Related Research Articles

Interferons are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses.

Caspases are a family of protease enzymes playing essential roles in programmed cell death. They are named caspases due to their specific cysteine protease activity – a cysteine in its active site nucleophilically attacks and cleaves a target protein only after an aspartic acid residue. As of 2009, there are 12 confirmed caspases in humans and 10 in mice, carrying out a variety of cellular functions.

Vaccinia virus is a large, complex, enveloped virus belonging to the poxvirus family. It has a linear, double-stranded DNA genome approximately 190 kbp in length, which encodes approximately 250 genes. The dimensions of the virion are roughly 360 × 270 × 250 nm, with a mass of approximately 5–10 fg. The vaccinia virus is the source of the modern smallpox vaccine, which the World Health Organization (WHO) used to eradicate smallpox in a global vaccination campaign in 1958–1977. Although smallpox no longer exists in the wild, vaccinia virus is still studied widely by scientists as a tool for gene therapy and genetic engineering.

Serpins are a superfamily of proteins with similar structures that were first identified for their protease inhibition activity and are found in all kingdoms of life. The acronym serpin was originally coined because the first serpins to be identified act on chymotrypsin-like serine proteases. They are notable for their unusual mechanism of action, in which they irreversibly inhibit their target protease by undergoing a large conformational change to disrupt the target's active site. This contrasts with the more common competitive mechanism for protease inhibitors that bind to and block access to the protease active site.
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins.
Modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) is an attenuated (weakened) strain of the vaccinia virus. It is being used as a vaccine against smallpox and mpox, having fewer side effects than smallpox vaccines derived from other poxviruses.
Virokines are proteins encoded by some large DNA viruses that are secreted by the host cell and serve to evade the host's immune system. Such proteins are referred to as virokines if they resemble cytokines, growth factors, or complement regulators; the term viroceptor is sometimes used if the proteins resemble cellular receptors. A third class of virally encoded immunomodulatory proteins consists of proteins that bind directly to cytokines. Due to the immunomodulatory properties of these proteins, they have been proposed as potentially therapeutically relevant to autoimmune diseases.

Interleukin-1 alpha also known as hematopoietin 1 is a cytokine of the interleukin 1 family that in humans is encoded by the IL1A gene. In general, Interleukin 1 is responsible for the production of inflammation, as well as the promotion of fever and sepsis. IL-1α inhibitors are being developed to interrupt those processes and treat diseases.

Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the IL1B gene. There are two genes for interleukin-1 (IL-1): IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. IL-1β precursor is cleaved by cytosolic caspase 1 to form mature IL-1β.
The NS1 influenza protein (NS1) is a viral nonstructural protein encoded by the NS gene segments of type A, B and C influenza viruses. Also encoded by this segment is the nuclear export protein (NEP), formally referred to as NS2 protein, which mediates the export of influenza virus ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes from the nucleus, where they are assembled.

Caspase-1/Interleukin-1 converting enzyme (ICE) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that proteolytically cleaves other proteins, such as the precursors of the inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β and interleukin 18 as well as the pyroptosis inducer Gasdermin D, into active mature peptides. It plays a central role in cell immunity as an inflammatory response initiator. Once activated through formation of an inflammasome complex, it initiates a proinflammatory response through the cleavage and thus activation of the two inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18) as well as pyroptosis, a programmed lytic cell death pathway, through cleavage of Gasdermin D. The two inflammatory cytokines activated by Caspase-1 are excreted from the cell to further induce the inflammatory response in neighboring cells.

Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is a species of DNA poxvirus that causes the human skin infection molluscum contagiosum. Molluscum contagiosum affects about 200,000 people a year, about 1% of all diagnosed skin diseases. Diagnosis is based on the size and shape of the skin lesions and can be confirmed with a biopsy, as the virus cannot be routinely cultured. Molluscum contagiosum virus is the only species in the genus Molluscipoxvirus. MCV is a member of the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae of family Poxviridae. Other commonly known viruses that reside in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae are variola virus and monkeypox virus.

Murine respirovirus, formerly Sendai virus (SeV) and previously also known as murine parainfluenza virus type 1 or hemagglutinating virus of Japan (HVJ), is an enveloped, 150-200 nm–diameter, negative sense, single-stranded RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It typically infects rodents and it is not pathogenic for humans or domestic animals
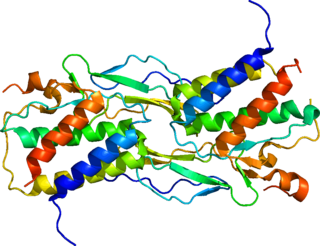
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL15 gene. IL-15 is an inflammatory cytokine with structural similarity to Interleukin-2 (IL-2). Like IL-2, IL-15 binds to and signals through a complex composed of IL-2/IL-15 receptor beta chain (CD122) and the common gamma chain. IL-15 is secreted by mononuclear phagocytes following infection by virus(es). This cytokine induces the proliferation of natural killer cells, i.e. cells of the innate immune system whose principal role is to kill virally infected cells.
Chemokine ligands 4 previously known as macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP-1β), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CCL4 gene. CCL4 belongs to a cluster of genes located on 17q11-q21 of the chromosomal region. Identification and localization of the gene on the chromosome 17 was in 1990 although the discovery of MIP-1 was initiated in 1988 with the purification of a protein doublet corresponding to inflammatory activity from supernatant of endotoxin-stimulated murine macrophages. At that time, it was also named as "macrophage inflammatory protein-1" (MIP-1) due to its inflammatory properties.
Inhibitors of apoptosis are a group of proteins that mainly act on the intrinsic pathway that block programmed cell death, which can frequently lead to cancer or other effects for the cell if mutated or improperly regulated. Many of these inhibitors act to block caspases, a family of cysteine proteases that play an integral role in apoptosis. Some of these inhibitors include the Bcl-2 family, viral inhibitor crmA, and IAP's.

Caspase-6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CASP6 gene. CASP6 orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. Caspase-6 has known functions in apoptosis, early immune response and neurodegeneration in Huntington's and Alzheimer's disease.

Serpin B9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINB9 gene. PI9 belongs to the large superfamily of serine proteinase inhibitors (serpins), which bind to and inactivate serine proteinases. These interactions are involved in many cellular processes, including coagulation, fibrinolysis, complement fixation, matrix remodeling, and apoptosis .[supplied by OMIM]

The Interleukin-1 family is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults.
Members of the very wide interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) family are characterized by extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains and intracellular Toll/Interleukin-1R (TIR) domain. It is a group of structurally homologous proteins, conserved throughout the species as it was identified from plants to mammals. Proteins of this family play important role in host defence, injury and stress. There are four main groups of TIR domain-containing proteins in animals; Toll-like receptors, Interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R), cytosolic adaptor proteins and insect and nematode Toll. Each of these groups is involved mainly in host defence; Toll receptors are also involved in embryogenesis.
References
- ↑ Kettle S, Blake NW, Law KM, Smith GL (January 1995). "Vaccinia virus serpins B13R (SPI-2) and B22R (SPI-1) encode M(r) 38.5 and 40K, intracellular polypeptides that do not affect virus virulence in a murine intranasal model". Virology. 206 (1): 136–47. doi:10.1016/S0042-6822(95)80028-X. PMID 7831769.
- ↑ Kettle S, Alcamí A, Khanna A, Ehret R, Jassoy C, Smith GL (March 1997). "Vaccinia virus serpin B13R (SPI-2) inhibits interleukin-1beta-converting enzyme and protects virus-infected cells from TNF- and Fas-mediated apoptosis, but does not prevent IL-1beta-induced fever". J. Gen. Virol. 78 ( Pt 3) (3): 677–85. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-3-677 . PMID 9049422.
- ↑ Law RH, Zhang Q, McGowan S, Buckle AM, Silverman GA, Wong W, Rosado CJ, Langendorf CG, Pike RN, Bird PI, Whisstock JC (2006). "An overview of the serpin superfamily". Genome Biol. 7 (5): 216. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-5-216 . PMC 1779521 . PMID 16737556.
- ↑ Lopez-Castejon G, Brough D (August 2011). "Understanding the mechanism of IL-1β secretion". Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22 (4): 189–95. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.10.001. PMC 3714593 . PMID 22019906.
- ↑ Legrand FA, Verardi PH, Chan KS, Peng Y, Jones LA, Yilma TD (February 2005). "Vaccinia viruses with a serpin gene deletion and expressing IFN-gamma induce potent immune responses without detectable replication in vivo". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (8): 2940–5. Bibcode:2005PNAS..102.2940L. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409846102 . PMC 548597 . PMID 15705716.
- ↑ "family:"serpin family poxviruses subfamily"". UniProt.