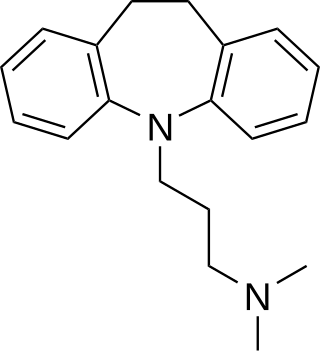
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants, which is important for the management of depression. They are second-line drugs next to SSRIs. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms. Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), which contain four rings of atoms, are a closely related group of antidepressant compounds.

Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs) are a class of antidepressants that were first introduced in the 1970s. They are named after their tetracyclic chemical structure, containing four rings of atoms, and are closely related to the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), which contain three rings of atoms.

Monoamine transporters (MATs) are protein structures that function as integral plasma-membrane transporters to regulate concentrations of extracellular monoamine neurotransmitters. Three major classes of MATs are responsible for the reuptake of their associated amine neurotransmitters. MATs are located just outside the synaptic cleft (peri-synaptically), transporting monoamine transmitter overflow from the synaptic cleft back to the cytoplasm of the pre-synaptic neuron. MAT regulation generally occurs through protein phosphorylation and posttranslational modification. Due to their significance in neuronal signaling, MATs are commonly associated with drugs used to treat mental disorders as well as recreational drugs. Compounds targeting MATs range from medications such as the wide variety of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors such as fluoxetine (Prozac) to stimulant medications such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) and amphetamine in its many forms and derivatives methamphetamine (Desoxyn) and lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse). Furthermore, drugs such as MDMA and natural alkaloids such as cocaine exert their effects in part by their interaction with MATs, by blocking the transporters from mopping up dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters from the synapse.

Amitriptyline, sold under the brand name Elavil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant primarily used to treat cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS), major depressive disorder and a variety of pain syndromes from neuropathic pain to fibromyalgia to migraine and tension headaches. Due to the frequency and prominence of side effects, amitriptyline is generally considered a second-line therapy for these indications.

Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant drugs used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), social phobia, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the more widely used selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which act upon serotonin only.

Desipramine, sold under the brand name Norpramin among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used in the treatment of depression. It acts as a relatively selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, though it does also have other activities such as weak serotonin reuptake inhibitory, α1-blocking, antihistamine, and anticholinergic effects. The drug is not considered a first-line treatment for depression since the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants, which have fewer side effects and are safer in overdose.

Clomipramine, sold under the brand name Anafranil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). It is used for the treatment of obsessive–compulsive disorder, panic disorder, major depressive disorder, and chronic pain. It may increase the risk of suicide in those under the age of 25. It is primarily taken by mouth. It has also been used to treat premature ejaculation.

Nortriptyline, sold under the brand name Pamelor, among others, is a medication used to treat depression. This medicine is also sometimes used for neuropathic pain, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), smoking cessation and anxiety. As with many antidepressants, its use for young people with depression and other psychiatric disorders may be limited due to increased suicidality in the 18-24 population initiating treatment. Nortriptyline is a less preferred treatment for ADHD and stopping smoking. It is taken by mouth.

Trimipramine, sold under the brand name Surmontil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) which is used to treat depression. It has also been used for its sedative, anxiolytic, and weak antipsychotic effects in the treatment of insomnia, anxiety disorders, and psychosis, respectively. The drug is described as an atypical or "second-generation" TCA because, unlike other TCAs, it seems to be a fairly weak monoamine reuptake inhibitor. Similarly to other TCAs however, trimipramine does have antihistamine, antiserotonergic, antiadrenergic, antidopaminergic, and anticholinergic activities.

The norepinephrine transporter (NET), also known as noradrenaline transporter (NAT), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the solute carrier family 6 member 2 (SLC6A2) gene.

Dosulepin, also known as dothiepin and sold under the brand name Prothiaden among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) which is used in the treatment of depression. Dosulepin was once the most frequently prescribed antidepressant in the United Kingdom, but it is no longer widely used due to its relatively high toxicity in overdose without therapeutic advantages over other TCAs. It acts as a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) and also has other activities including antihistamine, antiadrenergic, antiserotonergic, anticholinergic, and sodium channel-blocking effects.

Nomifensine is a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor, i.e. a drug that increases the amount of synaptic norepinephrine and dopamine available to receptors by blocking the dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake transporters. This is a mechanism of action shared by some recreational drugs like cocaine and the medication tametraline. Research showed that the (S)-isomer is responsible for activity.
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), is a type of drug that acts as a combined reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It does this by concomitantly inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. Inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters increases their extracellular concentrations and, therefore, results in an increase in serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission.

Indatraline hydrochloride is an antidepressive agent and non-selective monoamine transporter inhibitor that blocks the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, with similar efficacy to cocaine. However, the effects of indatraline have a slower onset and longer duration than cocaine, suggesting that the compound may be used to treat cocaine addiction. Lu 19-005 has been shown to block the action of methamphetamine and MDMA in laboratory experiments.

Nisoxetine, originally synthesized in the Lilly research laboratories during the early 1970s, is a potent and selective inhibitor for the reuptake of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) into synapses. It currently has no clinical applications in humans, although it was originally researched as an antidepressant. Nisoxetine is now widely used in scientific research as a standard selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It has been used to research obesity and energy balance, and exerts some local analgesia effects.

Medifoxamine, previously sold under the brand names Clédial and Gerdaxyl, is an atypical antidepressant with additional anxiolytic properties acting via dopaminergic and serotonergic mechanisms which was formerly marketed in France and Spain, as well as Morocco. The drug was first introduced in France sometime around 1990. It was withdrawn from the market in 1999 (Morocco) and 2000 (France) following incidences of hepatotoxicity.

Oxaprotiline, also known as hydroxymaprotiline, is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor belonging to the tetracyclic antidepressant (TeCA) family and is related to maprotiline. Though investigated as an antidepressant, it was never marketed.
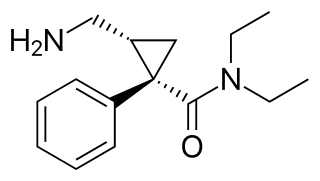
Levomilnacipran is an antidepressant which was approved in the United States in 2013 for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of milnacipran, and has similar effects and pharmacology, acting as a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI).
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or serotonin-specific re-uptake inhibitor (SSRIs), are a class of chemical compounds that have contributed to the major advances as antidepressants where they have revolutionised the treatment of depression and other psychiatric disorders. The SSRIs are therapeutically useful in the treatment of panic disorder (PD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), and anorexia. There is also clinical evidence of SSRIs efficiency in the treatment of the negative symptoms of schizophrenia and their ability to prevent cardiovascular diseases.

Nordoxepin, also known as N-desmethyldoxepin, is the major active metabolite of the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) doxepin (Sinequan). It has been found to play a significant role in the antidepressant effects of doxepin.



















