
Taylor County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 143,208. Its county seat is Abilene. The county was created in 1858 and later organized in 1878. It is named for Edward Taylor, George Taylor, and James Taylor, three brothers who died at the Battle of the Alamo.

Eastland County is a county located in central West Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 17,725. The county seat is Eastland. The county was founded in 1858 and later organized in 1873. It is named for William Mosby Eastland, a soldier during the Texas Revolution and the only officer to die as a result of the "Black Bean executions" of the Mier Expedition.

Comanche County is a county located on the Edwards Plateau in Central Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 13,594. The county seat is Comanche. The county was founded in 1856 and is named for the Comanche Native American tribe.

Coleman County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 7,684. The county seat is Coleman. The county was founded in 1858 and organized in 1864. It is named for Robert M. Coleman, a signer of the Texas Declaration of Independence and soldier at the Battle of San Jacinto.

Brown County is a county in west-central Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 38,095. Its county seat is Brownwood. The county was founded in 1856 and organized in 1858. It is named for Henry Stevenson Brown, a commander at the Battle of Velasco, an early conflict between Texians and Mexicans.
Scouting in Texas has a long history, from the 1910s to the present day, serving thousands of youth in programs that suit the environment in which they live. Scouting, also known as the Scout Movement, is a worldwide youth movement with the stated aim of supporting young people in their physical, mental and spiritual development, so that they may play constructive roles in society.

Comanche is a city located in Comanche County in the U.S. state of Texas. The population was 4,335 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Comanche County. Comanche is a popular stop for hunters.

Big Spring is a city in and the county seat of Howard County, Texas, United States, at the crossroads of U.S. Highway 87 and Interstate 20. With a population of 27,282 as of the 2010 census, it is the largest city between Midland to the west, Abilene to the east, Lubbock to the north, and San Angelo to the south. Big Spring was established as the county seat of Howard County in 1882; it is the largest community in the county.
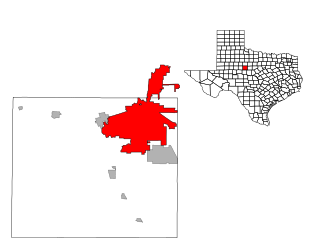
Abilene is a city in Taylor and Jones Counties in Texas, United States. Its population was 125,182 at the 2020 census, making it the 27th-most populous city in the state of Texas. It is the principal city of the Abilene metropolitan statistical area, which had an estimated population of 169,893, as of 2016. It is the county seat of Taylor County. Dyess Air Force Base is located on the west side of the city.

West Texas is a loosely defined part of the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the arid and semi-arid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Abilene, and Del Rio.

Abilene State Park is a 529.4-acre (214.2 ha) park near Lake Abilene south of Abilene, Texas. It features camping, trailer facilities, picnicking, shelters, a swimming pool, and hiking. A large grove of oak, cedar, elm and pecan trees, now a favorite picnic area, was once a campground for Comanche Indians. The park is located about 15 miles (24 km) southwest of Abilene, on FM 89.

KLST, virtual channel 8, is a CBS-affiliated television station licensed to San Angelo, Texas, United States. The station is owned by Nexstar Media Group, which also operates NBC affiliate KSAN-TV under joint sales and shared services agreements (JSA/SSA) with owner Mission Broadcasting. The two stations share studios on Armstrong Street in San Angelo; KLST's transmitter is located near Eola, Texas.

The United States District Court for the Northern District of Texas is a United States district court. Its first judge, Andrew Phelps McCormick, was appointed to the court on April 10, 1879. The court convenes in Dallas, Texas with divisions in Fort Worth, Amarillo, Abilene, Lubbock, San Angelo and Wichita Falls. It has jurisdiction over 100 counties in the northern and central parts of the U.S. state of Texas.

KTXS-TV, virtual channel 12, is a dual ABC/CW-affiliated television station serving Abilene, Texas, United States that is licensed to Sweetwater. Owned by the Hunt Valley, Maryland–based Sinclair Broadcast Group, it is a sister station to low-power MeTV affiliate KTES-LD, channel 40. Both stations share studios on North Clack Street in Abilene, while KTXS-TV's transmitter is located near Trent, Texas.
Buffalo Hump was a War Chief of the Penateka band of the Comanche Indians. He came to prominence after the Council House Fight when he led the Comanches on the Great Raid of 1840.
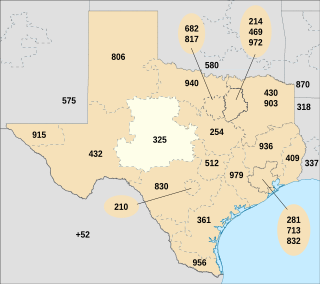
North American area code 325 is a state of Texas area code for telephone numbers in the Abilene and San Angelo areas. It was created, along with area code 432, on April 5, 2003, in a split from area code 915.

The Great Raid of 1840 was the largest raid ever mounted by Native Americans on white cities in what is now the United States. It followed the Council House Fight, in which Republic of Texas officials attempted to capture and take prisoner 33 Comanche chiefs who had come to negotiate a peace treaty, killing them together with two dozen of their family and followers. The Comanche tribe was supposed to have brought white hostages as their part of the negotiations but only brought one young woman. Arguments and fighting then broke out among the Texans and Comanches. The Texas Officials were determined to force the Comanche to release all white captives among them. To avenge what the Comanche viewed as a bitter betrayal by the Texans, the Comanche war chief Buffalo Hump raised a huge war party of many of the bands of the Comanche, and raided deep into white-settled areas of Southeast Texas.

The Texas–Indian wars were a series conflicts between settlers in Texas and the Southern Plains Natives during the 19th-century. Conflict between the Plains Indians and the Spanish began before other European and Anglo-American settlers were encouraged, first by Spain and then by the newly Independent Mexican government, to colonize Texas in order to provide a protective-settlement buffer in Texas between the Plains Indians and the rest of Mexico. As a consequence, conflict between Anglo-American settlers and Plains Indians occurred during the Texas Colonial period as part of Mexico. The conflicts continued after Texas secured its independence from Mexico in 1836, and did not end until thirty years after Texas became a state of the United States.

Fort Martin Scott is a restored United States Army outpost near Fredericksburg in the Texas Hill Country, United States, that was active from December 5, 1848, until April, 1853. It was part of a line of frontier forts established to protect travelers and settlers within Texas.


















