North Shore, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, has had two incarnations, the first from 1920 to 1927 as a five-member electorate, the second from 1981 to the present as a single-member electorate.
Balmain, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, has had three incarnations since it was established in 1880. It expanded from 1 to 2 to 3 to 4 members before being abolished in 1894. It was re-established in 1904 returning 1 member until 1920. When multiple member constituencies were established using the Hare-Clark single transferable vote in 1920, Balmain returned 5 members. It had a single member from 1927 when the state returned to single member electorates. It was abolished in 1991 and largely replaced by Port Jackson which included the Sydney CBD. It was re-established in 2007 when Port Jackson was abolished.
Albury, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, was created in 1880. It was abolished in 1920 when multiple member constituencies were established using the Hare-Clark single transferable vote. It was re-created in 1927 when the state returned to single member electorates.
Tweed, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, has had two incarnations, the first from 1894 to 1904, the second from 1999 until the present.
Newcastle, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, has had two incarnations, from 1859 until 1894 and from 1904 to the present.
Monaro, also known as Maneroo (1856–58), Monara (1858–1879) and Manaro (1894–1904), an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, has had two incarnations, from 1858 to 1920 and from 1927 to the present.
Parramatta, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, has continuously existed since the establishment of the Legislative Assembly in 1855.
Goulburn, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, has had two incarnations, from 1859 until 1991 and from 2007 to the present.

The 1917 New South Wales state election was held on 24 March 1917. This election was for all of the 90 seats in the 24th New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in single-member constituencies with a second ballot if a majority was not achieved on the first. The 23rd parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 21 February 1917 by the governor, Sir Gerald Strickland, on the advice of the premier William Holman.

The 1913 New South Wales state election was held on 6 December 1913. This election was for all of the 90 seats in the 23rd New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in single-member constituencies with a second ballot if a majority was not achieved on the first. The 22nd parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 6 November 1913 by the Governor, Sir Gerald Strickland, on the advice of the Premier William Holman.

The 1910 New South Wales state election was held on 14 October 1910 for all of the 90 seats in the 22nd New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in single-member constituencies with a second ballot if a majority was not achieved on the first. Both adult males and females were entitled to vote, but not Indigenous people. The 21st parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 14 September 1910 by the Governor, Lord Chelmsford, on the advice of the Premier Charles Wade.

The 1904 New South Wales state election was held on 6 August 1904 for all of the 90 seats in the 20th New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in single-member constituencies with a first past the post voting system. For the first time, women were entitled to vote. Both adult males and females were entitled to vote, but not Indigenous people. The 19th parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 16 July 1904 by the Governor, Sir Harry Rawson, on the advice of the Premier, Thomas Waddell.
Murray, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, has had two incarnations, the first from 1859 to 1999, the second from 2015 to the present.
The 1856 New South Wales colonial election was to return 54 members of Legislative Assembly composed of 34 electoral districts with 18 returning 1 member, 13 returning 2 members, two returning 3 members and one returning 4 members, all with a first past the post system. In multi-member districts, because each voter could cast more than one vote, it is not possible to total the votes to show the number of voters and voter turnout in these districts is estimated. 8 members from 6 districts were returned unopposed.

The 1889 New South Wales colonial election was held between 1 February and 16 February 1889. This election was for all of the 137 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 37 single-member constituencies, nineteen 2-member constituencies, ten 3-member constituencies and eight 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Part 1 of the Electoral Act of 1880 had awarded the right to vote to 'every male subject of Her Majesty of the full age of twenty-one years and absolutely free being a natural born or naturalized'. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 19 January 1889 by the Governor, Lord Carrington, on the advice of the Premier, George Dibbs.
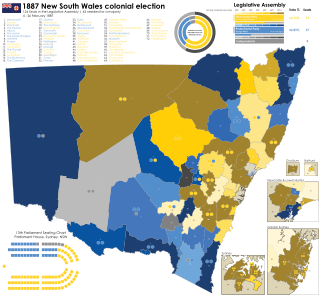
The 1887 New South Wales colonial election was held between 4 February and 26 February 1887. This election was for all of the 124 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 37 single-member constituencies, 23 2-member constituencies, seven 3-member constituencies and five 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Part 1 of the Electoral Act of 1880 had awarded the right to vote to 'every male subject of Her Majesty of the full age of twenty-one years and absolutely free being a natural born or naturalized'. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 26 January 1887 by the Governor, Lord Carrington, on the advice of the Premier, Sir Henry Parkes.
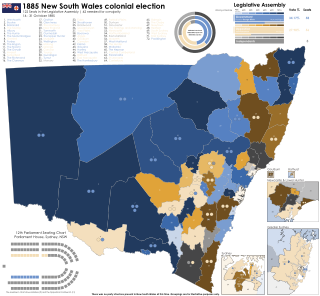
The 1885 New South Wales colonial election was held between 16 October and 31 October 1885. This election was for all of the 122 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 37 single-member constituencies, 24 2-member constituencies, seven 3-member constituencies and four 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Suffrage was limited to adult male British subjects, resident in New South Wales. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 7 October 1885 by the Governor, Lord Augustus Loftus, on the advice of the Premier, George Dibbs.

The 1872 New South Wales colonial election was held between 13 February and 28 March 1872. This election was for all of the 72 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly and it was conducted in 52 single-member constituencies, six 2-member constituencies and two 4-member constituencies, all with a first past the post system. Suffrage was limited to adult white males. The previous parliament of New South Wales was dissolved on 3 February 1872 by the Governor, Lord Belmore, on the advice of the Premier, Sir James Martin.
The 1858 New South Wales colonial election was to return 54 members of Legislative Assembly composed of 34 electoral districts with 18 returning 1 member, 13 returning 2 members, two returning 3 members and one returning 4 members, all with a first past the post system. In multi-member districts, because each voter could cast more than one vote, it is not possible to total the votes to show the number of voters and voter turnout in these districts is estimated. 17 members from 14 districts were returned unopposed. The electoral districts and boundaries were established under the Electoral Act 1851 (NSW) for the former Legislative Council.
Namoi, an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales had two incarnations, from 1880 to 1894 and from 1904 to 1950.








