The Attacks on High Wood, near Bazentin le Petit in the Somme département of northern France, took place between the British Fourth Army and the German 1st Army during the Battle of the Somme. After the Battle of Bazentin Ridge on 14 July 1916, High Wood lay undefended for most of the day but delays in communication and confusion caused by orders and counter-orders from British corps headquarters, which had overlapping responsibilities, led to the occupation of High Wood being forestalled by German reserves, which had moved forward to counter-attack British troops in the villages of Bazentin-le-Grand and Bazentin-le-Petit.

The Battle of Delville Wood(15 July – 3 September 1916) was a series of engagements in the 1916 Battle of the Somme in the First World War, between the armies of the German Empire and the British Empire. Delville Wood (Bois d'Elville), was a thick tangle of trees, chiefly beech and hornbeam, with dense hazel thickets, intersected by grassy rides, to the east of Longueval. As part of a general offensive starting on 14 July, which became known as the Battle of Bazentin Ridge (14–17 July), General Douglas Haig, Commander of the British Expeditionary Force, intended to capture the German second position between Delville Wood and Bazentin le Petit.

The Battle of Guillemont was an attack by the British Fourth Army on the village of Guillemont. The village is on the D 20 running east to Combles and the D 64 south-west to Montauban. Longueval and Delville Wood lie to the north-west and Ginchy to the north-east. The village was on the right flank of the British sector, near the boundary with the French Sixth Army. The Fourth Army had advanced close to Guillemont during the Battle of Bazentin Ridge (14–17 July) and the capture of the village was the culmination of British attacks which began on the night of 22/23 July. The attacks were intended to advance the right flank of the Fourth Army and eliminate a salient further north at Delville Wood. German defences ringed the wood and had observation over the French Sixth Army area to the south, towards the Somme river.
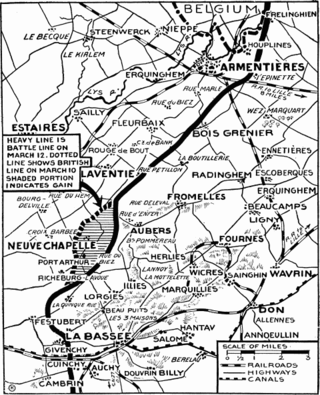
The Attack at Fromelles 19–20 July 1916, was a military operation on the Western Front during the First World War. The attack was carried out by British and Australian troops and was subsidiary to the Battle of the Somme. General Headquarters (GHQ) of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) had ordered the First Army and Second Army to prepare attacks to support the Fourth Army on the Somme, 50 mi (80 km) to the south, to exploit any weakening of the German defences opposite. The attack took place 9.9 mi (16 km) from Lille, between the Fauquissart–Trivelet road and Cordonnerie Farm, an area overlooked from Aubers Ridge to the south. The ground was low-lying and much of the defensive fortification by both sides consisted of building breastworks, rather than trenches.
The 8th Division was a unit of the Prussian/German Army. It was formed in Erfurt in November 1816 as a brigade and became a division on September 5, 1818. The division was subordinated in peacetime to the IV Army Corps. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The division was recruited primarily in the Province of Saxony, also known as Prussian Saxony and the smaller states of the German Empire around Prussian Saxony.
The 34th Division was a unit of the Prussian/German Army. It was formed on April 1, 1890, and was headquartered in Metz. The division was subordinated in peacetime to the XVI Army Corps. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The division was recruited heavily in the densely populated Rhine Province and in the Province of Westphalia, as its primary recruiting and garrison area was Lorraine, whose German population was insufficient to support the divisions of the XVI Army Corps.
The 3rd Guards Infantry Division was a unit of the German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on the mobilization of the German Army in August 1914 as part of the Guards Reserve Corps. The division was disbanded in 1919, during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. It was a division of the Prussian Guards and was thus raised and recruited throughout the Kingdom of Prussia from the elite of recruits.
The 51st Reserve Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in September 1914 and organized over the next month, arriving in the line in October. It was part of the first wave of new divisions formed at the outset of World War I, which were numbered the 43rd through 54th Reserve Divisions. The division was initially part of XXVI Reserve Corps. It was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 54th Reserve Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed in September 1914 and organized over the next month, arriving in the line in October. It was part of the first wave of new divisions formed at the outset of World War I, which were numbered the 43rd through 54th Reserve Divisions. The division was initially part of XXVII Reserve Corps. The division was disbanded in September 1918 and its assets distributed to other units. The division was primarily raised in the Kingdom of Württemberg, but the division's 245th Reserve Infantry Regiment, 26th Reserve Jäger Battalion, and several support units were from the Kingdom of Saxony. These non-Württemberg elements were all transferred out of the division at various points, making the division all-Württemberg by early 1917.
The 2nd Royal Bavarian Division was a unit of the Royal Bavarian Army which served alongside the Prussian Army as part of the Imperial German Army. The division was formed on November 27, 1815, as the Infantry Division of the Munich General Command. It was called the 2nd Army Division between 1822 and 1848, again between 1851 and 1859, and again from 1869 to 1872. It was called the 2nd Infantry Division from 1848 to 1851 and was named the Augsburg General Command from 1859 to 1869. From April 1, 1872, until mobilization for World War I, it was the 2nd Division. In Bavarian sources, it was not generally referred to as a "Royal Bavarian" division, as this was considered self-evident, but outside Bavaria, this designation was used for it, and other Bavarian units, to distinguish them from similarly numbered Prussian units. The division was headquartered in Ingolstadt from 1815 to 1817, in Regensburg from 1817 to 1822, and in Augsburg from 1822 to 1919, except for the period 1871-1873, when it was part of the German occupation forces in France. The division was part of the I Royal Bavarian Army Corps.
The 3rd Royal Bavarian Division was a unit of the Royal Bavarian Army which served alongside the Prussian Army as part of the Imperial German Army. The division was formed on November 27, 1815, as an Infantry Division of the Würzburg General Command. It was called the 3rd Army Division between 1822 and 1848, again between 1851 and 1859, and again from 1869 to 1872. It was called the 3rd Infantry Division from 1848 to 1851 and was named the Nuremberg General Command from 1859 to 1869. From April 1, 1872, until mobilization for World War I, it was the 3rd Division. In 1901, it had swapped division numbers with the 5th Division. In Bavarian sources, it was not generally referred to as a "Royal Bavarian" division, as this was considered self-evident, but outside Bavaria, this designation was used for it, and other Bavarian units, to distinguish them from similarly numbered Prussian units. The division was headquartered in Nuremberg from 1815 to 1843, in Ansbach from 1843 to 1848, and then again in Nuremberg until 1901, when after the renumbering of divisions, it became the 3rd Division in Landau and the division in Nuremberg became the 5th Division. The division was part of the II Royal Bavarian Army Corps.
The 5th Royal Bavarian Division was a unit of the Royal Bavarian Army which served alongside the Prussian Army as part of the Imperial German Army. The division was formed on October 1, 1890, in Landau as the 5th Division and swapped division numbers with the Nuremberg-based 3rd Royal Bavarian Division in 1901. In Bavarian sources, it was not generally referred to as a "Royal Bavarian" division, as this was considered self-evident, but outside Bavaria, this designation was used for it, and other Bavarian units, to distinguish them from similarly numbered Prussian units. The division was part of the III Royal Bavarian Army Corps.
The 6th Royal Bavarian Division was a unit of the Royal Bavarian Army which served within the Imperial German Army. The division was formed on April 1, 1900, and was headquartered in Regensburg. In Bavarian sources, it was not generally referred to as a "Royal Bavarian" division, as this was considered self-evident, but outside Bavaria, this designation was used for it, and other Bavarian units, to distinguish them from similarly numbered Prussian units. The division was part of the III Royal Bavarian Army Corps.

The 3rd Landwehr Division was an infantry division of the Imperial German Army during World War I. It was formed on the mobilization of the German Army in August 1914 under the "Higher Landwehr Commander 3". The Landwehr was the third category of the German Army, after the regular Army and the reserves. Thus Landwehr divisions were made up of older soldiers who had passed from the reserves, and were intended primarily for occupation and security duties rather than heavy combat. While the division was a Landwehr formation, at the beginning of the war it also had an attached Ersatz infantry brigade, made up of cadres from various regimental replacement battalions. The division was primarily raised in the Prussian provinces of Posen, Lower Silesia, and West Prussia. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.

The 4th Landwehr Division was an infantry division of the Imperial German Army during World War I. It was formed on mobilization of the German Army in August 1914 under the "Higher Landwehr Commander 4". The Landwehr was the third category of the German Army, after the regular Army and the reserves. Thus Landwehr divisions were made up of older soldiers who had passed from the reserves, and were intended primarily for occupation and security duties rather than heavy combat. The division was primarily raised in the Prussian provinces of Upper and Lower Silesia. It was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 105th Infantry Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed on May 5, 1915, and organized over the next few weeks. It was part of a wave of new infantry divisions formed in the spring of 1915. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.
The 107th Infantry Division was a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I. The division was formed on June 1, 1915, and organized over the next few weeks. It was part of a wave of new infantry divisions formed in 1915. The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I.

Bray-sur-Somme is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.

This is the order of battle for the Battle of the Somme. The Battle of the Somme was an offensive fought on the Western Front during World War I from 1 July to 18 November 1916 as one of the greatest engagements of the war. It was fought between French, British and Dominion forces and the German Empire in the Somme River valley and vicinity in northern France.

The Capture of Combles was a tactical incident that took place during the Battle of Morval, part of the Battle of the Somme, during the First World War. Combles lies 30 mi (48 km) north-east of Amiens and 10 mi (16 km) east of Albert, on the D 20 Rancourt–Guillemont road, 8 mi (13 km) south of Bapaume, in the Combles valley a hollow between outcrops of Bazentin Ridge, between Morval to the north, Ginchy to the north-west and Falfemont Farm to the west. North of the village the valley widens into a basin, which forks north-east around the Morval Spur. In late September 1914, military operations took place in the vicinity, when the II Bavarian Corps was engaged by French Territorial divisions in an encounter battle. The French divisions were forced back and the two divisions of the II Bavarian Corps, advanced westwards on the north side of the Somme, eventually being stopped around Maricourt, Montauban and Fricourt.