
Rusts are fungal plant pathogens of the order Pucciniales causing plant fungal diseases.

The Pucciniaceae are a family of rust fungi that cause plant diseases, mainly on cereals such as wheat. The family contains over 4900 species: many of them in the type genus Puccinia.

Alternaria is a genus of Deuteromycetes fungi. All species are known as major plant pathogens. They are also common allergens in humans, growing indoors and causing hay fever or hypersensitivity reactions that sometimes lead to asthma. They are present in the human mycobiome and readily cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised people such as AIDS patients.

Uromyces dianthi is a fungus species and plant pathogen infecting carnations and Euphorbia.
Uromyces euphorbiae is a fungal species and a plant pathogen infecting poinsettias.

Uromyces junci is a fungus species and plant pathogen which causes rust on various plants including (Rushes) Juncus species.
Uromyces betae is a fungal species and plant pathogen infecting beet.

Puccinia recondita is a fungus species and plant pathogen belonging to the order of Pucciniales and family Pucciniaceae.

Leucocoprinus is a genus of fungi in the family Agaricaceae. Its best-known member is the distinctive yellow mushroom Leucocoprinus birnbaumii, which is found in plant pots and greenhouses worldwide. The type species is Leucocoprinus cepistipes. The genus has a widespread distribution and contains over 80 recognised species, however many of these species are very scarcely recorded and little known with only a small number of Leucocoprinus species which are commonly observed. The majority of the species in this genus are exclusive to tropical environments however numerous species have become a common sight in plant pots and greenhouses resulting in them becoming well known worldwide.

Uromyces pisi-sativi is a fungal species and plant pathogen. It was originally found on Pea but it is found on a wide range of host plants.
Kotlabaea is a genus of fungi in the family Pyronemataceae.

Asterina is a large genus of fungi in the Asterinaceae family. It was then placed in Asterinales order later. The genus was circumscribed by French mycologist Joseph-Henri Léveillé in 1845.
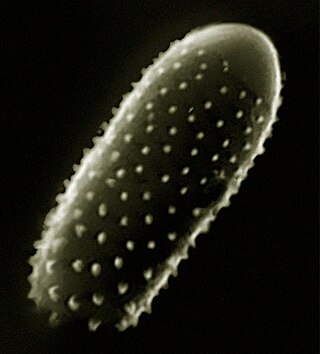
Melampsora is a genus of Basidiomycota fungi. Melampsora species are plant pathogens.
Hans Sydow was a German mycologist and the son of mycologist and lichenologist, Paul Sydow (1851–1925).

Aecidium is a genus of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales.
The Melanotaenium is a genus of smut fungi in the family Melanotaeniaceae.
Victor Félix Schiffner was an Austrian bryologist specializing in the study of hepatics.

František Bubák was a Czech mycologist and phytopathologist.
Heinrich Klebahn was a German mycologist and phytopathologist.
Pucciniosira is a genus of rust fungi belonging to the family Pucciniosiraceae.











