Related Research Articles

Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of gel electrophoresis used in biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose, one of the two main components of agar. The proteins may be separated by charge and/or size, and the DNA and RNA fragments by length. Biomolecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the charged molecules through an agarose matrix, and the biomolecules are separated by size in the agarose gel matrix.

Agarose is a heteropolysaccharide, generally extracted from certain red seaweed. It is a linear polymer made up of the repeating unit of agarobiose, which is a disaccharide made up of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose. Agarose is one of the two principal components of agar, and is purified from agar by removing agar's other component, agaropectin.

Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge.

Southern blot is a method used for detection and quantification of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples. This method is used in molecular biology. Briefly, purified DNA from a biological sample is digested with restriction enzymes, and the resulting DNA fragments are separated by using an electric current to move them through a sieve-like gel or matrix, which allows smaller fragments to move faster than larger fragments. The DNA fragments are transferred out of the gel or matrix onto a solid membrane, which is then exposed to a DNA probe labeled with a radioactive, fluorescent, or chemical tag. The tag allows any DNA fragments containing complementary sequences with the DNA probe sequence to be visualized within the Southern blot.

Borax and tincar ) is a salt, a hydrated or anhydrous borate of sodium, with the chemical formula Na2H20B4O17. It is a colorless crystalline solid that dissolves in water to make a basic solution.

Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) is a technique widely used in biochemistry, forensic chemistry, genetics, molecular biology and biotechnology to separate biological macromolecules, usually proteins or nucleic acids, according to their electrophoretic mobility. Electrophoretic mobility is a function of the length, conformation, and charge of the molecule. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool used to analyze RNA samples. When polyacrylamide gel is denatured after electrophoresis, it provides information on the sample composition of the RNA species.

Nucleic acid electrophoresis is an analytical technique used to separate DNA or RNA fragments by size and reactivity. Nucleic acid molecules which are to be analyzed are set upon a viscous medium, the gel, where an electric field induces the nucleic acids to migrate toward the anode. The separation of these fragments is accomplished by exploiting the mobilities with which different sized molecules are able to pass through the gel. Longer molecules migrate more slowly because they experience more resistance within the gel. Because the size of the molecule affects its mobility, smaller fragments end up nearer to the anode than longer ones in a given period. After some time, the voltage is removed and the fragmentation gradient is analyzed. For larger separations between similar sized fragments, either the voltage or run time can be increased. Extended runs across a low voltage gel yield the most accurate resolution. Voltage is, however, not the sole factor in determining electrophoresis of nucleic acids.

Protein electrophoresis is a method for analysing the proteins in a fluid or an extract. The electrophoresis may be performed with a small volume of sample in a number of alternative ways with or without a supporting medium, namely agarose or polyacrylamide. Variants of gel electrophoresis include SDS-PAGE, free-flow electrophoresis, electrofocusing, isotachophoresis, affinity electrophoresis, immunoelectrophoresis, counterelectrophoresis, and capillary electrophoresis. Each variant has many subtypes with individual advantages and limitations. Gel electrophoresis is often performed in combination with electroblotting or immunoblotting to give additional information about a specific protein.

Bromophenol blue, albutest is used as a pH indicator, an electrophoretic color marker, and a dye. It can be prepared by slowly adding excess bromine to a hot solution of phenolsulfonphthalein in glacial acetic acid.

Lithium borate, also known as lithium tetraborate is an inorganic compound with the formula Li2B4O7. A colorless solid, lithium borate is used in making glasses and ceramics.

Lithium acetate (CH3COOLi) is a salt of lithium and acetic acid. It is often abbreviated as LiOAc.
TBE or Tris/Borate/EDTA, is a buffer solution containing a mixture of Tris base, boric acid and EDTA.
TE buffer is a commonly used buffer solution in molecular biology, especially in procedures involving DNA, cDNA or RNA. "TE" is derived from its components: Tris, a common pH buffer, and EDTA, a molecule that chelates cations like Mg2+. The purpose of TE buffer is to solubilize DNA or RNA, while protecting it from degradation.

Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) is a technique used for the separation of large DNA molecules by applying to a gel matrix an electric field that periodically changes direction. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is a method used to separate large segments of DNA using an alternating and cross field. In a uniform magnetic field, components larger than 50kb move through the gel in a zigzag pattern, allowing for more effective separation of DNA molecules. This method is commonly used in microbiology for typing bacteria and is a valuable tool for epidemiological studies and gene mapping in microbes and mammalian cells. It also played a role in the development of large-insert cloning systems such as bacterial and yeast artificial chromosomes.
TAE buffer is a buffer solution containing a mixture of Tris base, acetic acid and EDTA.

A molecular-weight size marker, also referred to as a protein ladder, DNA ladder, or RNA ladder, is a set of standards that are used to identify the approximate size of a molecule run on a gel during electrophoresis, using the principle that molecular weight is inversely proportional to migration rate through a gel matrix. Therefore, when used in gel electrophoresis, markers effectively provide a logarithmic scale by which to estimate the size of the other fragments.
SB buffer is a buffer solution used in agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. "SB" is a commercial trademark of Faster Better Media LLC for their sodium boric acid-based conductive medium, which is based on the publications of Brody and Kern.

An electrophoretic color marker is a chemical used to monitor the progress of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) since DNA, RNA, and most proteins are colourless. The color markers are made up of a mixture of dyes that migrate through the gel matrix alongside the sample of interest. They are typically designed to have different mobilities from the sample components and to generate colored bands that can be used to assess the migration and separation of sample components.

Affinity electrophoresis is a general name for many analytical methods used in biochemistry and biotechnology. Both qualitative and quantitative information may be obtained through affinity electrophoresis. Cross electrophoresis, the first affinity electrophoresis method, was created by Nakamura et al. Enzyme-substrate complexes have been detected using cross electrophoresis. The methods include the so-called electrophoretic mobility shift assay, charge shift electrophoresis and affinity capillary electrophoresis. The methods are based on changes in the electrophoretic pattern of molecules through biospecific interaction or complex formation. The interaction or binding of a molecule, charged or uncharged, will normally change the electrophoretic properties of a molecule. Membrane proteins may be identified by a shift in mobility induced by a charged detergent. Nucleic acids or nucleic acid fragments may be characterized by their affinity to other molecules. The methods have been used for estimation of binding constants, as for instance in lectin affinity electrophoresis or characterization of molecules with specific features like glycan content or ligand binding. For enzymes and other ligand-binding proteins, one-dimensional electrophoresis similar to counter electrophoresis or to "rocket immunoelectrophoresis", affinity electrophoresis may be used as an alternative quantification of the protein. Some of the methods are similar to affinity chromatography by use of immobilized ligands.
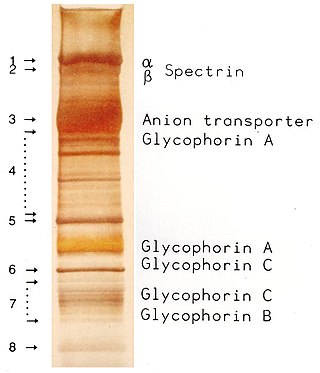
SDS-PAGE is a discontinuous electrophoretic system developed by Ulrich K. Laemmli which is commonly used as a method to separate proteins with molecular masses between 5 and 250 kDa. The combined use of sodium dodecyl sulfate and polyacrylamide gel eliminates the influence of structure and charge, and proteins are separated by differences in their size. At least up to 2012, the publication describing it was the most frequently cited paper by a single author, and the second most cited overall.
References
- ↑ Brody, J.R., Kern, S.E. (2004): History and principles of conductive media for standard DNA electrophoresis.Anal Biochem. 333(1):1-13. doi : 10.1016/j.ab.2004.05.054 PMID 15351274 PDF
- ↑ Sodium boric acid: a tris-free, cooler conductive medium for DNA electrophoresis.Biotechniques 36(2):214-215. PMID 14989083 PDF Archived 2011-07-24 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Brody, J.R., Calhoun, E.S., Gallmeier, E., Creavalle, T.D., Kern, S.E. (2004): Ultra-fast high-resolution agarose electrophoresis of DNA and RNA using low-molarity conductive media.Biotechniques 37(4):598-602. PMID 15517972 PDF [ permanent dead link ]