
An earthquake occurred on November 27, 2005, at 13:52 IRST on the sparsely populated Qeshm Island off Southern Iran, killing 13 people and devastating 13 villages. It was Iran's second major earthquake of 2005, following the one at Zarand in February. The epicenter was about 1,500 kilometers (930 mi) south of Tehran, close to Iran's southern borders. Initial measurements showed that the earthquake registered about 6.0 on the moment magnitude scale, although that was reduced to 5.8 after further analysis. More than 400 minor aftershocks followed the main quake, 36 of which were greater than magnitude 2.5. The earthquake occurred in a remote area during the middle of the day, limiting the number of fatalities. Iranian relief efforts were effective and largely adequate, leading the country to decline offers of support from other nations and UNICEF.

Dashti County is in Bushehr province, Iran. Its capital is the city of Khvormuj.
The 2002 Bou'in-Zahra earthquake occurred on 22 June 2002. The epicenter was near the city of Bou'in-Zahra in Qazvin province, a region of northwestern Iran which is crossed by several major faults that is known for destructive earthquakes. The shock measured 6.5 on the scale, had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), and was followed by more than 20 aftershocks. At least 230 people were killed and 1,500 more were injured.
The 1997 Ardabil earthquake occurred on 28 February with a moment magnitude of 6.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The strike-slip earthquake occurred in northern Iran, near the city of Ardabil.
The 2008 Qeshm earthquake occurred on 10 September in the Hormozgān Province of southern Iran, 850 kilometres (528 mi) south of Tehran. Its epicenter was near the port city of Bandar Abbas, where an earthquake two years prior had caused damage. The earthquake measured 5.9 on the moment magnitude scale and 6 on the surface wave scale, killing seven people and injuring up to 45. Causing both catastrophic and minor damage, the earthquake devastated up to 200 villages throughout southern Iran, but left the port city of Bandar Abbas almost unscathed. Citizens reportedly panicked when the earthquake hit, emptying into the parks of the city and other open areas.
The 1985 Rapel Lake earthquake occurred on 8 April at with a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum perceived intensity of VI (Strong). The shock was centered 75 kilometres (47 mi) southwest of Santiago, Chile, with a focal depth of 37.8 km (23 mi).
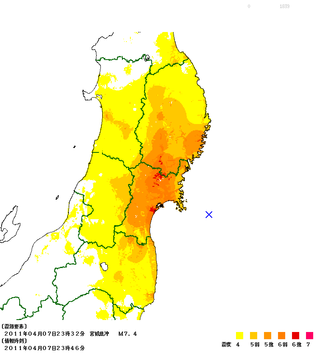
The April 2011 Miyagi earthquake occurred off the coast of Miyagi Prefecture, approximately 66 kilometres (41 mi) east of Sendai, Japan. The 7.1 thrust earthquake was classified as an aftershock of the March 11 Tōhoku earthquake, and occurred at 23:32 JST (14:32 UTC) on Thursday, 7 April 2011.
Shonbeh and Tasuj District is in Dashti County, Bushehr province, Iran. Its capital is the city of Shonbeh.
Shonbeh is a city in, and the capital of, Shonbeh and Tasuj District of Dashti County, Bushehr province, Iran. It also serves as the administrative center for Shonbeh Rural District.
The 2012 Indian Ocean earthquakes were magnitude 8.6 and 8.2 Mw undersea earthquakes that struck near the Indonesian province of Aceh on 11 April at 15:38 local time. Initially, authorities feared that the initial earthquake would cause a tsunami and warnings were issued across the Indian Ocean; however, these warnings were subsequently cancelled. These were unusually strong intraplate earthquakes and the largest strike-slip earthquake ever recorded.
The 2012 East Azerbaijan earthquakes – also known as the Ahar earthquakes – occurred on 11 August 2012, at 16:53 Iran Standard Time, near the cities of Ahar and Varzaqan in Iran's East Azerbaijan province, approximately 60 kilometers from Tabriz. They comprised a doublet separated by eleven minutes, with magnitudes of 6.4 and 6.2 . At least 306 people died and more than 3,000 others were injured, primarily in the rural and mountainous areas to the northeast of Tabriz. The shocks were felt in Armenia and the Republic of Azerbaijan, though no major damage was reported.
The 2013 Dashtestan earthquake struck near the city of Borazjan in southern Iran on November 28 at a depth of 16.4 km (10.2 mi). The shock had a moment magnitude of 5.6 on the Richter scale and a maximum perceived intensity of VII on the Mercalli intensity scale. The earthquake killed at least 7 people and injured 45 others.
The 2013 Saravan earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 7.7 at 15:14 pm IRDT (UTC+4:30) on 16 April. The shock struck a mountainous area between the cities of Saravan and Khash in Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Iran, close to the border with Pakistan, with a duration of about 25 seconds. The earthquake occurred at an intermediate depth in the Arabian plate lithosphere, near the boundary between the subducting Arabian plate and the overriding Eurasian plate at a depth of about 80 km.

On 12 November 2017 at 18:18 UTC, an earthquake with a moment magnitude of 7.3 occurred on the Iran–Iraq border, with the Iraqi Kurdish city of Halabja, and the Kurdish dominated places of Ezgeleh, Salas-e Babajani County, Kermanshah province in Iran, closest to the epicentre, 30 kilometres (19 mi) south of the city of Halabja, Iraqi Kurdistan.
The first and most destructive of the 2020 Iran–Turkey earthquakes occurred on 23 February, near Khoy in north-west Iran, close to the border with Turkey, killing 9 people in Başkale, Van. It hit at 9:23 a.m. local time with a magnitude of 5.8 at a depth of 6 kilometres and the epicenter was Qotur district, according to the Iranian Seismological Center (IRSC). About 10 hours later the same area was hit by another major earthquake of 6.0 Mw .
An earthquake struck approximately 53 kilometres SSE of the town of Mansfield, in the Victorian Alps of Australia on 22 September 2021, at 09:15 local time. The earthquake measured 5.9 on the moment magnitude scale. The earthquake caused minor structural damage in parts of Melbourne and left one person injured. The earthquake was also felt in New South Wales, Australian Capital Territory, South Australia and Tasmania. The earthquake was substantially stronger than the 1989 Newcastle earthquake that measured 5.6 and killed 13 people.
The 2019 East Azerbaijan earthquake occurred at 03:17 local-time on November 8, 2019. This earthquake had a moment magnitude of 5.9 and had a shallow depth of 20 km.
The 2022 Hormozgan earthquakes were doublet earthquakes that struck southern Iran on 1 July, 2022. The earthquakes, which occurred around two hours apart, killed seven people and injured dozens more.
The 1957 Farsinaj earthquake struck Hamadan province, Iran on 13 December at 05:15 local time. The moment magnitude 6.5 earthquake struck at a depth of 15 km (9.3 mi). The epicenter of the earthquake was located in the seismically active Zagros Mountains. The mountain range was also the location for several historic earthquakes. The earthquake occurred near two segments of the active strike-slip Main Recent Fault. At least 1,130 people died, including over 700 in the village of Farsinaj. Additional deaths also occurred in Dehasiyab, Sarab, and other villages. The earthquake left an estimated 15,000 homeless; poor weather conditions including a winter storm on 21 December killed another 20 people. Several deadly and damaging aftershocks in that month killed a total of 38 people.
The 1958 Firuzabad earthquake was the second destructive earthquake to strike Hamadan province, Iran, in nine months. The 6.7 earthquake occurred at a depth of 15 km (9.3 mi) on 16 August at 22:43 local time. It caused severe damage to over 170 villages in the province. Due to several strong foreshocks, most of the population fled their homes and the death toll only stood at 132 and another 948 were injured. A destructive aftershock on 21 September killed another 16 people.






