology, chemistry, biomedical engineering, informatics, and an applied form of biochemistry.
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be absent, mild or severe. Mild symptoms include a decreased ability to think, headaches, nausea, and poor balance. Severe symptoms include confusion, seizures, and coma; death can ensue.

Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly, often due to high intensity exercise over a short period of time. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some of the muscle breakdown products, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and can cause acute kidney injury.

Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L while levels less than 2.1 mmol/L are defined as hypocalcemic. Mildly low levels that develop slowly often have no symptoms. Otherwise symptoms may include numbness, muscle spasms, seizures, confusion, or cardiac arrest.
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemia. Those with a mild increase that has developed slowly typically have no symptoms. In those with greater levels or rapid onset, symptoms may include abdominal pain, bone pain, confusion, depression, weakness, kidney stones or an abnormal heart rhythm including cardiac arrest.
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) is a group of metabolic abnormalities that can occur as a complication from the treatment of cancer, where large amounts of tumor cells are killed off (lysed) from the treatment, releasing their contents into the bloodstream. This occurs most commonly after the treatment of lymphomas and leukemias and in particular when treating non-Hodgkin lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. This is a potentially fatal complication and patients at increased risk for TLS should be closely monitored while receiving chemotherapy and should receive preventive measures and treatments as necessary. TLS can also occur on its own although this is less common.
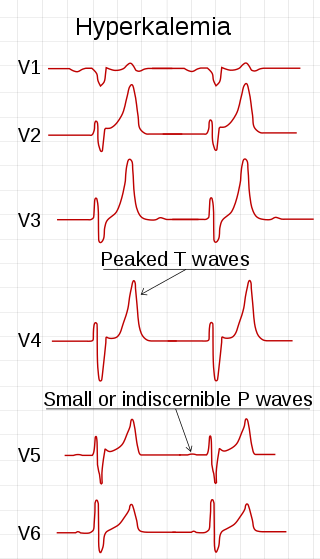
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.5 mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasionally when severe it can cause palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, or numbness. Hyperkalemia can cause an abnormal heart rhythm which can result in cardiac arrest and death.

Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid–base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by consuming too little or too much electrolyte as well as excreting too little or too much electrolyte. Examples of electrolytes include calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, and sodium.

A urine test is any medical test performed on a urine specimen. The analysis of urine is a valuable diagnostic tool because its composition reflects the functioning of many body systems, particularly the kidneys and urinary system, and specimens are easy to obtain. Common urine tests include the routine urinalysis, which examines the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of the urine; urine drug screening; and urine pregnancy testing.
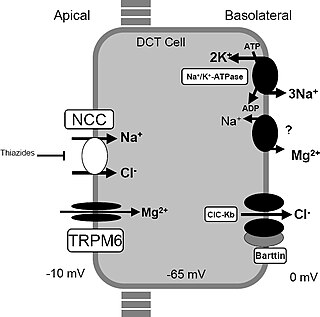
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. It is the most frequent hereditary salt-losing tubulopathy. Gitelman syndrome is caused by disease-causing variants on both alleles of the SLC12A3 gene. The SLC12A3 gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter, which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney.
The anion gap is a value calculated from the results of multiple individual medical lab tests. It may be reported with the results of an electrolyte panel, which is often performed as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel.
Magnesium deficiency is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is a low level of magnesium in the body. It can result in multiple symptoms. Symptoms include tremor, poor coordination, muscle spasms, loss of appetite, personality changes, and nystagmus. Complications may include seizures or cardiac arrest such as from torsade de pointes. Those with low magnesium often have low potassium.

Metabolic alkalosis is a metabolic condition in which the pH of tissue is elevated beyond the normal range (7.35–7.45). This is the result of decreased hydrogen ion concentration, leading to increased bicarbonate, or alternatively a direct result of increased bicarbonate concentrations. The condition typically cannot last long if the kidneys are functioning properly.

Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare inherited disease characterised by a defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which results in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic. A closely associated disorder, Gitelman syndrome, is milder than both subtypes of Bartter syndrome.
Phosphate nephropathy or nephrocalcinosis is an adverse renal condition that arises with a formation of phosphate crystals within the kidney's tubules. This renal insufficiency is associated with the use of oral sodium phosphate (OSP) such as C.B. Fleet's Phospho soda and Salix's Visocol, for bowel cleansing prior to a colonoscopy.
Ethylene glycol poisoning is poisoning caused by drinking ethylene glycol. Early symptoms include intoxication, vomiting and abdominal pain. Later symptoms may include a decreased level of consciousness, headache, and seizures. Long term outcomes may include kidney failure and brain damage. Toxicity and death may occur after drinking even in a small amount as ethylene glycol is more toxic than other diols.
Post-mortem chemistry, also called necrochemistry or death chemistry, is a subdiscipline of chemistry in which the chemical structures, reactions, processes and parameters of a dead organism is investigated. Post-mortem chemistry plays a significant role in forensic pathology. Biochemical analyses of vitreous humor, cerebrospinal fluid, blood and urine is important in determining the cause of death or in elucidating forensic cases.
A renal diet is a diet aimed at keeping levels of fluids, electrolytes, and minerals balanced in the body in individuals with chronic kidney disease or who are on dialysis. Dietary changes may include the restriction of fluid intake, protein, and electrolytes including sodium, phosphorus, and potassium. Calories may also be supplemented if the individual is losing weight undesirably.
References
- ↑ Reddi, A.S. (2014). Fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base disorders: clinical evaluation and management. Springer. pp. 13−4. ISBN 978-1-4614-9082-1.
- ↑ Kamel, K.S.; Halperin, M.L. (2021). "Use of Urine Electrolytes and Urine Osmolality in the Clinical Diagnosis of Fluid, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Disorders". Kidney International Reports. 6 (5): 1211–1224. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2021.02.003. PMC 8116912 . PMID 34013099. S2CID 233917331.
- ↑ Umbrello, M.; Formenti, P.; Chiumello, D. (2020). "Urine Electrolytes in the Intensive Care Unit: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice". Anesthesia & Analgesia . 131 (5): 1456–1470. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000004994. PMID 33079869. S2CID 220414625.
- ↑ Wu, X. (2010). "Urinalysis: A Review of Methods and Procedures". Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America. 22 (1): 121–128. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2009.10.012. PMID 20193886.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Reference range list from Uppsala University Hospital ("Laborationslista"). Artnr 40284 Sj74a. Issued on April 22, 2008
- ↑ "MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia: Fractional excretion of sodium" . Retrieved 11 July 2022.
- ↑ Lederer, E. (8 January 2021). "Hypokalemia Workup". Medscape . Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- 1 2 medscape.com - Urine Calcium: Laboratory Measurement and Clinical Utility Archived 2011-09-06 at the Wayback Machine By Kevin F. Foley, PhD, DABCC; Lorenzo Boccuzzi, DO. Posted: 12/26/2010; Laboratory Medicine. 2010;41(11):683–686. © 2010 American Society for Clinical Pathology. In turn citing:
- Wu HBA. Tietz Guide to Clinical Laboratory Tests. 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Saunders, Elsevier; 2006.