
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.

5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1B also known as the 5-HT1B receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR1B gene. The 5-HT1B receptor is a 5-HT receptor subtype.

5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1D, also known as HTR1D, is a 5-HT receptor, but also denotes the human gene encoding it. 5-HT1D acts on the central nervous system, and affects locomotion and anxiety. It also induces vasoconstriction in the brain.

8-OH-DPAT is a research chemical of the aminotetralin chemical class which was developed in the 1980s and has been widely used to study the function of the 5-HT1A receptor. It was one of the first major 5-HT1A receptor full agonists to be discovered.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

The 5-HT7 receptor is a member of the GPCR superfamily of cell surface receptors and is activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) The 5-HT7 receptor is coupled to Gs (stimulates the production of the intracellular signaling molecule cAMP) and is expressed in a variety of human tissues, particularly in the brain, the gastrointestinal tract, and in various blood vessels. This receptor has been a drug development target for the treatment of several clinical disorders. The 5-HT7 receptor is encoded by the HTR7 gene, which in humans is transcribed into 3 different splice variants.

5-Carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) is a tryptamine derivative closely related to the neurotransmitter serotonin.

YM-348 is an indazole derivative drug which acts as a potent and selective 5-HT2C receptor agonist, with an EC50 of 1nM and 15x selectivity over 5-HT2A, although it only has moderate selectivity of 3x over the closely related 5-HT2B receptor. It has thermogenic and anorectic effects in animal studies, making it potentially useful for the treatment of obesity.

CP-94253 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective serotonin 5-HT1B receptor agonist, with approximately 25x and 40x selectivity over the closely related 5-HT1D and 5-HT1A receptors. It has a range of behavioral effects, based on animal testing. The effects include the following: promoting wakefulness by increasing dopamine release in the brain; reducing food intake and promoting satiety; enhancing the reinforcing effects of cocaine; and possible antidepressant effects. A recent study found that "Regardless of sex, CP94253 decreased cocaine intake after abstinence and during resumption of SA [self-administration] and decreased cue reactivity" suggesting that agonism of the inhibitory 5-HT2B receptors may diminish the cognitive reward of cocaine usage and increased use of the drug without a period of abstinence may be a product of test subjects trying to achieve a previously rewarding experience through larger dosages of cocaine.

SB-269970 is a drug and research chemical developed by GlaxoSmithKline used in scientific studies. It is believed to act as a selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist (EC50 = 1.25 nM) (or possibly inverse agonist). A subsequent study in guinea pig at a concentration of 10 μM showed that it also blocks the α2-adrenergic receptor. The large difference in test concentrations however confirms the selectivity of SB-269970 for the 5-HT7 receptor.
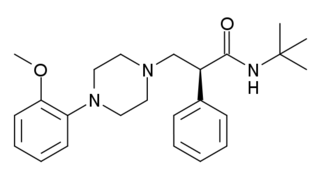
WAY-100135 is a serotonergic drug of the phenylpiperazine family which is used in scientific research. It acts as potent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, and was originally believed to be highly selective, but further studies have demonstrated that it also acts as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1D receptor (pKi = 7.58; virtually the same affinity for 5-HT1A), and to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT1B receptor (pKi = 5.82). These findings may have prompted the development of the related compound WAY-100635, another purportedly selective and even more potent 5-HT1A antagonist, which was synthesized shortly thereafter. However, WAY-100635 turned out to be non-selective as well, having been shown to act additionally as a potent D4 receptor agonist later on.

GR-127935 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist at the serotonin receptors 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D. It has little effect when given by itself but blocks the antiaggressive effect of 5-HT1B agonists, and alters release of serotonin in the brain, as well as reducing drug-seeking behaviour in cocaine addicted rats.

LY-307,452 is a drug used in neuroscience research, which was among the first compounds found that acts as a selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3), and was useful in early studies of this receptor family, although it has largely been replaced by newer drugs such as LY-341,495. Its molecular formula is C21H25NO4

CGS-12066A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT1B receptor with lower affinity for the three 5-HT2 receptor subtypes. It is used for studying the role of the 5-HT1B receptor in various processes including perception of pain and the sleep-wake cycle.
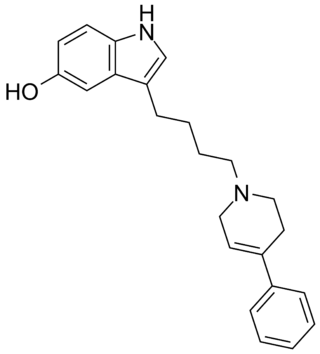
Roxindole (EMD-49,980) is a dopaminergic and serotonergic drug which was originally developed by Merck KGaA for the treatment of schizophrenia. In clinical trials its antipsychotic efficacy was only modest but it was unexpectedly found to produce potent and rapid antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. As a result, roxindole was further researched for the treatment of depression instead. It has also been investigated as a therapy for Parkinson's disease and prolactinoma.

SB-236057 is a compound which is a potent and selective inverse agonist for the serotonin receptor 5-HT1B, acting especially at 5-HT1B autoreceptors on nerve terminals. It produces a rapid increase in serotonin levels in the brain, and was originally researched as a potential antidepressant. However subsequent research found that SB-236,057 also acts as a potent teratogen, producing severe musculoskeletal birth defects when rodents were exposed to it during pregnancy. This has made it of little use for research into its original applications, yet has made it useful for studying embryonic development instead.

LY-456220 is a potent and selective serotonin 5-HT1D receptor antagonist which has been used in research to study the function of presynaptic 5-HT1D autoreceptors. LY-456220 lacks significant affinity for the 5-HT1B, α1 adrenergic, and dopamine D2 receptors.


















