
The Indonesian island of Sumatra is located in a highly seismic area of the world. In addition to the subduction zone off the west coast of the island, Sumatra also has a large strike-slip fault, the Great Sumatran Fault also known as Semangko Fault, running the entire length of the island. This fault zone accommodates most of the strike-slip motion associated with the oblique convergence between the Indo-Australian and Eurasian plates. The fault ends in the north just below the city of Banda Aceh, which was devastated in the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. After the December 2004 earthquake, pressure on the Great Sumatran Fault has increased tremendously, especially in the north.
An earthquake occurred on 31 May 1935 between 2:30 am and 3:40 am at Quetta, Balochistan, British India, close to the border with southern Afghanistan. The earthquake had a magnitude of 7.7 Mw and anywhere between 30,000 and 60,000 people died from the impact. It was recorded as the deadliest earthquake to strike South Asia until 2005. The quake was centred 4 km south-west of Ali Jaan, Balochistan, British India.

The 2002 Hindu Kush earthquakes struck in northern Afghanistan during the month of March. At least 166 people were killed with a very large and intermediate-depth mainshock on March 3. Three weeks later, at least 1,200 were killed during a moderate but shallow event that had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The M7.4 and M6.1 reverse events were focused in the Hindu Kush mountain range area.
The 2003 Bachu earthquake occurred on 24 February at 10:03 local time in the Xinjiang Autonomous Region in northwest China. The epicentre was located near to the town of Jiashi and Bachu County, approximately 105 km east of Kashgar and 310 km west of Aksu.

The 2008 Ziarat earthquakes hit the Pakistani province of Balochistan on October 29 with a moment magnitude of 6.4. The US Geological Survey reported that the first earthquake occurred 60 km (37 mi) north of Quetta and 185 km (115 mi) southeast of the Afghanistan city of Kandahar at 04:09 local time at a depth of 15 km (9.3 mi), at 30.653°N, 67.323°E. It was followed by another shallower magnitude 6.4 earthquake at a depth of 14 km (8.7 mi) approximately 12 hours after the initial shock, at 30.546°N, 67.447°E. 215 people were confirmed dead. More than 200 were injured, and 120,000 were rendered homeless. Qamar Zaman Chaudhry, director general of Pakistan Meteorological Department, stated the quake epicenter was 70 miles (110 km) north of Quetta, and about 600 km (370 mi) southwest of Islamabad.

The 2013 Bushehr earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 6.3 on April 9 in Iran. The shock's epicenter was in the province of Bushehr, near the city of Khvormuj and the towns of Kaki and Shonbeh. At least 37 people were killed, mostly from the town of Shonbeh and villages of Shonbeh-Tasuj district, and an estimated 850 people were injured.
The 2013 Balochistan earthquakes took place in late September in southwestern Pakistan. The mainshock had a moment magnitude of 7.7 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). At least 825 people were killed and hundreds more were injured. On 28 September, a M6.8 aftershock occurred to the north at a depth of 14.8 kilometres, killing at least 22 people.
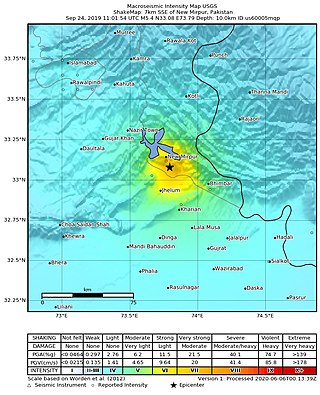
The 2019 Kashmir earthquake struck regions of Pakistan with an epicentre in Azad Kashmir on 24 September at 16:02 local time. It had a magnitude of 5.4 and a maximum felt intensity of VII on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale or VIII on the European macroseismic scale. There was severe damage in Mirpur District, causing the deaths of 40 people and injuring a further 850. The epicentre of the shallow quake was near the city of Mirpur, Pakistan. The tremors were felt in the Kashmir region, Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab (India), Uttarakhand and northern parts of India including New Delhi.
The 2021 Assam earthquake struck 11 km away from Dhekiajuli, Assam, India at 07:51 (IST) on April 28, 2021 with a moment magnitude of 6.0 at 34.0 km (21.1 mi) depth. The quake struck with an epicenter 140 km north of the main city of Guwahati. It resulted in two fatalities and at least 12 injuries.
The 1555 Kashmir earthquake occurred at around midnight in the month of Ashvin in the Hindu calendar, or September in the Gregorian calendar, although the exact day of occurrence is not known. The earthquake seriously impacted the Kashmir Valley in present-day Pakistan and northwestern India. A moment magnitude (Mw ) of 7.6 to 8.0 and Modified Mercalli intensity of XII (Extreme) has been estimated for the earthquake. Thought to be one of the most destructive in the Kashmir Valley, the earthquake caused serious widespread damage and ground effects, killing an estimated 600–60,000 individuals.
On 9 July 2019, at 8:36 PM (PST), an earthquake measuring 5.6 jolted the province of North Cotabato, Davao del Sur, and other nearby provinces. The National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council reported one dead and three injured in Makilala after the earthquake, and a total of 164 families affected in Cotabato Province. Near the epicenter of the earthquake, the severity of strong ground motion was assigned VI (Strong) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. A total of 106 schools, 119 houses, and 14 other infrastructures were damaged by the earthquake.
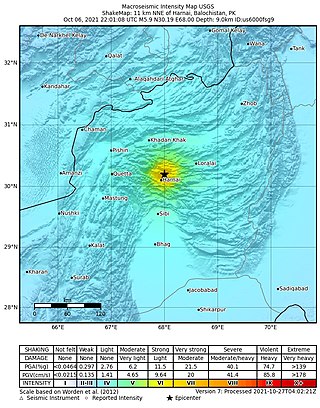
An earthquake struck Pakistan's province of Balochistan near the city of Harnai on 7 October 2021. The moment magnitude 5.9 Mww quake struck in the early morning at 03:01 local time, killing at least 42 people and injuring 300 others. The earthquake occurred just one day before the anniversary of the 2005 Kashmir earthquake.
The 1983 Hindu Kush earthquake occurred south of Fayzabad, Badakhshan in northeast Afghanistan at 03:52 PST on December 31, 1983, near the border with Pakistan and the USSR. Striking 214.5 km beneath the Hindu Kush mountains, the moment magnitude 7.4 quake affected three countries, killing at least 26 people and injuring several hundred.
The 1992 Kohat earthquake struck Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province in Pakistan on May 20. The Mw 6.3 earthquake inflicted significant damage in the nearby city Kohat. An estimated 36 people died and 100 were injured in the Peshawar and Kohat districts. Four-hundred (400) homes were wiped out, affecting 2,100 residents in the region.
The 2021 Bali earthquake struck at 04:18 local time (UTC+08:00) when people were still sleeping on 15 October 2021. It resulted in 4 deaths and 73 more injured, despite having a moment magnitude of 4.7.
The 1998 Zhangbei–Shangyi earthquake occurred at 11:50 local time on 10 January with a moment magnitude of 5.7 at a depth of 14.1 km. It struck the province of Hebei in Zhangjiakou. At least 70 people died, 11,500 were injured and a further 44,000 families were homeless in the wake of the event. Damage was reported in the town of Zhangbei, Hebei Province, as well as to sections of the Great Wall of China.
The 1885 Kashmir earthquake, also known as the Baramulla earthquake occurred on 30 May in Srinagar. It had an estimated moment magnitude of Mw 6.3–6.8 and maximum Medvedev–Sponheuer–Karnik scale intensity of VIII (Damaging). At least 3,081 people died and severe damage resulted.
The 1980 Nepal earthquake devastated the Nepal–India border region on the evening of July 29. The epicenter of the 6.6 earthquake was located in Nepal, northwest of Khaptad National Park. At least 200 people died and 5,600 were injured in the disaster. Extensive damage occurred on both sides of the border, amounting to 245 million USD.
On April 1, 2002, a Mw 5.3 magnitude earthquake struck near the coast of Moro Province in Papua New Guinea. It struck at a depth of 80.5 km beneath the surface and had a focal mechanism corresponding to reverse faulting. The earthquake triggered a landslide that killed 36 people and injured 11.
An earthquake struck Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan on February 14, 2004. Extensive damage occurred and 24 people lost their lives.







