1,3-Butadiene is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene.
Paraldehyde is the cyclic trimer of acetaldehyde molecules. Formally, it is a derivative of 1,3,5-trioxane, with a methyl group substituted for a hydrogen atom at each carbon. The corresponding tetramer is metaldehyde. A colourless liquid, it is sparingly soluble in water and highly soluble in ethanol. Paraldehyde slowly oxidizes in air, turning brown and producing an odour of acetic acid. It attacks most plastics and rubbers and should be kept in glass bottles.

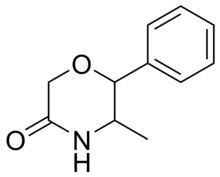
Phendimetrazine is a stimulant drug of the morpholine chemical class used as an appetite suppressant.
The Pictet–Spengler reaction is a chemical reaction in which a β-arylethylamine undergoes condensation with an aldehyde or ketone followed by ring closure. The reaction was first discovered in 1911 by Amé Pictet and Theodor Spengler. Traditionally, an acidic catalyst in protic solvent was employed with heating; however, the reaction has been shown to work in aprotic media in superior yields and sometimes without acid catalysis. The Pictet–Spengler reaction can be considered a special case of the Mannich reaction, which follows a similar reaction pathway. The driving force for this reaction is the electrophilicity of the iminium ion generated from the condensation of the aldehyde and amine under acid conditions. This explains the need for an acid catalyst in most cases, as the imine is not electrophilic enough for ring closure but the iminium ion is capable of undergoing the reaction.

Phenmetrazine is a stimulant drug first synthesized in 1952 and originally used as an appetite suppressant, but withdrawn from the market in the 1980s due to widespread abuse. It was initially replaced by its analogue phendimetrazine which functions as a prodrug to phenmetrazine, but now it is rarely prescribed, due to concerns of abuse and addiction. Chemically, phenmetrazine is a substituted amphetamine containing a morpholine ring.

4-Methylaminorex is a stimulant drug of the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline class that was first synthesized in 1960 by McNeil Laboratories. It is also known by its street name "U4Euh" ("Euphoria"). It is banned in many countries as a stimulant.

Aminorex is a weight loss (anorectic) stimulant drug. It was withdrawn from the market after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension. In the U.S., it is an illegal Schedule I drug, meaning it has high abuse potential, no accepted medical use, and a poor safety profile.

Mivacurium chloride is a short-duration non-depolarizing neuromuscular-blocking drug or skeletal muscle relaxant in the category of non-depolarizing neuromuscular-blocking drugs, used adjunctively in anesthesia to facilitate endotracheal intubation and to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation.

Oxazines are heterocyclic organic compounds containing one oxygen and one nitrogen atom in a cyclohexa-1,4-diene ring. Isomers exist depending on the relative position of the heteroatoms and relative position of the double bonds.

The substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamines represent a diverse chemical class of compounds derived from phenethylamines. This category encompasses numerous psychoactive substances with entactogenic, psychedelic, and/or stimulant properties, in addition to entheogens. These compounds find application as research chemicals, designer drugs, and recreational substances.

Neuropeptide Y receptor type 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPY5R gene.

AMG-3 (part of the AM cannabinoid series) is an analgesic drug which is a cannabinoid agonist. It is a derivative of Δ8-THC substituted with a dithiolane group on the 3-position side chain. AMG-3 is a potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors with a Ki of 0.32 nM at CB1 and 0.52 nM at CB2, and its particularly high binding affinity has led to it being used as a template for further structural development of novel cannabinoid drugs. It has sedative and analgesic effects, with analgesia lasting for up to 36 hours after administration.

SB-612,111 is an opioid receptor ligand which is a potent and selective antagonist for the nociceptin receptor (ORL-1), several times more potent than the older drug J-113,397. It does not have analgesic effects in its own right, but prevents the development of hyperalgesia, and also shows antidepressant effects in animal studies.
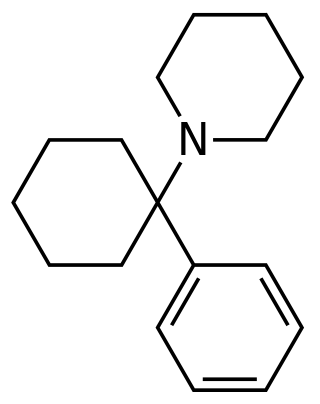
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.

JNJ-7925476 is a triple reuptake inhibitor antidepressant discovered by Johnson & Johnson, but never marketed.

G-130 is a drug with stimulant and anorectic effects, related to phenmetrazine.

Substituted phenylmorpholines, or substituted phenmetrazines alternatively, are chemical derivatives of phenylmorpholine or of the psychostimulant drug phenmetrazine. Most such compounds act as releasers of monoamine neurotransmitters, and have stimulant effects. Some also act as agonists at serotonin receptors, and compounds with an N-propyl substitution act as dopamine receptor agonists. A number of derivatives from this class have been investigated for medical applications, such as for use as anorectics or medications for the treatment of ADHD. Some compounds have also become subject to illicit use as designer drugs.
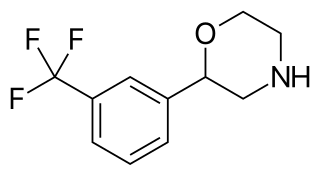
Flumexadol (INN) is a drug described and researched as a non-opioid analgesic which was never marketed. It has been found to act as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT2C receptors and, to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT2A receptor. According to Nilsson (2006) in a paper on 5-HT2C receptor agonists as potential anorectics, "The (+)-enantiomer of this compound showed [...] affinity for the 5-HT2C receptor (Ki) 25 nM) [...] and was 40-fold selective over the 5-HT2A receptor in receptor binding studies. Curiously, the racemic version [...], also known as 1841 CERM, was originally reported to possess analgesic properties while no association with 5-HT2C receptor activity was mentioned." It is implied that flumexadol might be employable as an anorectic in addition to analgesic. Though flumexadol itself has never been approved for medical use, oxaflozane is a prodrug of the compound that was formerly used clinically in France as an antidepressant and anxiolytic agent.