| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1991 in South Africa.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1991 in South Africa.

12 to 17 September - 1991 ATP Tour World Championships

Frederik Willem de Klerk was a South African politician who served as state president of South Africa from 1989 to 1994 and as deputy president from 1994 to 1996. As South Africa's last head of state from the era of white-minority rule, he and his government dismantled the apartheid system and introduced universal suffrage. Ideologically a social conservative and an economic liberal, he led the National Party (NP) from 1989 to 1997.
The following lists events that happened during 1995 in South Africa.
1994 in South Africa saw the transition from South Africa's National Party government who had ruled the country since 1948 and had advocated the apartheid system for most of its history, to the African National Congress (ANC) who had been outlawed in South Africa since the 1950s for its opposition to apartheid. The ANC won a majority in the first multiracial election held under universal suffrage. Previously, only white people were allowed to vote. There were some incidents of violence in the Bantustans leading up to the elections as some leaders of the Bantusans opposed participation in the elections, while other citizens wanted to vote and become part of South Africa. There were also bombings aimed at both the African National Congress and the National Party and politically-motivated murders of leaders of the opposing ANC and Inkatha Freedom Party (IFP).
The following lists events that happened during 1993 in South Africa.
1990 in South Africa saw the official start of the process of ending Apartheid. President of South Africa, eid. President F.W. de Klerk unbanned organisations that were banned by the government including the African National Congress, the South African Communist Party and the Pan Africanist Congress. The African National Congress, Umkhonto we Sizwe, suspends its armed activity within South Africa. Political prisoners including Nelson Mandela were released. Nelson Mandela met ANC leader Oliver Tambo for the first time in 28 years at a meeting in Sweden. Mandela also traveled to England to thank the people for their support in the campaign to free him. South Africa withdrew its troops from Namibia, which was granted independence. 1990 also saw marches in support and against the formation of a new post-Apartheid South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1989 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1984 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1983 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1964 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1974 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1975 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1996 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1980 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1982 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1985 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1992 in South Africa.
The following lists events that happened during 1963 in South Africa.
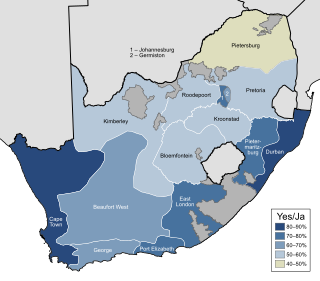
A referendum on ending apartheid was held in South Africa on 17 March 1992. The referendum was limited to white South African voters, who were asked whether or not they supported the negotiated reforms begun by State President F. W. de Klerk two years earlier, in which he proposed to end the apartheid system that had been implemented since 1948. The result of the election was a large victory for the "yes" side, which ultimately resulted in apartheid being lifted. Universal suffrage was introduced two years later for the country's first non-racial elections.

White South Africans are South Africans of European descent. In linguistic, cultural, and historical terms, they are generally divided into the Afrikaans-speaking descendants of the Dutch East India Company's original colonists, known as Afrikaners, and the Anglophone descendants of predominantly British colonists of South Africa. In 2016, 57.9% were native Afrikaans speakers, 40.2% were native English speakers, and 1.9% spoke another language as their mother tongue, such as Portuguese, Greek, or German. White South Africans are by far the largest population of White Africans. White was a legally defined racial classification during apartheid.

De Klerk, Klerk, De Klerck, Deklerck or Klerck is surname of Dutch and Frisian origin.