
Sir John Robertson was a London-born Australian politician and Premier of New South Wales on five occasions. Robertson is best remembered for land reform and in particular the Robertson Land Acts of 1861, which sought to open up the selection of Crown land and break the monopoly of the squatters.

Sir Daniel Cooper, 1st Baronet was a nineteenth-century politician, merchant and philanthropist in the Colony of New South Wales. He served as the first speaker of the Legislative Assembly of the colony and was a noted philatelist.

Samuel Deane Gordon was an Australian merchant, pastoralist and politician. He was a member of the New South Wales Legislative Council between 1861 and 1882. He was also a member of the New South Wales Legislative Assembly for three terms from 1856 until 1860.
The third Cowper ministry was the seventh ministry of the Colony of New South Wales, and third occasion of being led by Charles Cowper.

The third Robertson ministry was the fifteenth ministry of the Colony of New South Wales, and was led by John Robertson. It was the third of five occasions that Robertson was Premier. Robertson was elected in the first free elections for the New South Wales Legislative Assembly held in March 1856.
The second Parkes ministry was the sixteenth ministry of the Colony of New South Wales, and was led by Sir Henry Parkes. It was the second of five occasions that Parkes was Leader of the Government.
The fourth Robertson ministry was the seventeenth ministry of the Colony of New South Wales, and was led by Sir John Robertson. It was the fourth of five occasions that Robertson led the Government. Robertson was elected in the first free elections for the New South Wales Legislative Assembly held in March 1856.

The third Parkes ministry was the nineteenth ministry of the Colony of New South Wales, and was led by Sir Henry Parkes in a coalition with Sir John Robertson. It was the third of five occasions that Parkes was Leader of the Government.
The fifth Robertson ministry was the 22nd ministry of the Colony of New South Wales, and was led by the Premier, Sir John Robertson. It was the fifth and final occasion that Robertson was Premier. Robertson was elected in the first free elections for the New South Wales Legislative Assembly held in March 1856.

James Watson was an Australian politician, Colonial Treasurer of New South Wales 1878 to 1883.

John Fitzgerald Burns was an Australian politician, member of the Parliament of New South Wales, Postmaster-General in the 1870s and Colonial Treasurer in the 1880s.

Charles Cowper was an Australian politician, pastoralist and senior public servant, the son of Sir Charles Cowper who served as Premier of New South Wales on five separate occasions between 1856 and 1870. During the period 1860 to 1865 Cowper was the elected member of various electorates in support of his father's political faction. In the late 1860s he invested in pastoral runs in south-west Queensland, which ultimately led to financial losses due to prolonged drought conditions. After a short stint as Police Magistrate at Bourke, Cowper was appointed as the Water Police Magistrate in Sydney. In 1874 he was appointed Sheriff of New South Wales, a position he held until his retirement in 1896.

Sir John Lackey was a magistrate and politician in colonial New South Wales, President of the New South Wales Legislative Council 1892 to 1903.

The 1891 New South Wales colonial election was held in the then colony of New South Wales between 17 June to 3 July 1891. This election was for all of the 141 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 35 single-member constituencies, 20 2-member constituencies, 10 3-member constituencies and nine 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Part 1 of the Electoral Act of 1880 set the qualification for election on "every male subject of Her Majesty of the full age of twenty-one years and absolutely free being a natural born or naturalized subject". Seven seats were uncontested. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 6 June 1891 by the Governor, The Earl of Jersey, on the advice of the Premier, Sir Henry Parkes.
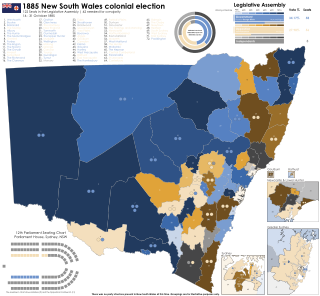
The 1885 New South Wales colonial election was held between 16 October and 31 October 1885. This election was for all of the 122 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 37 single-member constituencies, 24 2-member constituencies, seven 3-member constituencies and four 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Suffrage was limited to adult male British subjects, resident in New South Wales. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 7 October 1885 by the Governor, Lord Augustus Loftus, on the advice of the Premier, George Dibbs.
The 1880 New South Wales colonial election was held between 17 November and 2 December 1880. This election was for all of the 108 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 43 single-member constituencies, 25 2-member constituencies, one 3-member constituency and three 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Suffrage was limited to adult white males. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 9 November 1880 by the Governor, Lord Augustus Loftus, on the advice of the Premier, Sir Henry Parkes.

The 1872 New South Wales colonial election was held between 13 February and 28 March 1872. This election was for all of the 72 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 52 single-member constituencies, six 2-member constituencies and two 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Suffrage was limited to adult white males. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 3 February 1872 by the Governor, Lord Belmore, on the advice of the Premier, Sir James Martin.

The 1859 New South Wales colonial election was held between 9 June and 7 July 1859. This election was for all of the 80 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 58 single-member constituencies, seven 2-member constituencies and two 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Suffrage was limited to adult white males. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 11 April 1859 by the Governor, Sir William Denison, on the advice of the Premier, Charles Cowper.

The 1843 New South Wales colonial election was held between 15 June and 3 July 1843 and was Australia's first colonial election. This election was for 24 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Council and it was conducted in 15 single-member constituencies, two 2-member constituencies and one 5-member constituency, all with a first past the post system. This included 6 members in what became the Colony of Victoria and a single member for the coast north of Newcastle. The Legislative Council was a hybrid system with 36 members, 24 elected, 6 appointed by virtue of their office and 6 nominated. The appointments and elections were for five year terms.

The 1851 New South Wales colonial election was held between 12 and 25 September. This election was for 36 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Council. The 1848 election had been for 5 year terms however the parliament had been reconstituted following the separation of Victoria. At the same time the council was expanded from 36 to 54 members. The Legislative Council was a hybrid system with 18 appointed members and 36 elected. The Port Philip districts had 6 elected members, which meant there were an additional 18 seats. There were 3 new districts for the northern regions of what would later become Queensland, Stanley, Stanley Boroughs and the pastoral districts of Moreton, Wide Bay, Burnett, and Maranoa and 7 new pastoral districts in western New South Wales. The other 8 additional seats were distributed among the nineteen counties of New South Wales.

















