
Alberto Kenya Fujimori Inomoto was a Peruvian politician, professor, and engineer who served as the 54th Constitutional president of the Republic of Peru from 1990 to 2000. Of Japanese descent, Fujimori was an agronomist and university rector before entering politics. Generally recognized as a civilian-military dictatorship, his government was characterized by its use of propaganda, widespread political corruption, and human rights violations.

The president of Bolivia, officially known as the president of the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is head of state and head of government of Bolivia and the captain general of the Armed Forces of Bolivia.

Valentín Toribio Demetrio Agustin Paniagua Corazao was a Peruvian lawyer and politician who briefly served as 55th President of Peru from 2000 to 2001. Elected President of Congress on 16 November 2000, he ascended to the presidency as incumbent Alberto Fujimori and both his Vice Presidents resigned by 22 November 2000.

Lourdes Celmira Rosario Flores Nano is a Peruvian lawyer and politician who served as a councilwoman of Lima, Deputy from Lima from 1990 to 1992, Democratic Constituent Congresswoman from 1992 to 1995, Congresswoman from 1995 to 2000, and the Christian People's Party candidate for President of Peru in the 2001 and 2006 elections in which she ran under the National Unity.
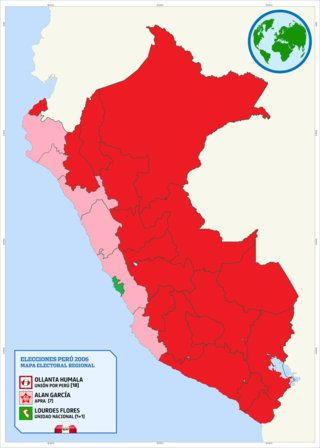
General elections were held in Peru in on 9 April 2006 to elect the President, two Vice-Presidents, 120 members of Congress and five members of the Andean Parliament for the 2006–2011 period. As the no presidential candidate received a majority of the vote, a second round was held on 4 June between the top two candidates, Ollanta Humala and Alan García. Garcia won the run-off with 52.63% to Humala's 47.37%. He was subsequently inaugurated on 28 July 2006, Peruvian Independence Day.

Mercedes Cabanillas Bustamante is a Peruvian educator and politician. A prominent member of the Peruvian Aprista Party, she served as Minister of Education in the first presidency of Alan García, making her the first woman to assume a cabinet position in the history of Peru. Most recently, she briefly served as Minister of Interior in Alan García's second presidency, a position subject to scrutiny as she was signaled as responsible of the repression of natives in the 2009 Amazon crisis, in Bagua, which forced her to resign, and effectively ended her political career.

General elections were held in Peru on 9 April 2000, with a run-off of the presidential election on 28 May. The elections were highly controversial and widely considered to have been fraudulent. Incumbent President Alberto Fujimori was re-elected for a third term with almost three-quarters of the vote. However, the elections were tainted with allegations of unconstitutionality, bribery, structural bias, and outright electoral fraud. Alejandro Toledo boycotted the second round of the presidential election, in which over 30% of ballots were declared invalid. Fujimori subsequently called for new elections after his scandal, fled Peru, and faxed in his resignation from a hotel in Japan.

Ollanta Moisés Humala Tasso is a Peruvian politician and former military officer who served as President of Peru from 2011 to 2016. Originally a socialist and left-wing nationalist, he is considered to have shifted towards neoliberalism and the political centre during his presidency.
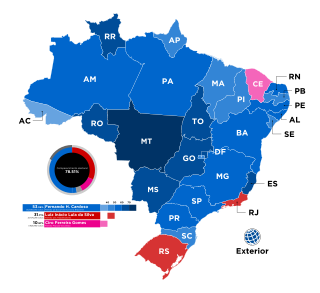
General elections were held in Brazil on 4 October 1998 to elect the President, National Congress and state governorships. If no candidate in the presidential election received more than 50% of the vote in the first round, a second-round runoff would have been held on 25 October. The election saw voting machines used for the first time in Brazilian history.

Omar Karim Chehade Moya is a Peruvian lawyer and politician. He worked as consultant lawyer in the Ad Hoc Anti-corruption Prosecution in judicial cases against former president Alberto Fujimori and his intelligence chief Vladimiro Montesinos. He was the Second Vice President of Peru in Ollanta Humala's presidency from 2011 until his resignation in 2012.

General elections were held in Peru on 8 April 1990, with a second round of the presidential elections on 10 June. This exercise was to elect the President of the Republic, two vice presidents, and the members of Congress. The elections filled 180 seats in the Chamber of Deputies and 60 seats in the Senate for the 1990-1995 governmental period.
General elections were held in Peru on 10 June 1945 to elect the President and both houses of Congress. In the presidential elections the result was a victory for José Luis Bustamante y Rivero of the National Democratic Front (FDN), who received 67% of the vote. The FDN also emerged as the largest party in both houses of Congress, winning 35 of the 49 seats in the Senate and 73 of the 153 seats in the Chamber of Deputies.
The Constituent Assembly was the tenth Constituent Assembly of Peru, convened by the government of General Francisco Morales Bermudez to facilitate the return of democracy following a decade of the self-styled Revolutionary Government of the Armed Forces. It was settled on 28 July 1978 and was led by Víctor Raúl Haya de la Torre, historical leader of the American Popular Revolutionary Alliance. Its main mission was to develop a new constitution replacing the old 1933 Constitution. This new Constitution was enacted and promulgated on 12 July 1979, and entered into force on 28 July 1980, on the opening of the constitutional government of the architect Fernando Belaúnde Terry. It was replaced 14 years later by the 1993 Constitution.

Luis Carlos Antonio Iberico Núnez is an Argentine-born Peruvian journalist and politician. Throughout his journalistic career, he served in various news stations during the 1980s and 1990s. He gained prominence for his fight against the Alberto Fujimori administration, denouncing several allegations of corruption involving the press. Alongside Fernando Olivera, he presented the first "Vladi-videos" that would prove the major corruption operations headed by Intelligence Chief Vladimiro Montesinos. His role in Fujimori's downfall would gain him support in a career in politics.
Alicia Leontina Felipa Blanco Montesinos de Salinas was a Peruvian educator and politician. In 1956 she was among the first group of women elected to Congress, serving until 1962.
Lola Blanco Montesinos de La Rosa Sánchez was a Peruvian educator and politician. In 1956 she was among the first group of women elected to Congress, serving until 1962.

Matilde Pérez Palacio Carranza was a Peruvian educator, journalist and politician. In 1956 she was among the first group of women elected to Congress, serving until 1962, and again between 1963 and 1968.
María Eleonora Silva y Silva was a Peruvian politician. In 1956 she was among the first group of women elected to Congress, serving until 1962.
Juana Magdalena Ubilluz de Palacios was a Peruvian educator and politician. In 1956 she was among the first group of women elected to Congress, serving until 1962.

On 7 December 2022, Pedro Castillo, the then-President of Peru, made an attempt to dissolve the Congress amidst looming removal proceedings. This move included the immediate imposition of a curfew, an attempt to establish an emergency government, and a call for the formation of a constituent assembly. Prior to this, Attorney General Patricia Benavides had accused Castillo of leading a criminal organization, a claim that contravened Article 117 of the Constitution of Peru. She had urged the Congress to remove him from office, leading to the third removal attempt against Castillo. Castillo defended his actions by arguing that the Congress, which had obstructed many of his policies, was serving oligopolistic businesses and had colluded with the Constitutional Court to undermine the executive branch, thereby creating a "congressional dictatorship". He also advocated for the immediate election of a constituent assembly, a demand that had been echoed since the 2020 Peruvian protests.


















