
Rhynchobdellida, the jawless leeches or freshwater leeches, are an order of aquatic leeches. Despite the common name "freshwater leeches", species are found in both sea and fresh water. They are defined by the presence of a protrusible proboscis instead of jaws, and having colourless blood. They move by "inchworming" and are found worldwide. The order contains 110 species, divided into 41 genera and three families. Members of the order range widely in length, usually between 7 and 40 mm. They are hermaphrodite. The order is not monophyletic.

Haemadipsidae are a family of jawed leeches. They are a monophyletic group of hirudiniform proboscisless leeches. These leeches have five pairs of eyes, with the last two separated by two eyeless segments. The family is monotypic, containing only the subfamily Haemadipsinae, though as the family can apparently be divided into two or three distinct lineages, at least one of the proposed splits, while not a distinct family, might be a valid subfamily.

Pearson's horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand and Vietnam.

The least horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand and Vietnam. It is a food source of the parasite Sinospelaeobdella, a jawed land leech.

The Chinese rufous horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, and Vietnam.

Euhirudinea, the true leeches, are an infraclass of the Hirudinea.

Arhynchobdellida, the proboscisless leeches, are a monophyletic order of leeches. They are defined by the lack of the protrusible proboscis that defines their sister taxon, the Rhynchobdellida. Arhynchobdellida is a diverse order, compromising both aquatic and terrestrial, besides sanguivorous and predatory, leeches. The order is divided into two suborders, Erpobdelliformes and Hirudiniformes.

The Hirudiniformes are one of the currently-accepted suborders of the proboscisless leeches (Arhynchobdellida). Their best-known member is the European medical leech, Hirudo medicinalis, and indeed most of the blood-sucking "worms" as which leeches are generally perceived belong to this group. In general, though some leeches suck blood, many are predators which hunt small invertebrates.

Glossiphoniidae are a family of freshwater proboscis-bearing leeches. These leeches are generally flattened, and have a poorly defined anterior sucker. Most suck the blood of freshwater vertebrates like amphibians, crocodilians and aquatic turtles, but some feed on invertebrates like oligochaetes and freshwater snails instead. Although they prefer other hosts, blood-feeding species will opportunistically feed from humans.

Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodies that can lengthen and contract. Both groups are hermaphrodites and have a clitellum, but leeches typically differ from the oligochaetes in having suckers at both ends and ring markings that do not correspond with their internal segmentation. The body is muscular and relatively solid; the coelom, the spacious body cavity found in other annelids, is reduced to small channels.

Phytobdella catenifera is a large terrestrial leech found in Peninsular Malaysia. John Percy Moore chose this species’ epithet ‘catenifera’ after the striking chain-striped pattern on the creature's back.

Erpobdellidae is a family of leeches. It is one of the four families belonging to the suborder Erpobdelliformes of the proboscisless leeches order, Arhynchobdellida.

Hirudinidae is a family of leeches belonging to the order Arhynchobdellida.

The Piscicolidae are a family of jawless leeches in the order Rhynchobdellida that are parasitic on fish. They occur in both freshwater and seawater, have cylindrical bodies, and typically have a large, bell-shaped, anterior sucker with which they cling to their host. Some of the leeches in this family have external gills, outgrowths of the body wall projecting laterally, the only group of leeches to exchange gases in this way.
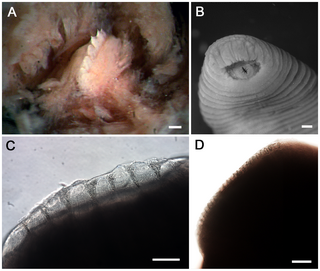
Praobdellidae is a family of hematophagous leeches which live on the mucous membranes of mammals and sometimes invertebrates. These are internal parasites that enter the body through natural orifices, and cause hirudiniases.
Sinospelaeobdella is a genus of jawed land leech, endemic to caves in China. It contains the species S. cavatuses and S. wulingensis, the latter being named after the Wuling Mountains where it was found.

Xerobdella is a genus of annelids belonging to the family Xerobdellidae.

Cylicobdellidae is a family of leeches belonging to the order Arhynchobdellida.
Macrobdellidae is a family of Nearctic leeches belonging to the order Arhynchobdellida.

















