
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet. Together with other beet cultivars, such as beetroot and chard, it belongs to the subspecies Beta vulgaris subsp. vulgaris but classified as var. saccharifera . Its closest wild relative is the sea beet.

Rusts are fungal plant pathogens of the order Pucciniales causing plant fungal diseases.

Beta vulgaris (beet) is a species of flowering plant in the subfamily Betoideae of the family Amaranthaceae. Economically, it is the most important crop of the large order Caryophyllales. It has several cultivar groups: the sugar beet, of greatest importance to produce table sugar; the root vegetable known as the beetroot or garden beet; the leaf vegetable known as chard or spinach beet or silverbeet; and mangelwurzel, which is a fodder crop. Three subspecies are typically recognised. All cultivars, despite their quite different morphologies, fall into the subspecies Beta vulgaris subsp. vulgaris. The wild ancestor of the cultivated beets is the sea beet.

Chard or Swiss chard is a green leafy vegetable. In the cultivars of the Flavescens Group, the leaf stalks are large and often prepared separately from the leaf blade; the Cicla Group is the leafy spinach beet. The leaf blade can be green or reddish; the leaf stalks are usually white, yellow or red.

Leaf vegetables, also called leafy greens, pot herbs, vegetable greens, or simply greens, are plant leaves eaten as a vegetable, sometimes accompanied by tender petioles and shoots. Leaf vegetables eaten raw in a salad can be called salad greens.

The sea beet, Beta vulgaris subsp. maritima, is a member of the family Amaranthaceae native to the coasts of Europe, northern Africa, and southern Asia.

Beta is a genus in the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae. The best known member is the common beet, Beta vulgaris, but several other species are recognised. Almost all have common names containing the word "beet". Wild Beta species can be found throughout the Atlantic coast of Europe, the Mediterranean coastline, the Near East, and parts of Asia including India.

Erysiphe betae is a fungal plant pathogen. It is a form of powdery mildew that can affect crops of sugar beet, that could cause up to a 30% yield loss. The fungus occurs worldwide in all regions where sugar beet is grown and it also infects other edible crops, e.g. beetroot.
Uromyces striatus is a fungal species and plant pathogen causing rust in Medicago species.

Cercospora beticola is a fungal plant pathogen which typically infects plants of the genus Beta, within the family of Chenopodiaceae. It is the cause of Cercospora leaf spot disease in sugar beets, spinach and swiss chard. Of these hosts, Cercospora leaf spot is the most economically impactful in sugar beets. Cercospora beticola is a deuteromycete fungus that reproduces using conidia. There is no teleomorph stage. C. beticola is a necrotrophic fungus that uses phytotoxins specifically Cercospora beticola toxin (CBT) to kill infected plants. CBT causes the leaf spot symptom and prevents root formation. Yield losses from Cercospora leaf spot are around 20 percent.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. betae is a destructive fungal plant pathogen. It causes Fusarium yellows or fusarium wilt, characterized by yellowing and dwarfing.

Neocamarosporium betae is a plant pathogen infecting Beta vulgaris (beet) and causes Phoma leaf spot. It was originally published and described in 1877 as Pleospora betae before being resolved as Neocamarosporium betae(Berl.) Ariyaw. & K.D. Hyde in 2015. It also causes leaf spot on Spinach plants.

Peronospora farinosa is a species name that has been widely applied to downy mildew on leaves of wild and cultivated Amaranthaceae: Amaranthus, Atriplex, Bassia, Beta, Chenopodium, Halimione, Salsola, Spinacia, etc. However, the species name has been taxonomically rejected as the original description contained reference to multiple species and could not unequivocally be attributed to a species of Peronospora. In the past, some of the species on important crop plants have been given names as formae speciales, notably f.sp. betae on sugar beet and f.sp. spinaciae on spinach. However, phylogentic reconstructions have revealed that these "forms" of Peronospora on different genera and their subdivisions, are distinct species, most of which already have previously published scientific names. Such host specialization possibly also exists with respect to the various wild amaranthaceous species given as hosts of P. farinosa.

Uromyces viciae-fabae var. viciae-fabae is a plant pathogen commonly known as faba-bean rust. The rust is distinguished by the typical rust-like marks on the stem and leaves, causing defoliation and loss of photosynthetic surface along with reduction in yield. The disease is fungal and is autoecious meaning it has one plant host. The rust of faba beans is macrocyclic, or contains 5 spores during its life cycle.

Beet necrotic yellow vein virus (BNYVV) is a plant virus, transmitted by the plasmodiophorid Polymyxa betae. The BNYVV is a member of the genus Benyvirus and is responsible for rhizomania, a disease of sugar beet that causes proliferation of thin rootlets, and leads to a smaller tap root with reduced sugar content. Infected plants are less able to take up water, and wilting can be observed during the warm period of the year. If the infection spreads to the whole plant, vein yellowing, necrosis and yellow spots appear on the leaves, giving the virus its name.

Uromyces is a genus of rust fungi in the family Pucciniaceae. The genus was described by Franz Unger in his 1833 work Die Exantheme der Pflanzen. They have a worldwide distribution but large occurrences happen in North America and Europe.

Uromyces pisi-sativi is a fungal species and plant pathogen. It was originally found on Pea but it is found on a wide range of host plants.
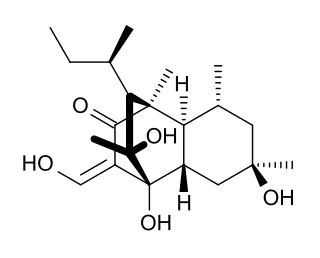
Betaenone A, like other betaenones, is a secondary metabolite isolated from the fungus Pleospora betae, a plant pathogen. Of the seven phytotoxins isolated in fungal leaf spots from sugar beet, it showed 73% growth inhibition.
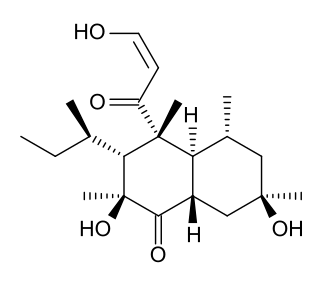
Betaenone C, like other betaenones, is a secondary metabolite isolated from the fungus Pleospora betae, a plant pathogen. Of the seven phytotoxins isolated in fungal leaf spots from sugar beet, it showed 89% growth inhibition. Betaenone C has been shown to act by inhibiting RNA and protein synthesis.

Patellifolia is a genus of flowering plants in the subfamily Betoideae of the family Amaranthaceae. These are mostly procumbent herbs occurring in the Western Mediterranean region and Macaronesia, with some isolated occurrences in North Africa and at the Horn of Africa. They are interesting as crop wild relatives of sugar beet.
















