The transport system of Finland is well-developed. Factors affecting traffic include the sparse population and long distance between towns and cities, and the cold climate with waterways freezing and land covered in snow for winter.

Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the Baltic states. It borders Estonia to the north, Lithuania to the south, Russia to the east, and Belarus to the southeast and shares a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi), with a population of 1.9 million. The country has a temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Riga. Latvians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts and speak Latvian, one of the only two surviving Baltic languages. Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population.
Transportation in Sweden is carried out by car, bus, train, tram, boat or aeroplane.

The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomous areas of the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Åland. The representatives are members of parliament in their respective countries or areas and are elected by those parliaments. The Council holds ordinary sessions each year in October/November and usually one extra session per year with a specific theme. The council's official languages are Danish, Finnish, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish, though it uses only the mutually intelligible Scandinavian languages—Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish—as its working languages. These three comprise the first language of around 80% of the region's population and are learned as a second or foreign language by the remaining 20%.

The Øresund or Öresund Bridge is a combined railway and motorway bridge across the Øresund strait between Denmark and Sweden. It is the longest in Europe with both roadway and railway combined in a single structure, running nearly 8 kilometres from the Swedish coast to the artificial island Peberholm in the middle of the strait. The crossing is completed by the 4-kilometre (2.5 mi) Drogden Tunnel from Peberholm to the Danish island of Amager.

The national flag of Norway is red with a navy blue Scandinavian cross bordered in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog, the flag of Denmark.

Left-hand traffic (LHT) and right-hand traffic (RHT) are the practices, in bidirectional traffic, of keeping to the left side or to the right side of the road, respectively. They are fundamental to traffic flow, and are sometimes referred to as the rule of the road. The terms right- and left-hand drive refer to the position of the driver and the steering wheel in the vehicle and are, in automobiles, the reverse of the terms right- and left-hand traffic. The rule also extends to where on the road a vehicle is to be driven, if there is room for more than one vehicle in the one direction, as well as the side on which the vehicle in the rear overtakes the one in the front. For example, a driver in an LHT country would typically overtake on the right of the vehicle being overtaken.

Dagen H (H-day), today usually called "Högertrafikomläggningen", was on 3 September 1967, the day in which Sweden switched from driving on the left-hand side of the road to the right. The "H" stands for "Högertrafik", the Swedish word for right-hand traffic. It was by far the largest logistical event in Sweden's history.

The Øresund Region, also known as Greater Copenhagen for marketing purposes, is a metropolitan region encompassing the Capital Region of Denmark and Zealand, in eastern Denmark, and Scania, in southern Sweden. Centred around the Øresund strait and the two cities which lie on either side, Copenhagen in Denmark and Malmö in Sweden, the region is connected by the Øresund Bridge, which spans the strait at its southern end, and the HH Ferry route between Helsingør, Denmark, and Helsingborg, Sweden, at the narrowest point of the strait.

Traffic Message Channel (TMC) is a technology for delivering traffic and travel information to motor vehicle drivers. It is digitally coded using the ALERT C or TPEG protocol into Radio Data System (RDS) carried via conventional FM radio broadcasts. It can also be transmitted on Digital Audio Broadcasting or satellite radio. TMC allows silent delivery of dynamic information suitable for reproduction or display in the user's language without interrupting audio broadcast services. Both public and commercial services are operational in many countries. When data is integrated directly into a navigation system, traffic information can be used in the system's route calculation.

Stockholm Municipality or the City of Stockholm is a municipality in Stockholm County in east central Sweden. It has the largest population of the 290 municipalities of the country, but one of the smallest areas, making it the second most densely populated. It is also the most populous municipality in the Nordic countries.

The Stockholm congestion tax, also referred to as the Stockholm congestion charge, is a congestion pricing system implemented as a tax levied on most vehicles entering and exiting central Stockholm, Sweden. The congestion tax was implemented on a permanent basis on August 1, 2007, after a seven-month trial period between January 3, 2006 and July 31, 2006. It was inspired by Singapore's Electronic Road Pricing (ERP) system, which first introduced it in 1975.
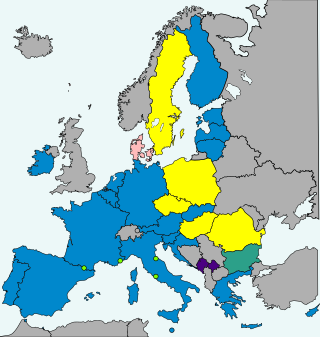
A non-binding referendum on introduction of the euro was held in Sweden on 14 September 2003. The majority voted not to adopt the euro, and thus Sweden decided in 2003 not to adopt the euro for the time being. Had they voted in favour, the plan was that Sweden would have adopted the euro on 1 January 2006.
Vision Zero is a multi-national road traffic safety project that aims to achieve a roadway system with no fatalities or serious injuries involving road traffic. It started in Sweden and was approved by their parliament in October 1997. A core principle of the vision is that "Life and health can never be exchanged for other benefits within the society" rather than the more conventional comparison between costs and benefits, where a monetary value is placed on life and health, and then that value is used to decide how much money to spend on a road network towards the benefit of decreasing risk.

The Nordic countries are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden; the autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland; and the autonomous region of Åland.

The Nordic Resistance Movement is a pan-Nordic neo-Nazi movement in the Nordic countries and a political party in Sweden. Besides Sweden, it is established in Norway, Denmark and Iceland, and formerly in Finland before it was banned in 2019. Terrorism expert Magnus Ranstorp has described the NRM as a terrorist organization due to their aim of abolishing democracy along with their paramilitary activities and weapons caches. In 2022, some members of the United States Congress began calling for the organization to be added to the United States Department of State list of Foreign Terrorist Organizations.
H-dagurinn or Hægri dagurinn on 26 May 1968 was the day that Iceland changed from left hand traffic to right hand traffic. The change itself occurred formally at 6:00 am.
Karlskoga Motorstadion, also known as Gelleråsen Arena, is the oldest permanent motorsport race track in Sweden. The circuit is located 6 km (3.7 mi) north of Karlskoga. The layout is such that the whole track can be seen from all spectator areas.

Stockholm Skavsta Airport, or Nyköping Airport is an international airport near Nyköping, Sweden, 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) northwest of its urban area and approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi) southwest of Stockholm. It is served by low-cost airlines and cargo operators, and is the fifth-largest airport in Sweden, with an ability to handle 2.5 million passengers annually.
















