Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight saving(s), daylight savings time, daylight time (United States and Canada), or summer time (United Kingdom, European Union, and others), is the practice of advancing clocks to make better use of the longer daylight available during summer so that darkness falls at a later clock time. The typical implementation of DST is to set clocks forward by one hour in spring or late winter, and to set clocks back by one hour to standard time in the autumn (or fall in North American English, hence the mnemonic: "spring forward and fall back").
In Australia, referendums are public votes held on important issues where the electorate may approve or reject a certain proposal. In contemporary usage, polls conducted on non-constitutional issues are known as plebiscites, with the term referendum being reserved solely for votes on constitutional changes, which is legally required to make a change to the Constitution of Australia.

Sir Eric Archibald Willis was an Australian politician, Cabinet Minister and the 34th Premier of New South Wales, serving from 23 January 1976 to 14 May 1976. Born in Murwillumbah in 1922, Willis was educated at Murwillumbah High School and the University of Sydney, where he obtained a Bachelor of Arts with double honours. Enlisting during World War II, Willis served on the homefront and later served in New Guinea and the Philippines. He continued to serve the Citizen Military Forces until 1958.
A group voting ticket (GVT) is a shortcut for voters in a preferential voting system, where a voter can indicate support for a list of candidates instead of marking preferences for individual candidates. For multi-member electoral divisions with single transferable voting, a group or party registers a GVT before an election with the electoral commission. When a voter selects a group or party above the line on a ballot paper, their vote is distributed according to the registered GVT for that group.

Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Eastern Standard Time, Australian Central Standard Time and Australian Western Standard Time.
A referendum concerning reform of the New South Wales Legislative Council was put to New South Wales voters on 25 May 1991. The referendum coincided with that year's New South Wales general election. The change passed comfortably. The text of the question was:
Do you approve of the Bill entitled 'A Bill for an Act:
(a) to reduce the number of politicians in the Legislative Council and to reduce their maximum term of office; and
(b) to apply to the Legislative Council the same method of filling casual vacancies as applies to the Senate ?
Uralla-Walcha was an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, including the towns of Uralla and Walcha. It was originally created in 1894, when multi-member districts were abolished, and the three member district of New England was largely divided between Uralla-Walcha, Armidale and Bingara. The district was abolished in 1904 as a result of the 1903 New South Wales referendum, which reduced the number of members of the Legislative Assembly from 125 to 90, and was divided between Armidale and Bingara.

Most of the United States observes daylight saving time (DST), the practice of setting the clock forward by one hour when there is longer daylight during the day, so that evenings have more daylight and mornings have less. Exceptions include Arizona, Hawaii, and the territories of American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the United States Virgin Islands. The Uniform Time Act of 1966 established a uniform set of rules for states opting to observe daylight saving time.
Daylight Saving for South East Queensland (DS4SEQ) was a political party in Queensland, Australia. It was a single-issue party, run by volunteers, that advocated the introduction of Daylight Saving into Queensland, or at the very least into South East Queensland under a dual-time zone arrangement - with the remainder of the state to maintain standard time. The party proposed a possible dual time zone, which included the following 15 local and regional government areas: Brisbane, Fraser Coast, Gold Coast, Goondiwindi, Gympie, Ipswich, Lockyer, Logan, Moreton Bay, Redland, Scenic Rim, Somerset, Southern Downs, Sunshine Coast, and Toowoomba. The party was officially registered with the Electoral Commission of Queensland (ECQ) in December 2008 and was not registered with the Australian Electoral Commission. In August 2012, DS4SEQ submitted a request to the ECQ to deregister the party, and this process was finalised in October 2012. DS4SEQ maintains a presence as a lobby group and may potentially re-register as a political party in the future. Jason Furze was leader of the party from December 2008 until June 2011.

Each state and territory of Australia determines whether or not to use daylight saving time (DST). However, during World War I and World War II all states and territories had daylight saving by federal law, under the defence power in section 51 of the constitution. In 1968, Tasmania was the first state since the war to adopt daylight saving. In 1971, New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and the Australian Capital Territory also adopted daylight saving, while Western Australia and the Northern Territory did not. Queensland abandoned daylight saving in 1972. Queensland and Western Australia have observed daylight saving over the past 40 years from time to time on a trial basis.
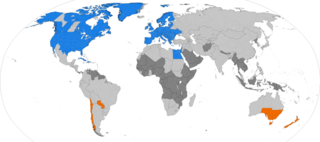
Parts of Australia, New Zealand and Fiji are areas of Oceania that currently observe daylight saving time (DST).
The 1981 New South Wales referendum was held on 19 September 1981, the same day as the state election. The referendum contained two questions:
- Do you approve a Bill for an Act to extend the maximum period between general elections for the Legislative Assembly from 3 years to 4 years?
- Do you approve a Bill for an Act to require Members of Parliament to disclose certain pecuniary interests and other matters?
A referendum concerning the reduction of the members of the New South Wales Legislative Assembly was put to voters on 16 December 1903, in conjunction with the 1903 federal election. The referendum was conducted on the basis of optional preferential voting. However, preferences were not counted, as an overwhelming majority voted to reduce the number of members to 90.
The 1978 New South Wales referendum was held on 17 June 1978 and contained a single question:
Do you approve of the Bill entitled 'A Bill for an Act to provide for the election of members of the Legislative Council directly by the people'.
On October 18, 2021, a referendum was held in Alberta, Canada on two questions, whether equalization payments should be eliminated from the Constitution of Canada, and whether the province should observe daylight saving time year-round. The referendum was held as part of the 2021 Alberta municipal elections and the Senate nominee election.
A referendum concerning the reform of the New South Wales Legislative Council was put to New South Wales voters on 13 May 1933 and was passed by the voters with a margin of 2.94%. The text of the question was:
Do you approve of the Bill entitled "A Bill to reform the constitution and alter the Powers of the Legislative Council; to reduce and limit the number of Members of the Legislative Council; to reconstitute the Legislative Council in accordance with the reformed constitution; to amend the Constitution Act, 1902, and certain other Acts; and for purposes connected therewith."
There have been 18 referendums in New South Wales, 8 of which concerned proposals to amend the New South Wales Constitution, half of which concerned the Legislative Council. While the Constitution of Australia was adopted after the 1898 and 1899 referendums in all of the proposed states, the constitution of New South Wales, promulgated in 1902, was an Act of the Parliament of New South Wales which could be amended by parliament. Since 1927 the constitution has included provisions that can only be amended following approval in a referendum. 8 of the referendums, including 5 on the sale of alcohol, did not involve any proposed amendment to the constitution. While these have traditionally been called referendums, they could also be described as plebiscites.
A referendum concerning the closing hour for licensed premises and registered clubs was put to voters on 15 February 1947. The referendum was conducted on the basis of optional preferential voting. Preferences were not counted as a majority voted to maintain the 6:00 pm closing time.
A referendum concerning the closing hour for licensed premises and registered clubs was put to voters in New South Wales on 13 November 1954.
A referendum concerning whether hotels should be allowed to trade on Sundays was put to voters in New South Wales on 29 November 1969 but was unsuccessful.




