
Dumfries and Galloway is one of 32 unitary council areas of Scotland and is located in the western Southern Uplands. It comprises the historic counties of Dumfriesshire, Stewartry of Kirkcudbright and Wigtownshire, the latter two of which are collectively known as Galloway. The administrative centre is the town of Dumfries.

The River Dee is a river in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It rises in the Cairngorms and flows through southern Aberdeenshire to reach the North Sea at Aberdeen. The area it passes through is known as Deeside, or Royal Deeside in the region between Braemar and Banchory because Queen Victoria came for a visit there in 1848 and greatly enjoyed her visit. She and her husband, Prince Albert, replaced an old castle there and built Balmoral Castle.

Tweeddale is a committee area and lieutenancy area in the Scottish Borders Council district, southeastern Scotland. Its boundaries correspond to the historic county of Peeblesshire.

The River Nith is a river in south-west Scotland. The Nith rises in the Carsphairn hills of East Ayrshire, more precisely between Prickeny Hill and Enoch Hill, 4.4 miles (7.1 km) east of Dalmellington. For the majority of its course it flows in a southerly direction through Dumfries and Galloway and then into the Solway Firth at Airds point.

The Kyles of Bute form a narrow sea channel that separates the northern end of the Isle of Bute from the Cowal peninsula in Argyll and Bute, on the Scottish mainland. The surrounding hillsides are roughly wooded, and overlooked by rocky tops and areas of moorland.

Loch Shiel is a freshwater loch situated 20 kilometres (12 mi) west of Fort William in the Highland council area of Scotland. At 28 kilometres long it is the 4th longest loch in Scotland, and is the longest to have retained a natural outflow without any regulation of its water level, being 120 m (393 ft) deep. Its nature changes considerably along its length, being deep and enclosed by mountains in the north east and shallow surrounded by bog and rough pasture in the south west, from which end the 4 km River Shiel drains to the sea in Loch Moidart near Castle Tioram.
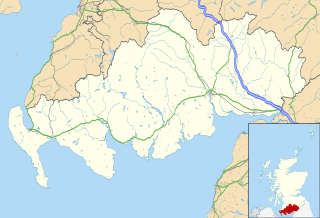
Gatehouse of Fleet is a town in the civil parish of Girthon, Kirkcudbrightshire, within the district council region of Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, which has existed since the mid-18th century, although the area has been inhabited since much earlier. Much of its development was attributable to the entrepreneur James Murray's decision to build his summer home, Cally House there in 1763. The house is now the Cally Palace Hotel.

Loch Tummel is a long, narrow loch, 7 km (4.3 mi) north west of Pitlochry in the council area of Perth and Kinross, Scotland. It is fed and drained by the River Tummel, which flows into the River Tay about 13 km (8.1 mi) south-east of the Clunie Dam at the loch's eastern end.

The River Earn in Scotland leaves Loch Earn at St Fillans and runs east through Strathearn, then east and south, joining the River Tay near Abernethy. The Earn is about 74 kilometres (46 mi) long. It passes by Comrie, Crieff and Bridge of Earn. The river is fast flowing, with many shoals, whilst the surrounding land is generally flat and is occasionally subject to flooding.

Glen Strathfarrar is a glen in the Highland region of Scotland, near Loch Ness. Glen Strathfarrar is named for the River Farrar, which runs through the glen, and which derives from the Pictish var, and was known to the Romans as Varrar. The full name is a curious 'Gaelicisation' of the Gaelic: as a strath is an elongated glen, a title of 'Glen Strath' is tautological, and it is therefore likely that an English-only speaker, ignorant of the meaning of 'Strath' when transcribing the map of the location, recorded that this was the 'Glen of Strathfarrar'.

Rough Firth is an inlet on the northern coast of the Solway Firth in the Stewartry area of Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. The firth lies between Almorness Point and Castlehill Point, and contains Rough Island. The village of Kippford stands near the head of the firth where the Urr Water reaches the sea; the only other coastal settlement of any size is Rockcliffe. The area is designated as the East Stewartry Coast National Scenic Area, one of the forty national scenic areas (NSAs) in Scotland.

South Lewis, Harris and North Uist is a large national scenic area (NSA) in the Western Isles of Scotland. It is one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development. The designated area covers 202,388 ha in total, of which 112,301 ha is on land, with a further 90,087 ha being marine, making it the largest of the NSAs in both total and marine area. The designated area includes the mountainous south west of Lewis, all of Harris, the Sound of Harris and the northern part of North Uist.

National scenic area (NSA) is a conservation designation used in Scotland, and administered by NatureScot. The designation's purpose is to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to protect them from inappropriate development. There are currently 40 national scenic areas (NSAs) in Scotland, covering 13% of the land area of Scotland. The areas protected by the designation are considered to represent the type of scenic beauty "popularly associated with Scotland and for which it is renowned". As such they tend to be mainly found in remote and mountainous areas, with a review in 1997 noting a potential weakness of national scenic areas was that the original selection placed undue emphasis on mountainous parts of the country. National scenic areas do however also cover seascapes, with approximately 26% of the total area protected by the designation being marine. The designation is primarily concerned with scenic qualities, although designated national scenic areas may well have other special qualities, for example related to culture, history, archaeology, geology or wildlife. Areas with such qualities may be protected by other designations that overlap with the NSA designation.

Ben Nevis and Glen Coe is a national scenic area (NSA) covering part of the Highlands of Scotland surrounding Ben Nevis and Glen Coe, in which certain forms of development are restricted. It is one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development. The Ben Nevis and Glen Coe NSA covers 903 km2 (349 sq mi) of land, lying within the Highland, Argyll and Bute and Perth and Kinross council areas. A further 19 km2 (7.3 sq mi) of the NSA are marine, covering the sea loch of Loch Leven.

Hoy and West Mainland is a national scenic area (NSA) covering parts of the islands of Hoy and Mainland in the Orkney Islands of Scotland, as well as parts of the surrounding sea. It is one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection by restricting certain forms of development. The Hoy and West Mainland NSA covers 24,407 ha in total, consisting of 16,479 ha of land with a further 7928 ha being marine.

The Loch Rannoch and Glen Lyon National Scenic Area is a national scenic area (NSA) covering the area surrounding Loch Rannoch, Glen Lyon, and the Ben Lawers ranges of mountains in Scotland. It is one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development by restricting certain forms of development. The Loch Rannoch and Glen Lyon NSA covers 48,625 ha, most of which lies in the council area of Perth and Kinross, with a small portion lying in Stirling.

Morar, Moidart and Ardnamurchan is a national scenic area (NSA) covering the coastal scenery of three peninsulas in the western Highlands of Scotland: Ardnamurchan, Moidart and Morar. It is one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development by restricting certain forms of development. The Morar, Moidart and Ardnamurchan NSA covers 36,956 ha in total, consisting of 17,220 ha of land with a further 19,736 ha being marine.

North West Sutherland is a national scenic area (NSA) covering the mountains and coastal scenery of the northwestern part of the county of Sutherland in the highlands of Scotland. The designated area covers the mountains of Foinaven, Arkle and Ben Stack as well as the coastal scenery surrounding Loch Laxford and Handa Island. It is one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection by restricting certain forms of development. The North West Sutherland NSA covers 26,565 ha in total, consisting of 23,415 ha of land with a further 3,151 ha being marine.

Scarba, Lunga and the Garvellachs is the name of one of the 40 national scenic areas of Scotland. The designated area covers the islands of Scarba, Lunga and the Garvellachs, all of which lie in the Firth of Lorn, along with much of the surrounding seascape. The national scenic areas are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection by restricting certain forms of development, and are considered to represent the type of scenic beauty "popularly associated with Scotland and for which it is renowned". The Scarba, Lunga and the Garvellachs NSA covers 6,542 ha in total, consisting of 2,139 ha of land with a further 4,402 ha being marine.

The Upper Tweeddale National Scenic Area lies in the Borders region of Scotland. It is one of 40 national scenic areas (NSA) in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure their protection from inappropriate development. The designated area covers 12,770 ha of countryside surrounding the upper reaches of the River Tweed between Broughton and Peebles.






















