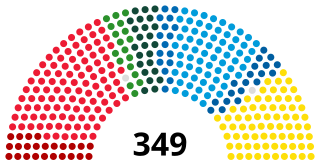
The Riksdag is the legislature and the supreme decision-making body of the Kingdom of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members, elected proportionally and serving, since 1994, fixed four-year terms. The 2022 Swedish general election is the most recent general election.

Elections in Sweden are held once every four years. At the highest level, all 349 members of Riksdag, the national parliament of Sweden, are elected in general elections. Elections to the 20 county councils and 290 municipal assemblies – all using almost the same electoral system – are held concurrently with the legislative elections on the second Sunday in September.

General elections were held in Sweden in 1866. They were the first elections for the new Second Chamber in the Riksdag, which would serve a three-year term. Suffrage was given to men over the age of 21 who either had a taxable income of at least 800 riksdaler a year, owned a property worth at least 1,000 riksdaler, or rented a property taxed to at least 6,000 riksdaler. This meant that around 5.5% of the population were able to vote, a slight reduction from the 6% that had been eligible under the previous Estates system. The changes had been approved following a 60,000-strong petition and a vote in the House of Nobility in December 1865 during which crowds had gathered outside to pressure the nobles into approving it.

General elections were held in Sweden in 1869 to elect the Second Chamber of the Riksdag for a three-year term. In urban areas the elections were direct, whilst in some rural areas the vote was indirect, using electors.

General elections were held in Sweden in 1872 to elect the Second Chamber of the Riksdag for a three-year term. Following the elections, the Lantmanna Party was the largest party, holding 90 of the 194 seats.

General elections were held in Sweden in 1875 to elect the Second Chamber of the Riksdag for a three-year term. Following the elections, the Lantmanna Party remained the largest party, holding 92 of the 198 seats.

General elections were held in Sweden in 1878 to elect the Second Chamber of the Riksdag for a three-year term. Following the elections, the Lantmanna Party remained the largest party, holding 92 of the 204 seats.

Halland County is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established in 1970 when the Riksdag changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It is conterminous with the county of Halland. The constituency currently elects 10 of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 258,794 registered electors.
Sweden held a general election on 15 September 1968, to elect the members of the Second chamber of the Riksdag. This was to be the final bicameral Riksdag elected. As of 2020, this was the final time a party has held an outright majority in the Riksdag after the Social Democrats won 125 out of the 233 seats.

Malmö Municipality is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established in 1994 from parts of Fyrstadskretsen following the reorganisation of the constituencies in Malmöhus County. It is conterminous with the municipality of Malmö. The constituency currently elects 10 of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 251,172 registered electors.

Blekinge County is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established in 1970 when the Riksdag changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It is conterminous with the county of Blekinge. The constituency currently elects five of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 121,789 registered electors.

Kronoberg County is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established in 1970 when the Riksdag changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It is conterminous with the county of Kronoberg. The constituency currently elects six of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 147,910 registered electors.

Jämtland County is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established in 1970 when the Riksdag changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It is conterminous with the county of Jämtland. The constituency currently elects four of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 101,363 registered electors.
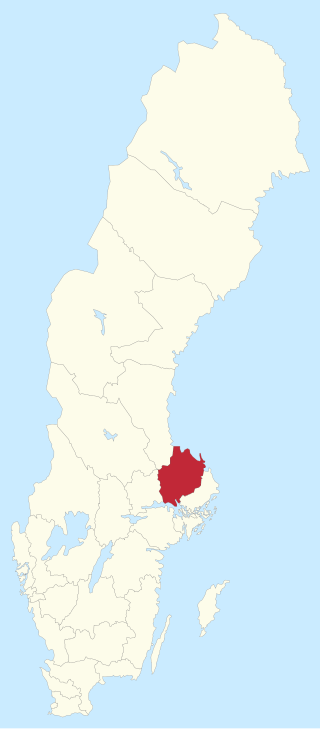
Uppsala County is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established in 1970 when the Riksdag changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It is conterminous with the county of Uppsala. The constituency currently elects 12 of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 292,255 registered electors.

Västernorrland County is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established in 1970 when the Riksdag changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It is conterminous with the county of Västernorrland. The constituency currently elects eight of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 188,542 registered electors.

Västra Götaland County North is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established as Älvsborg County North in 1970 when the Riksdag was changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It was renamed Västra Götaland County North in 1998 when the counties of Älvsborg, Gothenburg and Bohus and Skaraborg were merged to create Västra Götaland. The constituency currently consists of the municipalities of Åmål, Bengtsfors, Dals-Ed, Färgelanda, Lysekil, Mellerud, Munkedal, Orust, Sotenäs, Strömstad, Tanum, Trollhättan, Uddevalla and Vänersborg. The constituency currently elects eight of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 208,144 registered electors.
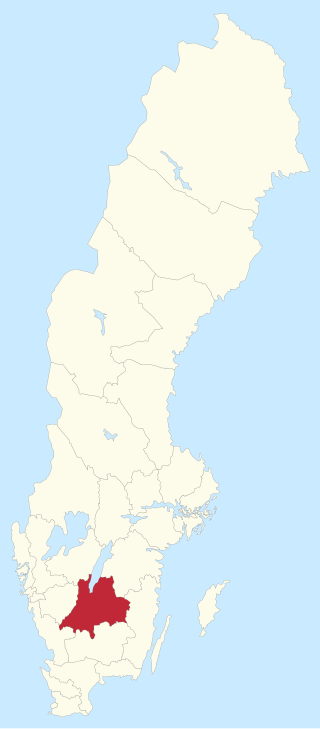
Jönköping County is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established in 1970 when the Riksdag changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It is conterminous with the county of Jönköping. The constituency currently elects 11 of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 271,666 registered electors.

Västra Götaland County East is one of the 29 multi-member constituencies of the Riksdag, the national legislature of Sweden. The constituency was established as Skaraborg County in 1970 when the Riksdag changed from a bicameral legislature to a unicameral legislature. It was renamed Västra Götaland County East in 1998 when the counties of Älvsborg, Gothenburg and Bohus and Skaraborg were merged to create Västra Götaland. The constituency currently consists of the municipalities of Essunga, Falköping, Götene, Grästorp, Gullspång, Hjo, Karlsborg, Lidköping, Mariestad, Skara, Skövde, Tibro, Tidaholm, Töreboda and Vara. The constituency currently elects eight of the 349 members of the Riksdag using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 general election it had 207,560 registered electors.

Members of Parliament in Sweden sit in the Riksdag.

General elections will be held in Sweden on 13 September 2026 to elect the 349 members of the Riksdag. They in turn will elect the prime minister. In case of a snap election, the parliamentary term would not be reset and general elections would still be held in September 2026 together with regional and municipal elections.














