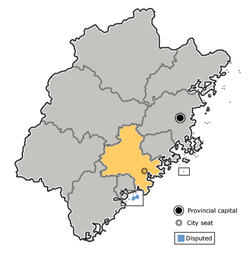
Putian, also known as Puyang (莆阳) and Puxian (莆仙), historically known as Hinghwa/Hinghua, is a prefecture-level city in Fujian Province, People's Republic of China. It borders Fuzhou to the north, Quanzhou to the south, and the Taiwan Strait's Xinghua Bay to the east. Mulan River flows through the city.

is a county located in central Fujian province, People's Republic of China. It is under the administration of Quanzhou City and covers an area of 2,232 square kilometres (862 sq mi) with a total population of 332,148.

Zhuanglang County is a rural county under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Pingliang in the east of Gansu Province, China. It borders Ningxia to the north, the Gansu county-level divisions of Huating City to the east, Zhangjiachuan County to the southeast, Qin'an County to the southwest, and Jingning County to the west. Nearby major cities include Pingliang, Tianshui, Guyuan, and Lanzhou.
Pingnan County is an inland county in northeastern Fujian province, People's Republic of China. It is located in the cultural region of Mindong (闽东), and lies in the west of Ningde City.
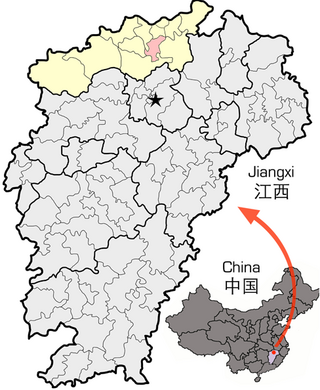
Lushan City, formerly Xingzi County, is a county-level city in the north of Jiangxi Province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Jiujiang.

Xiapu is a county in the municipal region of Ningde, Fujian, People's Republic of China, located along a stretch of East China Sea coast, with many harbours and islands. It is bordered by Fuding City and Zherong County to the north, Fu'an City and Ningde's urban area to the west, and Luoyuan County, Fuzhou and the Matsu Islands of Lienchiang County, Republic of China (Taiwan) to the south.

Weixi Lisu Autonomous County is an autonomous county of Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, in northwest Yunnan province, China. The titular ethnic group is the Lisu people.

is a county of central Fujian province, People's Republic of China. It is placed under the jurisdiction of the Sanming City.

Sunwu County is a county under the administration of Heihe City in the north of Heilongjiang province, China, situated on the bank of Amur River, which demarcates the Sino-Russian border. The length of border line within Sunwu county is 36 km (22 mi).

Shanglin County is a county of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Nanning, the capital of Guangxi. It borders the prefecture-level city of Laibin to the northeast.

Luzhai County is under the administration of Liuzhou, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. The easternmost county-level division of Liuzhou City, it borders the prefecture-level cities of Guilin to the north and east and Laibin to the southeast.
Lingchuan County is a county in the northeast of Guangxi, China. It is under the administration of Guilin city.
Luocheng Mulao Autonomous County is an ethnic Mulao county of northern Guangxi, China. It is under the administration of Hechi City. It is the only Mulao autonomous county in China.

Qinglong County is a county in the southwest of Guizhou province, China. It is under the administration of the Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture. It has a population of 234,162 as of 2020, 56% belonging to ethnic minorities. Qinglong is named after the Qinglong mountain, before 1941 it was called Annang County (安南县). The county was a frontline of the 1854–1873 Miao Rebellions.

Nanpi is a county in the east of Hebei province, China, bordering Shandong province to the south. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Cangzhou. As of 2020, it has a population of around 350,000 residing in an area of 836 km2 (323 sq mi).

Daming County is a county under the jurisdiction of Handan City in far southern Hebei Province, China. It was formerly one of the capitals of the Northern Song.

Chongyang County is a county of southeastern Hubei province, People's Republic of China, bordering Hunan province to the west and Jiangxi province to the southeast. It is under the administration of Xianning City.
Lishu County is a county of western Jilin province, China, bordering Liaoning to the southwest. It is under the administration of Siping City, with a population of 800,000 residing in an area of 3,900 km2 (1,500 sq mi).

Guangling County is in the northeast of Shanxi province, China. It is under the administration of Datong city. Guangling is a basin surrounded by Taihang Mountains. The temperature ranges from −34.0 to 38.2 °C, with an annual mean of 7.0 °C (44.6 °F). Guangling has nine township level divisions. Famous tourist attractions include: Temple of Water God (水神堂), Temple of Holy Spring (圣泉寺), Zhao Great Wall (赵长城). Local products include: papercut, millet, sunflower seeds, dry Tofu etc.
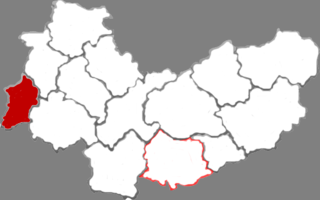
Baode is a county in the northwest of Shanxi province, China, bordering Shaanxi province to the west. It is under the administration of Xinzhou city, and is its westernmost county-level division.