
The 1978 Tabas earthquake occurred on September 16 at 19:05:55 local time in central Iran. The shock measured 7.4 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX+ (Violent). The death toll was in the range of 15,000–25,000, with severe damage occurring in the town of Tabas.
An earthquake affected several villages in the Kerman province of Iran on February 22, 2005, at . The shock measured 6.4 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Zarand is located 740 km southeast of Tehran. The maximum recorded peak ground acceleration was 0.51 g at Shirinrud dam. The United States' National Earthquake Information Center and the Belgian' Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters both show that 612 died and 1,411 were injured in the event.
The 1972 Nicaragua earthquake occurred at 12:29:44 a.m. local time on December 23 near Managua, the capital of Nicaragua. It had a moment magnitude of 6.3 and a maximum MSK intensity of IX (Destructive). The epicenter was 28 km (17 mi) northeast of the city centre and a depth of about 10 km (6.2 mi). The earthquake caused widespread casualties among Managua's residents: 4,000–11,000 were killed, 20,000 were injured and over 300,000 were left homeless.
The 1929 Kopet Dag earthquake took place at 15:37 UTC on 1 May with a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). It occurred in the Kopet Dag area of Iran and caused up to 3,800 casualties along the Iran-Turkmenistan border. More than 1,100 were injured.
The 1930 Salmas earthquake occurred on in West Azerbaijan Province, Iran. The earthquake, which was among Iran's largest, measured 7.1 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). A damaging foreshock occurred fifteen hours prior to the main event and served as a warning to the people that felt it strongly. Reports from seismologists and seismological organizations indicate that up to 3,000 fatalities may have occurred in northwest Iran and southeast Turkey.
The 1984 Morgan Hill earthquake occurred on April 24 at in the Santa Clara Valley of Northern California. The shock had a moment magnitude of 6.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The epicenter was located near Mount Hamilton in the Diablo Range of the California Coast Ranges. Nearby communities sustained serious damage with financial losses of at least US$7.5 million.
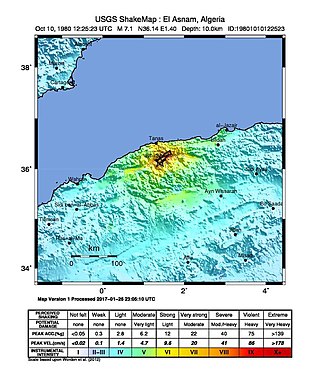
The 1980 El Asnam earthquake occurred on October 10 at with a moment magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme). The shock occurred in the Algerian town of El Asnam. The shocks were felt over 550 km (340 mi) away, with the initial earthquake lasting 35 seconds. It was the largest earthquake in Algeria, and was followed three hours later by a magnitude 6.2 aftershock. The earthquake created about 42 km (26 mi) of surface rupture and had a vertical slip of up to 4.2 m (14 ft). No foreshocks were recorded. The earthquake was found to have occurred very close to the epicenter of the 1954 Chlef earthquake using joint epicenter determination techniques. It occurred at a previously unknown reverse fault.
The 1982 North Yemen earthquake hit near the city of Dhamar, North Yemen on December 13. Measuring 6.2 on the moment magnitude scale, with a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale, as many as 2,800 people were killed and another 1,500 injured. The shock occurred within several hundred kilometers of a plate boundary in a geologically complex region that includes active volcanoes and seafloor spreading ridges. Yemen has a history of destructive earthquakes, though this was the first instrumentally recorded event to be detected on global seismograph networks.
The 1967 Mudurnu earthquake or more correctly, the 1967 Mudurnu Valley earthquake occurred at about 18:57 local time on 22 July near Mudurnu, Bolu Province, north-western Turkey. The magnitude 7.4 earthquake was one of a series of major and intermediate quakes that have occurred in modern times along the North Anatolian Fault since 1939.
The 1927 Jericho earthquake was a devastating event that shook Mandatory Palestine and Transjordan on July 11 at . The epicenter of the earthquake was in the northern area of the Dead Sea. The cities of Jerusalem, Jericho, Ramle, Tiberias, and Nablus were heavily damaged and at least 287 were estimated to have been killed.
The 1969 Sharm El Sheikh earthquake occurred on March 31 off the southern Sinai Peninsula in northeastern Egypt. The epicenter was located near Shadwan island, southwest of the city of Sharm El Sheikh, at the confluence of the Red Sea and the Gulf of Suez. This normal-slip shock measured 6.6 on the moment magnitude scale, had a maximum reported intensity of VII on the Mercalli intensity scale, and was responsible for several deaths and injuries.
Events from the year 1953 in Iran.
The 2010 Damghan earthquake occurred in northern Iran at on August 27 with a moment magnitude of 5.8 and maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. This strike-slip event damaged and destroyed a number of small villages in a sparsely populated region near the Alborz mountain range. It left four people dead, 40 injured, and about 800 without homes. The deaths and injuries in this moderate event were attributed to the low-quality construction styles that are typical of the area. The Iranian Strong Motion Network provided data by which seismologists determined the type and extent of the slip as well as the peak ground acceleration. Other large and destructive earthquakes have affected Semnan Province, including several events in 856 AD and 1953.
The 2004 Baladeh earthquake occurred on May 28 in northern Iran. This dip-slip earthquake had a moment magnitude of 6.3 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Total deaths for the event amounted to 35, with 278–400 injured, and $15.4 million in damage.
The 1963 Marj earthquake occurred on February 21 in northern Libya. The earthquake occurred at with a moment magnitude of 5.6 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Financial losses totaled $5 million USD, with 290–375 deaths, 375–500 injuries, and 12,000 homeless.
The 1941 Sa'dah earthquake or the Jabal Razih earthquake occurred on January 11 in Razih District of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen. The earthquake had a surface-wave magnitude of 5.8–6.5 and a shallow focal depth. Despite the moderate size of this earthquake, an estimated 1,200 people perished and at least 200 injured. With a maximum MSK-64 intensity assigned at VIII, it destroyed many villages and collapsed homes in the region of North Yemen.
In 1990, present day South Sudan was rocked by a series of violent earthquakes. It started with the largest event, a Mw 7.2, and continued with multiple very large aftershocks for the next couple of months. It contains some of the largest recorded earthquakes anywhere in Africa.
The 1957 Sangchal earthquake struck northern Iran's Mazandaran province on 2 July 1957. It had a moment magnitude of 6.6 or 7.1 (Mw ), focal depth of 15 km (9.3 mi), and maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). It devastated many communities in the Alborz Mountains and caused an estimated 1,500 fatalities. Damage was estimated at US$25 million.
The 1957 Farsinaj earthquake struck Hamadan, Iran on 13 December at 05:15 local time. The moment magnitude 6.5 earthquake destroyed 211 villages, killed approximately 1,130 people, and left another 900 injured.
The 1923 Torbat-e Heydarieh earthquake occurred in Razavi Khorasan province, Iran on 25 May. The Mw 6.0 earthquake, which had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), completely levelled the village of Quzan. The earthquake killed an estimated 2,200 people.


