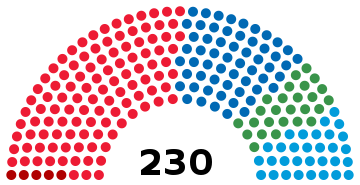
General elections were held in Sweden on 15 September 2002, alongside municipal and county council elections. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Riksdag, winning 144 of the 349 seats.

General elections were held in Sweden on 20 September 1998. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Riksdag, winning 131 of the 349 seats.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 14 September 1930. Despite losing ten seats, the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) remained the largest party in the Reichstag, winning 143 of the 577 seats, while the Nazi Party (NSDAP) dramatically increased its number of seats from 12 to 107. The Communists also increased their parliamentary representation, gaining 23 seats and becoming the third-largest party in the Reichstag.
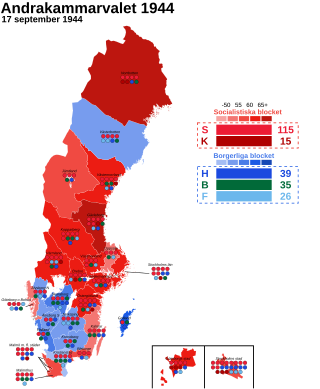
General elections were held in Sweden on 17 September 1944. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 115 of the 230 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag. Due to World War II, the four main parties continued to form a wartime coalition, only excluding the Communist Party.

General elections were held in Sweden on 19 September 1948. Despite a campaign by a large part of the Swedish press against socializing insurances, controlled foreign trade and rationing regulations still in use since the war, freshman Prime Minister and Social Democratic leader Tage Erlander managed to defeat the People's Party-led opposition under Bertil Ohlin by a higher election turnout. He maintained his government with only minor losses and the Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 112 of the 230 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag. Erlander was to stay on as Prime Minister until 1969.

General elections were held in Sweden on 16 September 1956. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 106 of the 231 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag. A Social Democratic-Farmers' League coalition government was formed by Prime Minister Tage Erlander after the election with 125 of the total of 231 seats. Although the non-socialist parties held a majority in the Second Chamber, the Social Democrats held a majority in the First Chamber, so a non-socialist government could not be formed.

General elections were held in Sweden on 15 September 1968. Held in the wake of the crushing of the Prague Spring, it resulted in a landslide victory for the Social Democratic government and Prime Minister Tage Erlander. It is one of two general elections in Swedish history where a single party received more than half of the vote. Erlander would resign the following year after an uninterrupted tenure of 23 years as head of government.

General elections were held in Sweden on 16 September 1979. Although the Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 154 of the 349 seats in the Riksdag, the liberal interim government of Ola Ullsten was succeeded by another centre-right coalition government composed of the People's Party, the Moderate Party and the Centre Party, led by Centre Party leader Thorbjörn Fälldin. The three parties together won 175 seats, compared to the 174 won by the Social Democrats and Communists. It was the only time that non-socialist parties retained power in an election between 1928 and 2010. The Moderates dramatically increased their representation in the Riksdag, becoming the largest party of the non-socialist bloc, a position they maintained until 2022.

General elections were held in Sweden on 15 September 1985. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Riksdag, winning 159 of the 349 seats. Its leader, Olof Palme, kept his position as prime minister. He would retain this position successfully until his assassination in 1986.

General elections were held in Sweden on 15 September 1991. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Riksdag, winning 138 of the 349 seats. However, it was the party's worst showing since 1928 with 37.7% of the vote.

General elections were held in Sweden on 18 September 1994. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Riksdag, winning 161 of the 349 seats. Led by Ingvar Carlsson, the party returned to power and formed a minority government after the election. This was the final time the Social Democrats recorded above 40% of the vote before the party's vote share steeply declined four years later and never recovered. The Greens also returned to the Riksdag in the 1994 elections, after a three-year absence.
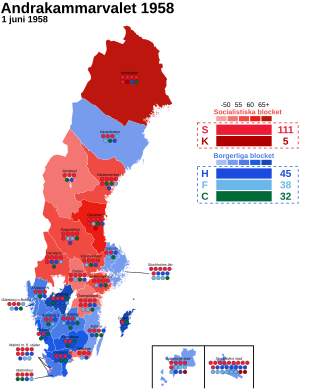
Early general elections were held in Sweden on 1 June 1958, after the defeat of the Social Democratic government's proposals for a new pensions system in a parliamentary vote. The Social Democrats remained the largest party, winning 111 of the 231 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag, and Tage Erlander's third government was returned to power. In accordance with the law, the new Chamber was elected only to complete the previous Chamber's term, which was due to end in 1960.
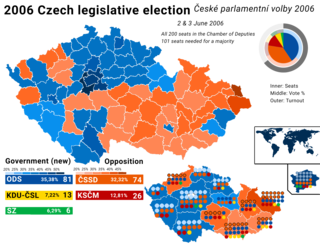
Parliamentary elections were held in the Czech Republic on 2 and 3 June 2006 to elect the members of the Chamber of Deputies.

The 1979 Italian general election was held in Italy on 3 June 1979. This election was called just a week before the European elections.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 6 and 7 July 1958. The communist Finnish People's Democratic League emerged as the largest party, but was unable to form a government.

Early general elections were held in Sweden between 10 and 26 September 1921, the first in Sweden under universal suffrage. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 93 of the 230 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag. Party leader Hjalmar Branting formed his second government.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland between 1 and 3 July 1933. The Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in Parliament with 78 of the 200 seats. However, Prime Minister Toivo Mikael Kivimäki of the National Progressive Party continued in office after the elections, supported by Pehr Evind Svinhufvud and quietly by most Agrarians and Social Democrats. They considered Kivimäki's right-wing government a lesser evil than political instability or an attempt by the radical right to gain power. Voter turnout was 62.2%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 8 May 1994, with a second round of voting in 174 of the 176 single member constituencies on 29 May. They resulted in the return to power of the Hungarian Socialist Party, the former Communist party, under the leadership of Gyula Horn, who became prime minister. The Socialists achieved a remarkable revival, winning an overall majority of 209 seats out of 386, up from 33 in 1990.
Parliamentary elections were held in Romania on 28 March 1948. They were the first elections held under communist rule; the communist-dominated parliament had declared Romania a people's republic after King Michael was forced to abdicate in December 1947.
Sweden held a general election around 19 September 1924. This was the second election under universal suffrage. In spite of a majority for the non-socialist parties, Social Democrat Hjalmar Branting was able to form a government, although his successor eventually saw the government fall and being replaced by a right-leaning Electoral League government.