
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth.

Triton is the largest natural satellite of the planet Neptune, and was the first Neptunian moon to be discovered, on October 11, 1846, by English astronomer William Lassell. It is the only large moon in the Solar System with a retrograde orbit, an orbit in the direction opposite to its planet's rotation. Because of its retrograde orbit and composition similar to Pluto, Triton is thought to have been a dwarf planet, captured from the Kuiper belt.

Rhea is the second-largest moon of Saturn and the ninth-largest moon in the Solar System, with a surface area that is comparable to the area of Australia. It is the smallest body in the Solar System for which precise measurements have confirmed a shape consistent with hydrostatic equilibrium. It was discovered in 1672 by Giovanni Domenico Cassini.

An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale.

The Chicxulub crater is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore, but the crater is named after the onshore community of Chicxulub Pueblo. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when a large asteroid, about ten kilometers in diameter, struck Earth. The crater is estimated to be 180 kilometers in diameter and 20 kilometers in depth. It is the second largest confirmed impact structure on Earth, and the only one whose peak ring is intact and directly accessible for scientific research.

Mare Orientale is a lunar mare. It is located on the western border of the near side and far side of the Moon, and is difficult to see from an Earthbound perspective. Images from spacecraft have revealed it to be one of the most striking large scale lunar features, resembling a target ring bullseye.
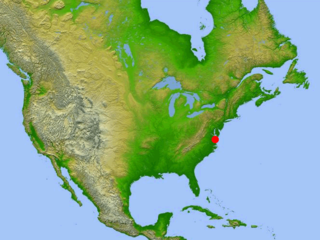
The Chesapeake Bay impact crater is a buried impact crater, located beneath the mouth of Chesapeake Bay, United States. It was formed by a bolide that struck the eastern shore of North America about 35.5 ± 0.3 million years ago, in the late Eocene epoch. It is one of the best-preserved "wet-target" impact craters in the world.

Manicouagan Reservoir is an annular lake in central Quebec, Canada, covering an area of 1,942 km2 (750 sq mi). The lake island in its centre is known as René-Levasseur Island, and its highest point is Mount Babel. The structure was created 214 (±1) million years ago, in the Late Triassic, by the impact of a meteorite 5 km (3 mi) in diameter. The lake and island are clearly seen from space and are sometimes called the "eye of Quebec". The lake has a volume of 137.9 km3 (33.1 cu mi).

The moons of Saturn are numerous and diverse, ranging from tiny moonlets only tens of meters across to the enormous Titan, which is larger than the planet Mercury. There are 146 moons with confirmed orbits. This number does not include the many thousands of moonlets embedded within Saturn's dense rings, nor hundreds of possible kilometer-sized distant moons that were seen through telescopes but not recaptured. Seven Saturnian moons are large enough to have collapsed into a relaxed, ellipsoidal shape, though only one or two of those, Titan and possibly Rhea, are currently in hydrostatic equilibrium. Three moons are particularly notable. Titan is the second-largest moon in the Solar System, with a nitrogen-rich Earth-like atmosphere and a landscape featuring river networks and hydrocarbon lakes. Enceladus emits jets of ice from its south-polar region and is covered in a deep layer of snow. Iapetus has contrasting black and white hemispheres as well as an extensive ridge of equatorial mountains among the tallest in the solar system.
Avak is an impact crater centered approximately 12 km (7.5 mi) southeast of Utqiagvik, Alaska, United States.
Flynn Creek crater, is an impact crater situated in Jackson County, approximately 8 km south of Gainesboro, Tennessee, USA. It was formed approximately 360 million years ago as a shallow, saucer-shaped crater, 3.8 km (2.4 mi) in diameter and about 150 m deep. A large central hill, highly deformed rim strata, and a breccia lens 40 m (130 ft) in thickness were produced during formation. Over 2 km2 of flat lying Middle and Upper Paleozoic limestone and dolomite were brecciated and mixed to a depth of 200 m (660 ft), and at least half of the breccia was ejected from the crater. The remaining breccia contains fragments ranging in size from small grains to megabreccia blocks 100 m (330 ft) in length. Undisturbed strata lie 100 m below the original crater floor.

The Kentland structure, also known as the Kentland crater or the Kentland disturbed area, is an impact structure located near the town of Kentland in Newton County, Indiana, United States.

Shoemaker is an impact structure, the deeply eroded remnant of a former impact crater, situated in arid central Western Australia, about 100 km (62 mi) north-northeast of Wiluna. It is named in honour of planetary geologist Eugene Shoemaker.

The Vredefort impact structure is one of the largest verified impact structures on Earth. The crater, which has since been eroded away, has been estimated at 170 kilometres (110 mi) to 300 km (190 mi) across when it was formed. The remaining structure, comprising the deformed underlying bedrock, is located in present-day Free State province of South Africa. It is named after the town of Vredefort, which is near its centre. The structure's central uplift is known as the Vredefort Dome. The impact structure was formed during the Paleoproterozoic Era, 2.023 billion years ago. It is the second-oldest known impact structure on Earth, after Yarrabubba.

Silverpit crater is a buried sub-sea structure under the North Sea off the coast of the island of Great Britain. The 20 km (12 mi) crater-like form, named after the Silver Pit—a nearby sea-floor valley recognized by generations of fishermen—was discovered during the routine analysis of seismic data collected during exploration for gas in the Southern North Sea Sedimentary Basin.

The Vichada River is a blackwater river in the country of Colombia, South America. It flows into the Orinoco River.

Ramgarh crater, also known as Ramgarh structure, Ramgarh Dome and Ramgarh astrobleme, is a meteor impact crater of 3.5 kilometres (2.2 mi) diameter in Kota plateau of Vindhya range located adjacent to Ramgarh village in Mangrol tehsil of Baran district in Rajasthan state of India. When formally accepted as the third crater in India, its diameter size would be between the two already confirmed craters in India - Dhala in Madhya Pradesh with 14 km diameter and Lonar in Buldhana district of Maharashtra with 1.8 km diameter.


















