
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes. Early on there are typically no symptoms. Later non-painful lymph node swelling, feeling tired, fever, night sweats, or weight loss for no clear reason may occur. Enlargement of the spleen and low red blood cells (anemia) may also occur. It typically worsens gradually over years.

Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, pemphigus vulgaris, myasthenia gravis and Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers. It is given by slow injection into a vein. Biosimilars of Rituxan include Blitzima, Riabni, Ritemvia, Rituenza, Rixathon, Ruxience, and Truxima.
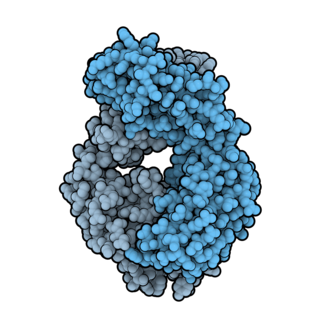
Ofatumumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody to CD20, which appears to inhibit early-stage B lymphocyte activation. Under the brand name Arzerra, it is approved for the treatment of certain types of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in the United States. Under the brand name Kesimpta, it is approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in the United States as well as in the EU and other regions.

Bendamustine, sold under the brand name Treanda among others, is a chemotherapy medication used in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), multiple myeloma, and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is given by injection into a vein.
Obinutuzumab, sold under the brand name Gazyva among others, is a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, originated by GlycArt Biotechnology AG and developed by Roche as a cancer treatment.

Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors are a class of medical drugs that are mainly used to treat advanced cancers. They function by inhibiting one or more of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes, which are part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. This signal pathway regulates cellular functions such as growth and survival. It is strictly regulated in healthy cells, but is always active in many cancer cells, allowing the cancer cells to better survive and multiply. PI3K inhibitors block the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and thus slow down cancer growth. They are examples of a targeted therapy. While PI3K inhibitors are an effective treatment, they can have very severe side effects and are therefore only used if other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Moxetumomab pasudotox, sold under the brand name Lumoxiti, is an anti-CD22 immunotoxin medication for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL) who have received at least two prior systemic therapies, including treatment with a purine nucleoside analog. Moxetumomab pasudotox is a CD22-directed cytotoxin and is the first of this type of treatment for adults with HCL. The drug consists of the binding fragment (Fv) of an anti-CD22 antibody fused to a toxin called PE38. This toxin is a 38 kDa fragment of Pseudomonas exotoxin A.
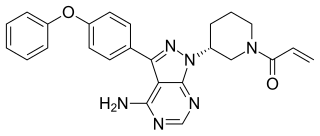
Ibrutinib, sold under the brand name Imbruvica among others, is a small molecule drug that inhibits B-cell proliferation and survival by irreversibly binding the protein Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK). Blocking BTK inhibits the B-cell receptor pathway, which is often aberrantly active in B cell cancers. Ibrutinib is therefore used to treat such cancers, including mantle cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia.

Idelalisib, sold under the brand name Zydelig, is a medication used to treat certain blood cancers.

Copanlisib is a drug which is approved by US FDA for the treatment of adult patients experiencing relapsed follicular lymphoma who have received at least two prior systemic therapies.

Venetoclax, sold under the brand names Venclexta and Venclyxto, is a medication used to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), or acute myeloid leukemia (AML).

Acalabrutinib, sold under the brand name Calquence, is a medication used to treat various types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic leukemia (CLL/SLL). It may be used both in relapsed as well as in treatment-naive settings.
Tisagenlecleucel, sold under the brand name Kymriah, is a CAR T cells medication for the treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) which uses the body's own T cells to fight cancer.

Umbralisib, sold under the brand name Ukoniq, is a medication for the treatment of marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) and follicular lymphoma (FL). It is taken by mouth.
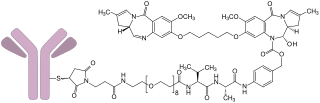
Loncastuximab tesirine, sold under the brand name Zynlonta, is a monoclonal antibody conjugate medication used to treat large B-cell lymphoma. It is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) composed of a humanized antibody targeting the protein CD19.
Verastem Oncology is an American pharmaceutical company that develops medicines to treat certain cancers. Headquartered and founded in Boston, Massachusetts, the firm is a member of NASDAQ Biotechnology Index.

Selinexor sold under the brand name Xpovio among others, is a selective inhibitor of nuclear export used as an anti-cancer medication. It works by blocking the action of exportin 1 and thus blocking the transport of several proteins involved in cancer-cell growth from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm, which ultimately arrests the cell cycle and leads to apoptosis. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action.

Indolent lymphoma, also known as low-grade lymphoma, is a group of slow-growing non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs). Because they spread slowly, they tend to have fewer signs and symptoms when first diagnosed and may not require immediate treatment. Symptoms can include swollen but painless lymph nodes, unexplained fever, and unintended weight loss.
Brexucabtagene autoleucel, sold under the brand name Tecartus, is a cell-based gene therapy medication for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Tafasitamab, sold under the brand name Monjuvi, is a medication used in combination with lenalidomide for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).














