
Tsagantegia is a genus of medium-sized ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The genus is monotypic, including only the type species, T. longicranialis. The specimen consists of a very partial individual, comprising the skull and lacking postcranial remains. Since it only preserves the skull, Tsagantegia is mainly characterized by its elongated snout and the flattened facial osteoderms, greatly differing from other ankylosaurs.

Sinemys is an extinct genus of turtle from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of China. Three species have been named: S. lens, the type species, from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian of Shandong; S. gamera, from the Valanginian-Albian of Nei Mongol, and S. brevispinus from Early Cretaceous of Nei Mongol. S. wuerhoensis, from the Aptian-Albian of Xinjiang, is not referrable to this genus. Specimen that may be belong to this genus were also known from Japan, although later abstract considered it as indeterminate sinemydid. The species S. gamera is noted for the presence of a pair of elongate spines projecting outwards and backwards from seventh costal of the carapace. These may have served a hydrodynamic function.
Kirgizemys is an extinct genus of turtle from Early Cretaceous of China, South Korea, Mongolia, Russia and Kyrgyzstan.

The Gaogou Formation is a fossiliferous geological formation located in the Xixia Basin of China. The formation dates back to the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Coniacian) and fossilized eggs of dinosaurs and turtles are commonly reported from the formation. Dinosaur taxa is also reported from the unit.
Anomalochelys is an extinct genus of land turtle from the Upper Cretaceous of Hokkaido, Japan, Guangdong, China.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2010.
The Nanxiong Formation is a Late Cretaceous geologic formation in Guangdong Province. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
The Jobu Formation is a Cretaceous geologic formation of Late Cenomanian age. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus. The oldest confirmed tyrannosaurid premaxillary tooth was recovered from the Jobu Formation. The mammal Sorlestes is also known from the formation.
Jiangxichelys is an extinct genus of nanhsiungchelyid turtle which existed in Ganzhou, Jiangxi Province, China during the latest Cretaceous epoch. It was first named by Haiyan Tong and Jinyou Mo in 2010 and the type species is Jiangxichelys ganzhouensis. It was an aquatic omnivore, as modern turtles are today.

Liaochelys is an extinct genus of sinemydid turtle which existed in western Liaoning, China during the early Cretaceous epoch. It was first named by Chang-Fu Zhou in 2010 and the type species is Liaochelys jianchangensis.

Trionyx is a genus of softshell turtles belonging to the family Trionychidae. In the past many species in the family were classified in this genus, but today T. triunguis, the African or Nile softshell turtle, is the only extant softshell still classified as Trionyx. The other species still assigned to this genus are only known from fossils. T. triunguis is a relatively large, aquatic piscivore.

Macrobaenidae is an extinct family of turtles, known from the Early Cretaceous to Paleogene of Laurasia. Their relationships to other turtles and whether they form a monophlyletic group are controversial. They are typically interpreted as stem or crown group cryptodires, but some more recent analyses have found them to lie outside crown group Testudines. Macrobaenids can be distinguished from other testudinatans by the presence of a carotid fenestra, cruciform plastron with strap-like epiplastra, and a lack of extragulars.

Sinemydidae is an extinct family of turtles from Cretaceous to Paleocene deposits in Asia and North America. Their exact position is engimatic, they have alternatively been considered stem-group cryptodires, but also "crownward stem-turtles" alongside Macrobaenidae, Paracryptodira, Xinjiangchelyidae, Thalassochelydia and Sandownidae outside of crown Testudines.

Basilemys is a large, terrestrial nanhsiungchelyid turtle from the Upper Cretaceous of North and Central America. Basilemys has been found in rocks dating to the Campanian and Maastrichtian subdivisions of the Late Cretaceous and is considered to be the largest terrestrial turtle of its time. In an analysis made by Sukhanov et al. on a nansiunghelyid turtle from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia, it was demonstrated that Asian nanhsiungchelyids gave rise to the North American nanhsiungchelyids.

Beibeilong is a genus of large caenagnathid dinosaurs that lived in China during the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 96 million to 88 million years ago. The genus contains a single species, Beibeilong sinensis. The species was named and described in 2017 through analysis of an embryonic skeleton and partial nest with large eggs that were discovered in the Gaogou Formation of China between 1992 and 1993.

Jeholochelys is an extinct genus of sinemydid turtle that lived during the Early Cretaceous of what is now China. The holotype specimen was discovered in the Jiufotang Formation of Sihedang in Lingyuan, western Liaoning. In 2018, the Chinese palaeontologist Shuai Shao and colleagues named the new genus and species Jeholochelys lingyuanensis based on the specimen. The generic name consists of "Jehol", which refers to the Jehol biota, and "chelys", which is Greek for turtle. The specific name refers to the type locality. Seven skeletons were described in the study, five nearly complete, and two consisting of shells, and hundreds of turtle fossils have been found in the area. The described specimens are kept in the Paleontological Museum of Liaoning.

Nanhsiungchelyidae is an extinct family of land turtles known from Cretaceous deposits in Asia and North America. Nanhsiungchelyids were more terrestrial than many of their contemporaries, and may have gone extinct at the end of the Cretaceous as a result.
The Ulaanoosh Formation, formerly Baruunbayan Formation, is a geologic formation in the Ömnögovi Province of southern Mongolia. The formation dates to the Albian to Cenomanian stages of the Cretaceous. The Ulaanoosh Formation has provided fossils of dinosaurs, turtles and dinosaur eggs assigned to Parafaveoloolithus sp.. In 2020, the neoceratopsian Beg tse was described from the alluvial sandstones, mudstones and conglomerates of the formation.

Kharakhutulia is a genus of nanhsiungchelyid turtle from the Upper Cretaceous. Its genus name refers to the location where it was found, namely the Khara Khutul fossil locality of Mongolia. Its species name refers to the scientist who collected the holotype specimen: Dr. Nikolai N. Kalandadze. Kharakhutulia has been found in rocks dating to the Cenomanian and Turonian subdivisions of the Late Cretaceous, and has thus far been exclusively found in Mongolia.
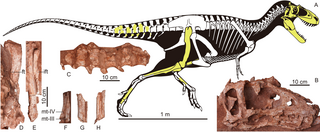
Asiatyrannus is an extinct genus of tyrannosaurine theropod dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Nanxiong Formation of China. The genus contains a single species, A. xui, known from a single specimen consisting of a skull and partial postcranial skeleton. Asiatyrannus is notable for its deep-snouted skull and small body size, in contrast to the gracile snout and larger size of the contemporary Qianzhousaurus. It represents the southernmost record of an Asian tyrannosaurid.










