Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as highly efficacious anti-depressants, as well as effective therapeutic agents for panic disorder and social phobia. They are particularly effective in treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and several other disorders.

Phenelzine, sold under the brand name Nardil, among others, is a non-selective and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class which is used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic. Along with tranylcypromine and isocarboxazid, phenelzine is one of the few non-selective and irreversible MAOIs still in widespread clinical use. It is available in Australia, The United Kingdom, The United States, and Canada. It is taken by mouth.

PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story is a book by Dr. Alexander Shulgin and Ann Shulgin, published in 1991. The subject of the work is psychoactive phenethylamine chemical derivatives, notably those that act as psychedelics and/or empathogen-entactogens. The main title, PiHKAL, is an acronym that stands for "Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved".

Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation.

Several alkaloids that function as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are found in the seeds of Peganum harmala, as well as tobacco leaves including harmine, harmaline, and harmalol, which are members of a group of substances with a similar chemical structure collectively known as harmala alkaloids. These alkaloids are of interest for their use in Amazonian shamanism, where they are derived from other plants. The harmala alkaloid harmine, once known as telepathine and banisterine, is a naturally occurring beta-carboline alkaloid that is structurally related to harmaline, and also found in the vine Banisteriopsis caapi. Tetrahydroharmine is also found in B. caapi and P. harmala. Dr. Alexander Shulgin has suggested that harmine may be a breakdown product of harmaline. Harmine and harmaline are both a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs). They can stimulate the central nervous system by inhibiting the metabolism of monoamine compounds such as serotonin and norepinephrine.

Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine" (literally, "working on dopamine"), dopamine being a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain. Dopaminergic brain pathways facilitate dopamine-related activity. For example, certain proteins such as the dopamine transporter (DAT), vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), and dopamine receptors can be classified as dopaminergic, and neurons that synthesize or contain dopamine and synapses with dopamine receptors in them may also be labeled as dopaminergic. Enzymes that regulate the biosynthesis or metabolism of dopamine such as aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase or DOPA decarboxylase, monoamine oxidase (MAO), and catechol O-methyl transferase (COMT) may be referred to as dopaminergic as well. Also, any endogenous or exogenous chemical substance that acts to affect dopamine receptors or dopamine release through indirect actions (for example, on neurons that synapse onto neurons that release dopamine or express dopamine receptors) can also be said to have dopaminergic effects, two prominent examples being opioids, which enhance dopamine release indirectly in the reward pathways, and some substituted amphetamines, which enhance dopamine release directly by binding to and inhibiting VMAT2.

Lophophine is a putative psychedelic and entactogen drug of the methylenedioxyphenethylamine class. It is the α-demethylated homologue of MMDA, and is also closely related to mescaline.

Aleph is a psychedelic hallucinogenic drug and a substituted amphetamine of the phenethylamine class of compounds, which can be used as an entheogen. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, Shulgin lists the dosage range as 5–10 mg. According to Shulgin, the effects of aleph typically last for 6 to 8 hours.

3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-methoxyamphetamine is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. It is also the N-methoxy analogue of MDA. MDMEO was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , the minimum dosage is listed as 180 mg. MDMEO may be found as white crystals. It produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MDMEO.

Substituted methylenedioxy- phenethylamines (MDxx) are a large chemical class of derivatives of the phenethylamines, which includes many psychoactive drugs that act as entactogens, psychedelics, and/or stimulants, as well as entheogens. These agents are used as research chemicals, designer drugs and as recreational substances.

2C-H (2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known substituted phenethylamine of the 2C family.

BOH, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-β-methoxyphenethylamine, is a drug of the phenethylamine class. It is the β-methoxy analog of methylenedioxyphenethylamine (MDPEA) and is also more distantly related to methylone. On account of its similarity to norepinephrine, the effects of BOH may be of a purely adrenergic nature.

3,4-Dimethoxyphenethylamine (DMPEA) is a chemical compound of the phenethylamine class. It is an analogue of the major human neurotransmitter dopamine where the 3- and 4-position hydroxy groups have been replaced with methoxy groups. It is also closely related to mescaline which is 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine.

MDHOET, or 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-hydroxyethylamphetamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. It is also the N-hydroxyethyl analogue of MDA. MDHOET was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , the minimum dosage is listed as 50 mg. MDHOET produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, effects, and toxicity of MDHOET.

Monoamine oxidase B, also known as MAOB, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAOB gene.

Substituted phenethylamines are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure; the class is composed of all the derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents.

4-Substituted-2,5-dimethoxyamphetamines (DOx) is a chemical class of substituted amphetamine derivatives featuring methoxy groups at the 2- and 5- positions of the phenyl ring, and a substituent such as alkyl or halogen at the 4- position of the phenyl ring. Most compounds of this class are potent and long-lasting psychedelic drugs, and act as highly selective 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptor partial agonists. A few bulkier derivatives such as DOAM have similarly high binding affinity for 5-HT2 receptors but instead act as antagonists, and so do not produce psychedelic effects though they retain amphetamine-like stimulant effects.

Amiflamine (FLA-336) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), thereby being a RIMA, and, to a lesser extent, semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO), as well as a serotonin releasing agent (SRA). It is a derivative of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. The (+)-enantiomer is the active stereoisomer.
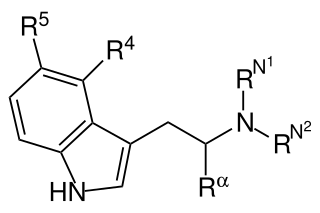
Substituted tryptamines, or serotonin analogues, are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms.
2C-T-16 is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It was originally named by Alexander Shulgin as described in his book PiHKAL, however while Shulgin began synthesis of this compound he only got as far as the nitrostyrene intermediate, and did not complete the final synthetic step. Synthesis of 2C-T-16 was finally achieved by Daniel Trachsel some years later, and it was subsequently reported as showing similar psychedelic activity to related compounds, with a dose range of 10–25 mg and a duration of 4–6 hours, making it around the same potency as the better-known saturated analogue 2C-T-7, but with a significantly shorter duration of action. Binding studies in vitro showed 2C-T-16 to have a binding affinity of 44nM at 5-HT2A and 15nM at 5-HT2C. 2C-T-16 and related derivatives are potent partial agonists of the 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors and induce a head-twitch response in mice.