
Podocarpus latifolius is a large evergreen tree up to 35 m high and 3 m trunk diameter, in the conifer family Podocarpaceae; it is the type species of the genus Podocarpus.
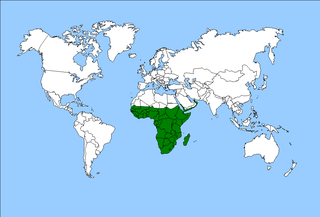
The Afrotropical realm is one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Sub-Saharan Africa, the southern Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region.

Vachellia tortilis, widely known as Acacia tortilis but now attributed to the genus Vachellia, is the umbrella thorn acacia, also known as umbrella thorn and Israeli babool, a medium to large canopied tree native to most of Africa, primarily to the savanna and Sahel of Africa, but also occurring in the Middle East.

Vachellia nilotica, more commonly known as Acacia nilotica, and by the vernacular names of gum arabic tree, babul, thorn mimosa, Egyptian acacia or thorny acacia, is a flowering tree in the family Fabaceae. It is native to Africa, the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent. It is also considered a 'weed of national significance' and an invasive species of concern in Australia, as well as a noxious weed by the federal government of the United States.

Vachellia xanthophloea is a tree in the family Fabaceae, commonly known in English as the fever tree. This species of Vachellia is native to eastern and southern Africa. It has also become a landscape tree in other warm climates, outside of its natural range.

Podocarpus milanjianus is a species of conifer in the family Podocarpaceae. It is native to the highlands and mountains of tropical Africa.

Vachellia is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae, commonly known as thorn trees or acacias. It belongs to the subfamily Mimosoideae. Its species were considered members of genus Acacia until 2009. Vachellia can be distinguished from other acacias by its capitate inflorescences and spinescent stipules. Before discovery of the New World, Europeans in the Mediterranean region were familiar with several species of Vachellia, which they knew as sources of medicine, and had names for them that they inherited from the Greeks and Romans.

Vachellia reficiens, commonly known as red-bark acacia, red thorn, false umbrella tree, or false umbrella thorn, is a deciduous tree or shrub of the pea family (Fabaceae) native to southern Africa, often growing in an upside-down cone shape and with a relatively flat crown.

Baikiaea insignis is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae.

Pittosporum viridiflorum is a protected tree in South Africa.

Vachellia robusta, the splendid thorn, is an Afrotropical tree species.
Newtonia buchananii is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae.

The Northern Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets are a tropical grasslands, savannas and shrublands ecoregion in eastern Africa. The ecoregion is mostly located in Kenya, extending north into southeastern South Sudan, northeastern Uganda and southwestern Ethiopia and south into Tanzania along the Kenya-Tanzania border.

The Southwestern Arabian foothills savanna, also known as the Southwestern Arabian Escarpment shrublands and woodlands, is a desert and xeric shrubland ecoregion of the southern Arabian Peninsula, covering portions of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Oman.

May Be’ati is an exclosure located in the Dogu'a Tembien woreda of the Tigray Region in Ethiopia. The area has been protected since 1968 by the local community.
Sango Bay forests are distinctive forests found in southwestern Uganda, near the border with Tanzania. The Sango Bay forests grow on seasonally-flooded lowlands near on the lower reaches of the Kagera River, just west of where it empties into Lake Nalubaale.

The Leeward Islands xeric scrub ecoregion covers the dry ('xeric'), non-forested areas of the Leeward Islands on the northeastern edge of the Caribbean Sea, stretching from the Virgin Islands in the west to Guadeloupe to the southeast. The non-forested areas are generally low scrub shrub, on the low elevations around the peripheries of the islands. Non-forested lower elevations in the region receive less rainfall and are typically semi-arid. A notable feature of the ecoregion is its position in the main hurricane track. The frequent damage to trees allows more pre-climax shrubs and trees to grow. There are a number of endemic species, as in common with islands.
Dialium polyanthum is a species of flowering plant, a medium to large tree in the family Fabaceae, subfamily Dialioideae.

Cassipourea malosana is a species of plant native to tropical Africa.
Croton macrostachyus is a species of flowering plant native to the mountains of Sub-Saharan Africa.















