
The Ford GT40 is a high-performance endurance racing car designed and built by the Ford Motor Company. It grew out of the "Ford GT" project, an effort to compete in European long-distance sports car races, against Ferrari, who had won the prestigious 24 Hours of Le Mans race from 1960 to 1965. Ford succeeded with the GT40, winning the 1966 through 1969 races.

Type VII U-boats were the most common type of German World War II U-boat. 703 boats were built by the end of the war. The lone surviving example, U-995, is on display at the Laboe Naval Memorial located in Laboe, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.

USS Illinois (BB-65) was the fifth Iowa-class fast battleship that was laid down for the United States Navy during World War II in the 1940s, although she would not be completed. The Navy had initially planned on building four of the Iowas and then developing a new, more powerful ship for what was to be BB-65. The pressing need for more warships at the outbreak of World War II in Europe led the Navy to conclude that new designs would have to be placed on hold to allow the shipbuilding industry to standardize on a small number of designs. As a result, BB-65 was ordered to the Iowa design in 1940. Illinois was laid down in December 1942, but work was given a low priority, and was still under construction at the end of World War II. She was canceled in August 1945, but her hull remained as a parts hulk until she was broken up in 1958.
A folding kayak is a direct descendant of the original Inuit kayak made of animal skins stretched over frames made from wood and bones. A modern folder has a collapsible frame made of some combination of wood, aluminium and plastic, and a skin made of a tough fabric with a waterproof coating. Many have integral air chambers inside the hull, making them virtually unsinkable.
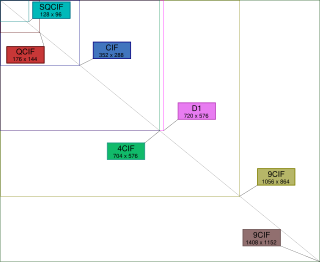
CIF, also known as FCIF, is a standardized format for the picture resolution, frame rate, color space, and color subsampling of digital video sequences used in video teleconferencing systems. It was first defined in the H.261 standard in 1988.

The Tambor-class submarine was a United States Navy submarine design, used primarily during World War II. They were the USN's first fully successful fleet submarine, and began the war close to the fighting. Six of the class were in Hawaiian waters or the Central Pacific on 7 December 1941, with Tautog at Pearl Harbor during the attack. They went on to see hard service; seven of the twelve boats in the class were sunk before the survivors were withdrawn from front-line service in early 1945; this was the highest percentage lost of any US submarine class. Tautog was credited with sinking 26 ships, the largest number of ships sunk by a US submarine in World War II. The Tambors attained the top speed of 21 knots (39 km/h) and range of 11,000 nautical miles (20,000 km) of the preceding Sargo class, and improvements included six bow torpedo tubes, a more reliable full diesel-electric propulsion plant, and improved combat efficiency with key personnel and equipment relocated to the conning tower. In some references, the Tambors are called the "T Class", and SS-206 through SS-211 are sometimes called the "Gar class".

The Mitsubishi Diamante is an automobile that was manufactured by Mitsubishi Motors from 1990 to 2005.

Canon EOS is an autofocus single-lens reflex camera (SLR) and mirrorless camera series produced by Canon Inc. Introduced in 1987 with the Canon EOS 650, all EOS cameras used 35 mm film until October 1996 when the EOS IX was released using the new and short-lived APS film. In 2000, the D30 was announced, as the first digital SLR designed and produced entirely by Canon. Since 2005, all newly announced EOS cameras have used digital image sensors rather than film. The EOS line is still in production as Canon's current digital SLR (DSLR) range, and, with the 2012 introduction of the Canon EOS M, Canon's mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera (MILC) system. In 2018 the system was further extended with the introduction of the EOS R camera, Canon's first full frame mirrorless interchangeable lens system.

The Porpoise class were submarines built for the United States Navy in the late 1930s, and incorporated a number of modern features that would make them the basis for subsequent Salmon, Sargo, Tambor, Gato, Balao, and Tench classes. In some references, the Porpoises are called the "P" class.

The Mark 2 family of railway carriages are British Rail's second design of carriages. They were built by British Rail workshops between 1964 and 1975 and were of steel construction.

The Cachalot-class submarines were a pair of medium-sized submarines of the United States Navy built under the tonnage limits of the London Naval Treaty of 1930. They were originally named V-8 and V-9, and so were known as "V-boats" even though they were unrelated to the other seven submarines constructed between World War I and World War II. An extensive study was conducted to determine the optimum submarine size under the treaty restrictions, factoring in total force, endurance, and percentage of the force that could be maintained on station far from a base, as in a Pacific war scenario. Joseph W. Paige of the Navy's Bureau of Construction and Repair (BuC&R) developed the basic design, but the builder, Electric Boat, was responsible for detailed arrangement; this was fairly bold, since Electric Boat had not built any new submarines since finishing four obsolescent boats for Peru. The previous V-boats were all built in naval shipyards. Cuttlefish was the first submarine built at EB's facility in Groton, Connecticut; construction of previous Electric Boat designs had been subcontracted to other shipyards, notably Fore River Shipbuilding of Quincy, Massachusetts.

Leonardo da Vinci was the last of three Conte di Cavour-class dreadnoughts built for the Regia Marina in the early 1910s. Completed just before the beginning of World War I, the ship saw no action and was sunk by a magazine explosion in 1916 with the loss of 248 officers and enlisted men. The Italians blamed Austro-Hungarian saboteurs for her loss, but it may have been accidental. Leonardo da Vinci was refloated in 1919 and plans were made to repair her. Budgetary constraints did not permit this, and her hulk was sold for scrap in 1923.

The Takanami-class destroyer is a class of destroyer serving with the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF). This warship is the slightly modified class of second-generation, general-purpose destroyers of the JMSDF.

The Ognevoy-class destroyers consisted of 26 destroyers built for the Soviet Navy during and immediately after World War II. The official Soviet designation was Project 30 and Project 30K. Construction was disrupted by the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941 and many ships were cancelled or scrapped. Only a single ship was completed during the war and the other 10 were finished in 1947–1950.

HMS Fortune was an Acasta-class destroyer, and the twenty-first ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name. She was launched in 1913 and was sunk at the Battle of Jutland in 1916.

The Plaxton Paramount was a design of coach bodywork built by Plaxton. It first appeared at the 1982 British Motor Show and was built until 1992.

The Ford Falcon (FG) is a full-sized car that was produced by Ford Australia from 2008 to 2014. It was the first iteration of the seventh and last generation of the Falcon. Its range no longer featured the Fairmont luxury badge, replaced instead by the G Series.

The C&C 27 is a family of Canadian sailboats, that was designed by Robert W. Ball and first built in 1970. The design is out of production.
The Silhouette also called the Silhouette 17, is a British trailerable sailboat that was designed by Robert Tucker as a pocket cruiser and first built in 1954.

















