
The fangtooth moray sometimes also known as tiger moray or bird-eye conger is a moray eel of the family Muraenidae found in warmer parts of the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including the Canary Islands, Madeira and various other islands. It entered the Mediterranean Sea from the Atlantic and is now found occasionally in the eastern Basin, from Levantine waters and off Turkey, Greece, Croatia and Sicily.

Rhynchoconger is a genus of eels in the family Congridae.
The longtrunk conger, also known as the short-tail conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Felipe Poey in 1860, originally under the genus Conger. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including southern Florida, Panama, the Guianas, and the Gulf of Guinea. It leads a benthic lifestyle, and inhabits sand and rock at a depth range of 11–63 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 36.3 centimeters.
The silver eel, also known as the Melliss's conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1870. It is a rare tropical, marine eel which is known solely from St. Helena, in the southeastern Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 67 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 42.8 centimetres.
The margintail conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Felipe Poey in 1867, originally under the genus Echelus. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, Bahamas, the Gulf of Mexico, Cuba, Venezuela, and Colombia. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 35–75 meters, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting sand and mud in the neritic zone. Males reach an average total length of 35 centimeters, but can reach a maximum TL of 51 cm.
The blackspot conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1870, originally under the genus Conger. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Madeira and Azores. It dwells at a depth range of 30–100 meters and burrows into sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 50 centimetres.
The Bullish conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977, originally under the genus Rhechias. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Gulf of Mexico to the Amazon, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 366–475 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 39.5 centimeters.
The neighbor conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Uroconger. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel that is known from the southwestern and western central Atlantic Ocean, including the Bahamas, Brazil, Cuba, and Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 101–503 metres (331–1,650 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 46.2 centimetres (18.2 in).
The grey conger, also known as the Antillean conger or simply the conger eel, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Felipe Poey in 1861. It is a tropical and subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean, including Cuba, Jamaica, and throughout northern South America. It dwells at a depth range of 120–400 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting coral reefs and rocky regions. Males can reach a maximum total length of 160 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 90 centimetres.
The manytooth conger, also known as the manytooth conger eel or simply the conger eel, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1958. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, Bermuda, the Antilles, the western Caribbean, and Brazil. It dwells at a depth range of 3–55 meters, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting rocky regions and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimeters, but more commonly reach a TL of 80 cm.
Gnathophis bracheatopos, the longeye conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1977. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the United States and the eastern Gulf of Mexico, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 55–110 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 35 centimeters.
Rhynchoconger ectenurus, known commonly as the longnose conger in Australia, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David Starr Jordan in Robert Earl Richardson in 1909, originally under the genus Leptocephalus. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the western Pacific Ocean, including northern Australia, Japan, the Korean Peninsula, and the eastern China Sea. It inhabits soft sediments on the continental shelf and slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 65 centimetres.
The whiptail conger, also known as the conger eel in Cuba, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Isaac Ginsburg in 1951, originally under the genus Congrina. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States in the northern Gulf of Mexico and northern South America. It is known to dwell at a depth of 203 meters (666 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 61 centimeters (24 in).
Rhynchoconger guppyi is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by John Roxborough Norman in 1925, originally under the genus Congromuraena. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean, northern South America and southern Brazil. It dwells at a depth range of 137 to 458 metres, and inhabits the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 95 centimetres (37 in).
The bignose conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Harvey Bollman in 1890. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, and Peru. It dwells at a depth range of 25–90 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 40 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 30 cm.

Rhynchoconger trewavasae is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Adam Ben-Tuvia in 1993. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western Indian Ocean, including the Gulf of Aqaba and possibly the Gulf of Suez. A single specimen was recorded in the Mediterranean Sea from Israel in 1993. It dwells at a depth range of 300 to 500 metres, and swims in a zigzag motion near the bottom. Males can reach a maximum total length of 57 centimetres (22 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 45 centimetres (18 in).

Cynoponticus savanna,, the Guayana pike-conger, pike-headed eel or sapphire eel, is an eel in the family Muraenesocidae. It was described by Edward Nathaniel Bancroft in 1831, originally under the genus Conger. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including Central America, the Caribbean and Brazil. It dwells at a maximum depth of 100 metres (330 ft), and inhabits muddy substrates in bays and estuaries. Males can reach a maximum total length of 150 centimetres (59 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 50 centimetres (20 in).
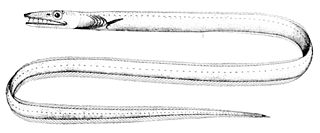
The blacktail pike-conger is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by George Brown Goode and Tarleton Hoffman Bean in 1896. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 203 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 36.6 centimeters.

Venefica procera is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by George Brown Goode and Tarleton Hoffman Bean in 1883, originally under the genus Nettastoma. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean, including North Carolina, USA, Suriname, the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. It dwells at a depth range of 326 to 2,304 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 109 centimeters (43 in).
The American sailfin eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by George Brown Goode and Tarleton Hoffman Bean in 1882. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States and the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. It frequently inhabits scallop grounds. Males can reach a maximum total length of 51 centimeters.







