Contents
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | 1913 in the United Kingdom Other events of 1913 List of years in Ireland | ||||
Events from the year 1913 in Ireland.
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | 1913 in the United Kingdom Other events of 1913 List of years in Ireland | ||||
Events from the year 1913 in Ireland.

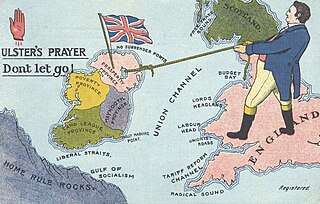
Unionism in Ireland is a political tradition that professes loyalty to the crown of the United Kingdom and to the union it represents with England, Scotland and Wales. The overwhelming sentiment of Ireland's Protestant minority, unionism mobilised in the decades following Catholic Emancipation in 1829 to oppose restoration of a separate Irish parliament. Since Partition in 1921, as Ulster unionism its goal has been to retain Northern Ireland as a devolved region within the United Kingdom and to resist the prospect of an all-Ireland republic. Within the framework of the 1998 Belfast Agreement, which concluded three decades of political violence, unionists have shared office with Irish nationalists in a reformed Northern Ireland Assembly. As of February 2024, they no longer do so as the larger faction: they serve in an executive with an Irish republican First Minister.

The Irish Citizen Army, or ICA, was a small paramilitary group of trained trade union volunteers from the Irish Transport and General Workers' Union (ITGWU) established in Dublin for the defence of workers' demonstrations from the Dublin Metropolitan Police. It was formed by James Larkin, James Connolly and Jack White on 23 November 1913. Other prominent members included Seán O'Casey, Constance Markievicz, Francis Sheehy-Skeffington, P. T. Daly and Kit Poole. In 1916, it took part in the Easter Rising, an armed insurrection aimed at ending British rule in Ireland.

James Larkin, sometimes known as Jim Larkin or Big Jim, was an Irish republican, socialist and trade union leader. He was one of the founders of the Irish Labour Party along with James Connolly and William O'Brien, and later the founder of the Irish Worker League, as well as the Irish Transport and General Workers' Union (ITGWU) and the Workers' Union of Ireland. Along with Connolly and Jack White, he was also a founder of the Irish Citizen Army. Larkin was a leading figure in the Syndicalist movement.
Events from the year 1920 in Ireland.
Events from the year 1914 in Ireland.
Events in the year 1912 in Ireland.
Events in the year 1911 in Ireland.
Events from the year 1892 in Ireland.

Ireland was part of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1922. For almost all of this period, the island was governed by the UK Parliament in London through its Dublin Castle administration in Ireland. Ireland underwent considerable difficulties in the 19th century, especially the Great Famine of the 1840s which started a population decline that continued for almost a century. The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw a vigorous campaign for Irish Home Rule. While legislation enabling Irish Home Rule was eventually passed, militant and armed opposition from Irish unionists, particularly in Ulster, opposed it. Proclamation was shelved for the duration following the outbreak of World War I. By 1918, however, moderate Irish nationalism had been eclipsed by militant republican separatism. In 1919, war broke out between republican separatists and British Government forces. Subsequent negotiations between Sinn Féin, the major Irish party, and the UK government led to the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty, which resulted in five-sixths of the island seceding from the United Kingdom, becoming the Irish Free State, with only the six northeastern counties remaining within the United Kingdom.

The Dublin lock-out was a major industrial dispute between approximately 20,000 workers and 300 employers that took place in Dublin, Ireland. The dispute, lasting from 26 August 1913 to 18 January 1914, is often viewed as the most severe and significant industrial dispute in Irish history. Central to the dispute was the workers' right to unionise.

The Larne gun-running was a major gun smuggling operation organised in April 1914 in Ireland by Major Frederick H. Crawford and Captain Wilfrid Spender for the Ulster Unionist Council to equip the Ulster Volunteer Force. The operation involved the smuggling of almost 25,000 rifles and between 3 and 5 million rounds of ammunition from the German Empire, with the shipments landing in Larne, Donaghadee, and Bangor in the early hours between Friday 24 and Saturday 25 April 1914. The Larne gun-running may have been the first time in history that motor-vehicles were used "on a large scale for a military-purpose, and with striking success".

Protestant Irish Nationalists are adherents of Protestantism in Ireland who also support Irish nationalism. Protestants have played a large role in the development of Irish nationalism since the eighteenth century, despite most Irish nationalists historically being from the Irish Catholic majority, as well as most Irish Protestants usually tending toward unionism in Ireland. Protestant nationalists have consistently been influential supporters and leaders of various movements for the political independence of Ireland from Great Britain. Historically, these movements ranged from supporting the legislative independence of the Parliament of the Kingdom of Ireland, to a form of home rule within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, to complete independence in an Irish Republic and a United Ireland.
Events from the year 1886 in Ireland.

William Martin Murphy was an Irish businessman, newspaper publisher and politician. A member of parliament (MP) representing Dublin from 1885 to 1892, he was dubbed "William Murder Murphy" among the Irish press and the striking members of the Irish Transport and General Workers' Union during the Dublin Lockout of 1913. He was arguably both Ireland's first "press baron" and the leading promoter of tram development.

Maria Winifred "Winnie" Carney, was an Irish republican, a participant in the 1916 Easter Rising in Dublin, and in Belfast—as a trade union secretary, women's suffragist, and socialist party member—a lifelong social and political activist. In March 2024, a statue to her was unveiled on the grounds of Belfast City Hall.

The Belfast Dock strike or Belfast lockout took place in Belfast, Ireland from 26 April to 28 August 1907. The strike was called by Liverpool-born trade union leader James Larkin who had successfully organised the dock workers to join the National Union of Dock Labourers (NUDL). The dockers, both Protestant and Catholic, had gone on strike after their demand for union recognition was refused. They were soon joined by carters, shipyard workers, sailors, firemen, boilermakers, coal heavers, transport workers, and women from the city's largest tobacco factory. Most of the dock labourers were employed by powerful tobacco magnate Thomas Gallaher, chairman of the Belfast Steamship Company and owner of Gallaher's Tobacco Factory.

Delia Larkin was a trade union organiser, journalist and actress, born to Irish parents in Liverpool, England. She was influenced by the activities of her brother, James Larkin, to move to Ireland, and was prominent during the 1913 Dublin Lockout. She was active in Irish trade union activities and was a founding secretary of the Irish Women Workers' Union.
Alice Brady (1898–1914) was a labour activist that was shot and killed during the 1913 Dublin Lock-out. She was shot accidentally in the hand by a worker and died two weeks later of tetanus. The worker was charged but acquitted of her murder. Members from the Irish Women Workers' Union used her funeral as a show of strength. A service was held on Saturday, 4 January 2014 to mark the centenary of Brady's funeral, and RTÉ One broadcast a documentary on the lockout involving descendants of participants and members of Brady's family.

Jennie Shanahan, was a member of the Irish Citizen Army and fought in the Easter Rising and the Irish War of Independence.

Captain James Robert "Jack" White, DSO (1879–1946) was an Irish republican and libertarian socialist. After colonial service in the British military, he entered Irish politics in 1913 working with Roger Casement in Ulster to detach fellow Protestants from Unionism as it armed to resist Irish Home Rule, and with James Connolly to defend the Irish Transport and General Workers' Union in the great Dublin lock-out. White rallied to the defence of those condemned for the 1916 Easter Rising, but the combination of his socialism and anti-clericalism placed him at odds with the principal currents of Irish republicanism. Until experience of Republican Spain in 1936 convinced him of the anarchist critique of the party-state, he associated with a succession of communist-aligned groups. His last public appearance was in 1945, at an Orange Hall in his home town of Broughshane, County Antrim, where he proposed himself as a "republican socialist" candidate in the upcoming United Kingdom general election.