In chemistry, an enantiomer is one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable, much as one's left and right hands are mirror images of each other that cannot appear identical simply by reorientation. A single chiral atom or similar structural feature in a compound causes that compound to have two possible structures which are non-superposable, each a mirror image of the other. Each member of the pair is termed an enantiomorph ; the structural property is termed enantiomerism. The presence of multiple chiral features in a given compound increases the number of geometric forms possible, though there may still be some perfect-mirror-image pairs.
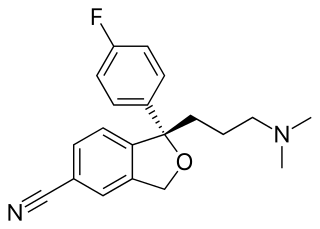
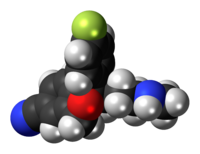
Escitalopram, sold under the brand names Cipralex and Lexapro, among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. Escitalopram is mainly used to treat major depressive disorder or generalized anxiety disorder. It is taken by mouth.

Citalopram, sold under the brand name Celexa among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, panic disorder, and social phobia. The antidepressant effects may take one to four weeks to occur. It is taken by mouth.
In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic form. Half of the optically active substance becomes its mirror image (enantiomer) referred as racemic mixtures. If the racemization results in a mixture where the D and L enantiomers are present in equal quantities, the resulting sample is described as a racemic mixture or a racemate. Racemization can proceed through a number of different mechanisms, and it has particular significance in pharmacology as different enantiomers may have different pharmaceutical effects.
ATC code N06Psychoanaleptics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N06 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.

The American Journal of Psychiatry is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of psychiatry, and is the official journal of the American Psychiatric Association. The first volume was issued in 1844, at which time it was known as the American Journal of Insanity. The title changed to the current form with the July issue of 1921.
Forest Laboratories was a company in the pharmaceutical industry incorporated in Delaware, with its principal office in New York City. It was known for licensing European pharmaceuticals for sale in the United States. On July 1, 2014, the company was acquired by Actavis.
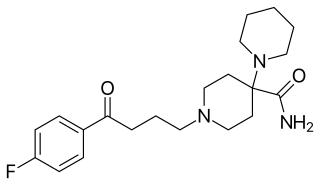
Pipamperone, also known as carpiperone and floropipamide or fluoropipamide, and as floropipamide hydrochloride (JAN), is a typical antipsychotic of the butyrophenone family used in the treatment of schizophrenia and as a sleep aid for depression. It is or has been marketed under brand names including Dipiperon, Dipiperal, Piperonil, Piperonyl, and Propitan. Pipamperone was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1961, and entered clinical trials in the United States in 1963.
Allosteric serotonin reuptake inhibitor is a type of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Currently only escitalopram, the S stereoisomer of the SSRI citalopram is included in this category. It is based on the observation that the R isomer of citalopram can decrease the potency and inhibit the effects of the S isomer, probably through an allosteric interaction between two distinct, non-overlapping binding sites for the two different isomers on the serotonin transporter. Escitalopram, thus, binds not only to the primary site, but also to the allosteric site. From known SSRIs also paroxetine has action to the allosteric site, about half potency of escitalopram.

A serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the neurotransmitter serotonin by blocking the action of the serotonin transporter (SERT). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of serotonin and, therefore, an increase in serotonergic neurotransmission. It is a type of monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI); other types of MRIs include dopamine reuptake inhibitors and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.
The number of new psychiatric drugs, and especially antidepressants on the market in Japan, is significantly less than Western countries.
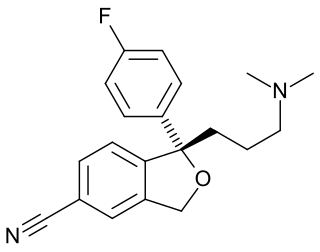
A reuptake inhibitor (RI) is a type of drug known as a reuptake modulator that inhibits the plasmalemmal transporter-mediated reuptake of a neurotransmitter from the synapse into the pre-synaptic neuron. This leads to an increase in extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter and an increase in neurotransmission. Various drugs exert their psychological and physiological effects through reuptake inhibition, including many antidepressants and psychostimulants.

Talopram, also known as phthalapromine, is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI) which was researched for the management of depression in the 1960s and 1970s but was never commercialized. Along with talsupram, talopram is structurally related to the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) citalopram, as well as to melitracen:
In 1971, the company hired Klaus Bøgesø as a medicinal chemist. Over the years Bøgesø turned out to have a Midas touch at the game of drug hunting, creating more molecules that made it to the market than almost any other medicinal chemist in the field. The challenge facing him in 1971 following his recruitment was to produce a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Like other companies at the time, Lundbeck had little interest in an SSRI. Bøgesø began from an accident in the laboratory. Trying to create a derivative of their norepinephrine reuptake inhibiting antidepressant melitracen, Lundbeck chemists accidentally produced a new chemical — a phenylphthalene. Against all the odds, just like melitracen, this was also a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Two potential antidepressants came out of this — talopram and tasulopram, which were pressed into clinical trials. Both however turned out to be energizing, and in a number of cases there were suicide attempts. The fact that there were suicide attempts appeared to confirm another proposal of Paul Kielholz, that activating antidepressants might lead to suicide. Lundbeck's experience suggested that norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors were likely to lead to just this problem. Lundbeck retreated, scared. If norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors were likely to trigger suicide, the greatest hazard of an antidepressant, then Kielholz's view suggested that an SSRI would be less likely to lead to suicide. Bøgesø's job was to see whether the new series of drugs could be converted into a series of SSRIs. Following a lead from Carlsson on how to do this, he converted talopram into citalopram, the most selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor to come to the market.
Robalzotan is a selective antagonist at the 5-HT1A receptor. It was shown to completely reverse the autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release induced by the administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors like citalopram in rodent studies. It was subsequently investigated by AstraZeneca as a potential antidepressant but like many other 5-HT1A ligands was discontinued. Later on it was researched for other indications such as irritable bowel syndrome but was dropped once again.

Didesmethylcitalopram is an active metabolite of the antidepressant drug citalopram (racemic). Didesmethylescitalopram is an active metabolite of the antidepressant escitalopram, the S-enantiomer of citalopram. Like citalopram and escitalopram, didesmethyl(es)citalopram functions as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), and is responsible for some of its parents' therapeutic benefits.

Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
The molecular formula C20H21FN2O (molar mass: 324.39 g/mol, exact mass: 324.1638 u) may refer to:
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or serotonin-specific re-uptake inhibitor (SSRIs), are a class of chemical compounds that have contributed to the major advances as antidepressants where they have revolutionised the treatment of depression and other psychiatric disorders. The SSRIs are therapeutically useful in the treatment of panic disorder (PD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) and anorexia. There is also clinical evidence of SSRIs efficiency in the treatment of the negative symptoms of schizophrenia and their ability to prevent cardiovascular diseases.