
The politics of Sweden take place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic constitutional monarchy. Executive power is exercised by the government, led by the Prime Minister. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament, elected within a multi-party system. The judiciary is independent, appointed by the government and employed until retirement. Sweden is formally a monarchy with a monarch holding symbolic power.

Höganäs Municipality is one of 290 municipalities of Sweden, in Skåne County in the southern part of the country. Its seat is located in the city of Höganäs.

Pajala Municipality is a municipality in Norrbotten County in northern Sweden, bordering Finland. Its seat is located in the locality of Pajala.

Askersund Municipality is a municipality in Örebro County in central Sweden. Its seat is located in the city of Askersund.

Hammarö Municipality is a municipality in Värmland County in west central Sweden. Its seat is located in the town of Skoghall.
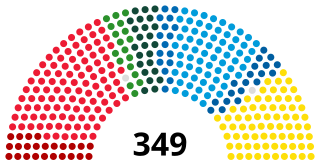
The Riksdag is the legislature and the supreme decision-making body of the Kingdom of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members, elected proportionally and serving, since 1994, fixed four-year terms. The 2022 Swedish general election is the most recent general election.

Elections in Sweden are held once every four years. At the highest level, all 349 members of Riksdag, the national parliament of Sweden, are elected in general elections. Elections to the 20 county councils and 290 municipal assemblies – all using almost the same electoral system – are held concurrently with the legislative elections on the second Sunday in September.

The prime ministerof Sweden is the head of government of the Kingdom of Sweden. The prime minister and their cabinet exercise executive authority in the Kingdom of Sweden and are subject to the Parliament of Sweden. The prime minister is nominated by the speaker of the Riksdag and is elected by the chamber by simple majority, using negative parliamentarianism. The Riksdag holds elections every four years, in the even year between leap years.

Region Gotland, officially Gotlands kommun, is a municipality that covers the entire island of Gotland in Sweden. The city of Visby is the municipality's seat. Gotland Municipality is the 39th most populous municipality in Sweden.
The period following the accession of Oscar II to the throne of Sweden in 1872 was marked by political conflict. The Lantmanna Party, representing peasant proprietors, dominated the Lower House of parliament, and demanded tax reductions and reforms of the system of military service. The Upper House opposed these positions. A compromise was reached in 1884 with reduction in land taxes and increased periods of military service, processes that continued in later years.

Since the introduction of parliamentarism in Sweden, six national referendums have been held. Legal provisions for referendums were introduced in 1922, one year after the adoption of universal suffrage. The Constitution of Sweden provides for binding referendums, but all referendums held as of 2012 have been non-binding. The latest referendum, on adopting the euro, was held on 14 September 2003.

General elections were held in Sweden on 15 September 2002, alongside municipal and county council elections. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Riksdag, winning 144 of the 349 seats.

Oscar Robert Themptander was a Swedish politician and public official who was Prime Minister of Sweden from 1884 to 1888 during the reign of King Oscar II, and Governor of Stockholm County from 1888 to 1896. He was also minister for finance.

Kiruna Municipality is a municipality in Norrbotten County in northernmost Sweden. Its seat is located in Kiruna. It is the northernmost municipality in Sweden, and at 20,715 square kilometres (7,998 sq mi) is Sweden's geographically largest covering roughly 4.604% of its total area. Finnish, Meänkieli and Sami have the official status of being minority languages in the municipality.

Early general elections were held in Sweden between 10 and 26 September 1921. It was the first elections held under universal suffrage, for both men and women. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 93 of the 230 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag. Party leader Hjalmar Branting formed his second government.

Kjell Stefan Löfven is a Swedish politician who has served as the President of European Socialists since October 2022. He previously served as Prime Minister of Sweden from October 2014 to November 2021 and leader of the Social Democratic Party from 2012 to 2021.
The Government of the Kingdom of Sweden is the national cabinet of Sweden, and the country's executive authority.

General elections were held in Sweden in 1878 to elect the Second Chamber of the Riksdag for a three-year term. Following the elections, the Lantmanna Party remained the largest party, holding 92 of the 204 seats.

General elections were held in Sweden in 1881 to elect the Second Chamber of the Riksdag for a three-year term. Following the elections, the Lantmanna Party remained the largest party, holding 101 of the 206 seats.

General elections will be held in Sweden on 13 September 2026 to elect the 349 members of the Riksdag. They in turn will elect the prime minister. In case of a snap election, the parliamentary term would not be reset and general elections would still be held in September 2026 together with regional and municipal elections.













