5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).

Tegaserod is a 5-HT4 agonist manufactured by Novartis and sold under the names Zelnorm and Zelmac for the management of irritable bowel syndrome and constipation. Approved by the FDA in 2002, it was subsequently removed from the market in 2007 due to FDA concerns about possible adverse cardiovascular effects. Before then, it was the only drug approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration to help relieve the abdominal discomfort, bloating, and constipation associated with irritable bowel syndrome. Its use was also approved to treat chronic idiopathic constipation.

Cabergoline, sold under the brand name Dostinex among others, is a dopaminergic medication used in the treatment of high prolactin levels, prolactinomas, Parkinson's disease, and for other indications. It is taken by mouth.
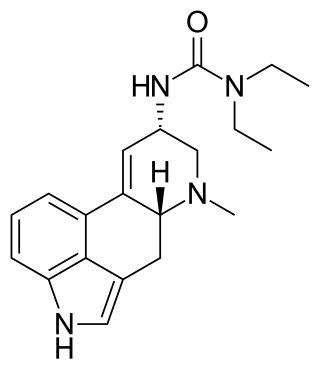
Lisuride, sold under the brand name Dopergin among others, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline class which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, migraine, and high prolactin levels. It is taken by mouth.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations. 5-HT is short for 5-hydroxy-tryptamine or serotonin. This is the main excitatory receptor subtype among the GPCRs for serotonin, although 5-HT2A may also have an inhibitory effect on certain areas such as the visual cortex and the orbitofrontal cortex. This receptor was first noted for its importance as a target of serotonergic psychedelic drugs such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms. Later it came back to prominence because it was also found to be mediating, at least partly, the action of many antipsychotic drugs, especially the atypical ones.
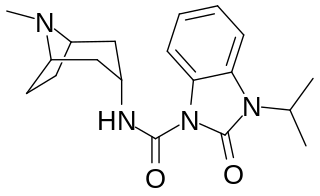
BIMU-8 is a drug which acts as a 5-HT4 receptor selective agonist. BIMU-8 was one of the first compounds of this class. The main action of BIMU-8 is to increase the rate of respiration by activating an area of the brain stem known as the pre-Botzinger complex.

8-OH-DPAT is a research chemical of the aminotetralin chemical class which was developed in the 1980s and has been widely used to study the function of the 5-HT1A receptor. It was one of the first major 5-HT1A receptor full agonists to be discovered.

The 5-HT7 receptor is a member of the GPCR superfamily of cell surface receptors and is activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) The 5-HT7 receptor is coupled to Gs (stimulates the production of the intracellular signaling molecule cAMP) and is expressed in a variety of human tissues, particularly in the brain, the gastrointestinal tract, and in various blood vessels. This receptor has been a drug development target for the treatment of several clinical disorders. The 5-HT7 receptor is encoded by the HTR7 gene, which in humans is transcribed into 3 different splice variants.

5-Carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) is a tryptamine derivative closely related to the neurotransmitter serotonin.

Itopride (INN; brand name Ganaton) is a prokinetic benzamide derivative. These drugs inhibit dopamine and acetylcholine esterase enzyme and have a gastrokinetic effect. Itopride is indicated for the treatment of functional dyspepsia and other gastrointestinal conditions. It is a combined D2 receptor antagonist and acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.

YM-348 is an indazole derivative drug which acts as a potent and selective 5-HT2C receptor agonist, with an EC50 of 1nM and 15x selectivity over 5-HT2A, although it only has moderate selectivity of 3x over the closely related 5-HT2B receptor. It has thermogenic and anorectic effects in animal studies, making it potentially useful for the treatment of obesity.

Cinitapride (trade names Cintapro, Pemix) is a gastroprokinetic agent and antiemetic agent of the benzamide class which is marketed in India, Mexico, Pakistan and Spain. It acts as an agonist of the 5-HT1 and 5-HT4 receptors and as an antagonist of the 5-HT2 receptors.

Dazopride (AHR-5531) is an antiemetic and gastroprokinetic agent of the benzamide class which was never marketed. It acts as a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist and 5-HT4 receptor agonist. In addition to its gastrointestinal effects, dazopride facilitates learning and memory in mice.
A prokinetic agent is a type of drug which enhances gastrointestinal motility by increasing the frequency or strength of contractions, but without disrupting their rhythm. They are used to treat certain gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal discomfort, bloating, constipation, heart burn, nausea, and vomiting; and certain gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome, gastritis, gastroparesis, and functional dyspepsia.
Osemozotan (MKC-242) is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist with some functional selectivity, acting as a full agonist at presynaptic and a partial agonist at postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. 5-HT1A receptor stimulation influences the release of various neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine. 5-HT1A receptors are inhibitory G protein-coupled receptor. Osemozotan has antidepressant, anxiolytic, antiobsessional, serenic, and analgesic effects in animal studies, and is used to investigate the role of 5-HT1A receptors in modulating the release of dopamine and serotonin in the brain, and their involvement in addiction to abused stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamine.

GR-113808 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective 5-HT4 serotonin receptor antagonist. It is used in researching the roles of 5-HT4 receptors in various processes, and has been used to test some of the proposed therapeutic effects of selective 5-HT4 agonists, such as for instance blocking the nootropic effects of 5-HT4 agonists, and worsening the respiratory depression produced by opioid analgesic drugs, which appears to be partly 5-HT4 mediated and can be counteracted by certain 5-HT4 agonists.
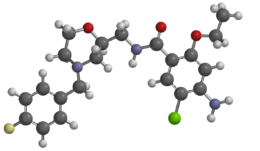
CJ-033466 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective 5-HT4 serotonin receptor partial agonist. In animal tests it stimulated gastrointestinal motility with 30 times the potency of cisapride, and with lower affinity for the hERG channel.

SB-206553 is a drug which acts as a mixed antagonist for the 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors. It has anxiolytic properties in animal studies and interacts with a range of other drugs. It has also been shown to act as a positive allosteric modulator of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Modified derivatives of SB-206553 have been used to probe the structure of the 5-HT2B receptor.