The Army National Guard (ARNG), in conjunction with the Air National Guard, is an organized militia force and a federal military reserve force of the United States Army. They are simultaneously part of two different organizations: the ARNG of each state, most territories, and the District of Columbia, as well as the federal ARNG, as part of the National Guard as a whole. It is divided into subordinate units stationed in each state or insular area, responsible to their respective governors or other head-of-government.

United States military bands include musical ensembles maintained by the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Coast Guard. More broadly, they can also include musical ensembles of other federal and state uniformed services, including the Public Health Service and NOAA Corps, the state defense forces, and the senior military colleges.

The Regular Army of the United States succeeded the Continental Army as the country's permanent, professional land-based military force. In modern times the professional core of the United States Army continues to be called the Regular Army. From the time of the American Revolution until after the Spanish–American War, state militias and volunteer regiments organized by the states supported the smaller Regular Army of the United States. These volunteer regiments came to be called United States Volunteers (USV) in contrast to the Regular United States Army (USA). During the American Civil War, about 97 percent of the Union Army was United States Volunteers.

A colonel in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force and Space Force, is the most senior field-grade military officer rank, immediately above the rank of lieutenant colonel and just below the rank of brigadier general. Colonel is equivalent to the naval rank of captain in the other uniformed services. By law, an officer previously required at least 22 years of cumulative service and a minimum of three years as a lieutenant colonel before being promoted to colonel. With the signing of the National Defense Authorization Act of 2019, military services now have the authorization to directly commission new officers up to the rank of colonel. The pay grade for colonel is O-6.
The Ancient and Honorable Artillery Company of Massachusetts is the oldest chartered military organization in North America and the third oldest chartered military organization in the world. Its charter was granted in March 1638 by the Great and General Court of Massachusetts Bay and signed by Governor John Winthrop as a volunteer militia company to train officers enrolled in the local militia companies across Massachusetts. With the professionalization of the US Military preceding World War I including the creation of the National Guard of the United States and the federalization of officer training, the company's mission changed to a supportive role in preserving the historic and patriotic traditions of Boston, Massachusetts, and the Nation. Today the Company serves as Honor Guard to the Governor of Massachusetts who is also its Commander in Chief. The headquarters is located on the 4th floor of Faneuil Hall and consists of an armory, library, offices, quartermaster department, commissary, and military museum with free admission.

The New Jersey Army National Guard consists of more than 6,000 Citizen-Soldiers. The New Jersey Army National Guard is currently engaged in multiple worldwide and homeland missions. Units have deployed to Iraq, Guantanamo Bay, Afghanistan, Germany, Kosovo, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and Egypt. The Guard has also deployed to help with the recovery from Hurricane Irma in Texas and the U.S. Virgin Islands, Hurricane Maria in Florida and Puerto Rico, and Hurricane Katrina in New Orleans.
The 198th Signal Battalion is an Expeditionary Signal Battalion in the Delaware Army National Guard. Delaware is known as the "First State," as referenced in their motto "First Regiment of First State." The unit specializes in command post node communications, providing broadband satellite voice and data connections for brigade sized battlefield elements. The unit includes Headquarters, Headquarters Company located in Wilmington, DE; A Company in Georgetown, DE; B Company in Hodges, SC; and C Company in Wilmington, DE. It is one of several National Guard units with colonial roots and campaign credit for the War of 1812.

The Massachusetts National Guard is the National Guard component for the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Founded as the Massachusetts Bay Colonial Militia on December 13, 1636, it contains the oldest units in the United States Army. What is today's Massachusetts National Guard evolved through many different forms. Originally founded as a defensive militia for Puritan colonists in the Massachusetts Bay Colony, the militia evolved into a highly organized and armed fighting force. The Massachusetts militia served as a central organ of the New England revolutionary fighting force during the early American Revolution and a major component in the Continental Army under George Washington.
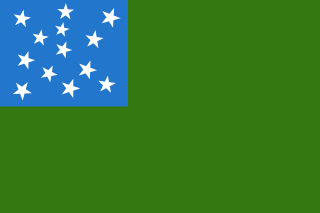
The Vermont National Guard is composed of the Vermont Army National Guard and the Vermont Air National Guard. Together, they are collectively known as the Green Mountain Boys. Both units use the original Revolutionary War-era Flag of the Green Mountain Boys as their banner. In 2009, they had 2,600 members.

The 7th Regiment of the New York Militia, aka the "Silk Stocking" regiment, was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Also known as the "Blue-Bloods" due to the disproportionate number of its members who were part of New York City's social elite, the 7th Militia was a pre-war New York Militia unit that was mustered into federal service for the Civil War.
The 258th Field Artillery Regiment or "Washington Greys" is a field artillery unit of the New York Army National Guard that traces its lineage from 1789 to present. Circa 1957–1966 it consisted of four battalions.

The Rhode Island Army National Guard (RIARNG) is the land force militia for the U.S. state of Rhode Island. It operates under Title 10 and Title 32 of the United States Code and operates under the command of the state governor while not in federal service. National Guard units may function under arms in a state status, therefore they may be called up for active duty by the governor to help respond to domestic emergencies and disasters, such as those caused by hurricanes, floods, or civil unrest.

The 211th Military Police Battalion is a unit of the Massachusetts Army National Guard. Its Headquarters and Headquarters Detachment is descended from the First Corps of Cadets, initially formed in 1741. It is one of several National Guard units with colonial roots. Its motto is Monstrat Viam – "It Points the Way." While it has served in five wars, the sub-unit's primary contribution to Massachusetts and to the United States was as an officer-producing institution for new regiments from the Revolutionary War through World War II.

The First Corps of Cadets of Massachusetts formed in 1741. Its motto is Monstrat Viam - "It Points the Way." While it has served in several wars, the sub-unit's primary contribution to Massachusetts and to the United States was as an officer-producing institution for new regiments from the Revolutionary War through World War II.
Twenty-four current units of the Army National Guard perpetuate the lineages of militia units mustered into federal service during the War of 1812. Militia units from nine states that were part of the Union by the end of the War of 1812, plus the District of Columbia, are the predecessors of eighteen units that currently exist in the Army National Guard. Two of the four units derived from Virginia militias are in the West Virginia National Guard; at the time of the War of 1812, West Virginia was still part of Virginia. Only two current units, the 155th Infantry, a component of the Mississippi National Guard derived from militia units organized in the Mississippi Territory and the 130th Infantry, a component of the Illinois National Guard derived from militia units formed in the Illinois Territory, are from states or territories west of the Appalachians. Unfortunately, no militia units from the states of Kentucky, Louisiana, Ohio or Tennessee, or from the Indiana, Michigan, Missouri or Louisiana Territories, where militia units played a major role in the fighting, have survived as units in the modern Army National Guard.

The Pennsylvania State Guard is the currently inactive official state defense force of the state of Pennsylvania, which was active during World War II and the Korean War. The unit was organized as a home guard composed of volunteers who were trained and organized as parallel to the state’s National Guard. As a part of Pennsylvania's official militia, the Pennsylvania State Guard was trained, organized, and funded by the state of Pennsylvania, answered to the governor, and could not be federalized or deployed abroad.

The 244th Air Defense Artillery Regiment is an air defense artillery regiment of the United States Army first formed on June 24, 1799 as the 6th Regiment of Infantry (NYNG).
The 240th Coast Artillery Regiment was a Coast Artillery Corps regiment in the Maine National Guard. It garrisoned the Harbor Defenses of Portland, Maine 1924–1944.

The 245th Coast Artillery Regiment was a Coast Artillery Corps regiment in the New York National Guard. It garrisoned the Harbor Defenses of New York, New York and predecessor commands 1924–1944.