| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 2015 in the Republic of Belarus .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 2015 in the Republic of Belarus .

Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi) with a population of 9.1 million, The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into six regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status.

The Byelorussian SSR was one of only two Soviet republics to be separate members of the United Nations. Both republics and the Soviet Union joined the UN when the organization was founded in 1945.

The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, and is its legal successor. It covers an area of 20,368,759 km2 (7,864,422 sq mi) and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political, and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security, including cross-border crime prevention.
An oblast is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term oblast is often translated into English as region or province. In some countries, oblasts are also known by cognates of the Russian term.

The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Byelorussia, was a republic of the Soviet Union (USSR). It existed between 1920 and 1922 as an independent state, and afterwards as one of fifteen constituent republics of the USSR from 1922 to 1991, with its own legislation from 1990 to 1991. The republic was ruled by the Communist Party of Byelorussia. Other names included White Russia or White Russian Soviet Socialist Republic.

The Union State of Russia and Belarus, officially also referred to as Union State, is a supranational union consisting of Belarus and Russia, with the stated aim of deepening the relationship between the two states through integration in economic and defence policy. Originally, the Union State aimed to create a confederation; however, both countries currently retain their independence.

The Eurasian Economic Community was a regional organisation between 2000 and 2014 which aimed for the economic integration of its member states. The organisation originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) on 29 March 1996, with the treaty on the establishment of the Eurasian Economic Community signed on 10 October 2000 in Kazakhstan's capital Astana by Presidents Alexander Lukashenko of Belarus, Nursultan Nazarbayev of Kazakhstan, Askar Akayev of Kyrgyzstan, Vladimir Putin of Russia, and Emomali Rahmon of Tajikistan. Uzbekistan joined the community on 7 October 2005, but later withdrew on 16 October 2008.
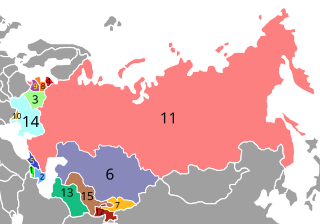
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union (FSU) or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they existed as Union Republics, which were the top-level constituents of the Soviet Union. There are 15 post-Soviet states in total: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Estonia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan. Each of these countries succeeded their respective Union Republics: the Armenian SSR, the Azerbaijan SSR, the Byelorussian SSR, the Estonian SSR, the Georgian SSR, the Kazakh SSR, the Kirghiz SSR, the Latvian SSR, the Lithuanian SSR, the Moldavian SSR, the Russian SFSR, the Tajik SSR, the Turkmen SSR, the Ukrainian SSR, and the Uzbek SSR. In Russia, the term "near abroad" is sometimes used to refer to the post-Soviet states other than Russia.
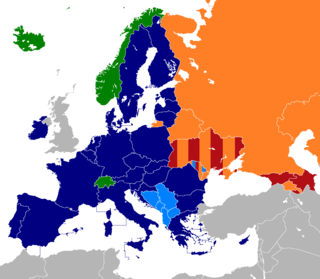
At present, there are six multi-lateral free trade areas in Europe, and one former free trade area in recent history. Note that there are also a number of bilateral free trade agreements between states and between trade blocks; and that some states participate in more than one free trade area.

The State Security Committee of the Republic of Belarus is the national intelligence agency of Belarus. Along with its counterparts in Transnistria and South Ossetia, it kept the unreformed name after declaring independence.

The prime minister of the Republic of Belarus is the deputy head of government of Belarus. Until 1991, it was known as the Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic as the head of the government of the constituent republic of the Soviet Union.

Mutual relations between the Republic of Belarus and the European Union (EU) were initially established after the European Economic Community recognised Belarusian independence in 1991.
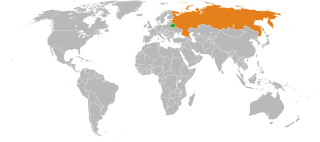
Belarus and Russia share a land border and constitute the supranational Union State. Several treaties have been concluded between the two nations bilaterally. Russia is Belarus' largest and most important economic and political partner. Both are members of various international organizations, including the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Eurasian Economic Union, the Collective Security Treaty Organization, and the United Nations.

The Eastern Partnership (EaP) is a joint initiative of the European Union, together with its member states, and six Eastern European countries. The EaP framework governs the EU's relationship with the post-Soviet states of Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, and Ukraine. The EaP is intended to provide a forum for discussions regarding trade, economic strategy, travel agreements, and other issues between the EU and its Eastern European neighbours. It also aims at building a common area of shared values of democracy, prosperity, stability, and increased cooperation. The project was initiated by Poland and a subsequent proposal was prepared in co-operation with Sweden. It was presented by the foreign ministers of Poland and Sweden at the EU's General Affairs and External Relations Council in Brussels on 26 May 2008. The Eastern Partnership was inaugurated by the EU in Prague, Czech Republic on 7 May 2009.

The economy of Belarus is an upper-middle income mixed economy. As a post-Soviet transition economy, Belarus rejected most privatisation efforts in favour of retaining centralised political and economic controls by the state. The highly centralized Belarusian economy emphasizes full employment and a dominant public sector. It has been described as a welfare state or market socialist. Belarus is the world's 74th-largest economy by GDP.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Belarus is the Belarusian government ministry which oversees the foreign relations of Belarus.
The EuroNest Parliamentary Assembly is the inter-parliamentary forum in which members of the European Parliament and the national parliaments of Ukraine, Moldova, Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia participate and forge closer political and economic ties with the European Union. It was established in 2011 by the European Commission as a component of the Eastern Partnership. After the elections in Belarus in 2010 were declared as flawed by the OSCE, the membership of Belarus in Euronest was automatically suspended. Belarus is welcome to re-join the Assembly once political requirements have been fulfilled. In 2015, Azerbaijan's membership was suspended due to the European Union's criticism of human rights abuses by the government. In September 2016, it was announced that Azerbaijan would take the necessary steps towards restoring ties. As of 2017, the combined population of Euronest members stands at 61,927,521 people.

The Eurasian Economic Union is an economic union of five post-Soviet states located in Eurasia. The EAEU has an integrated single market. As of 2023, it consists of 183 million people and a gross domestic product of over $2.4 trillion.

The Customs Union of the Eurasian Economic Union or EAEU Customs Union is a customs union of 5 post-Soviet states consisting of all the member states of the Eurasian Economic Union which initially became effective on January 1, 2010 at the date of implementation of the common external tariff (CET) as the Customs Union of the Eurasian Economic Community or Customs Union of Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan. It was inherited from the Eurasian Economic Community and is now regulated by Part Two of the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union, EAEU Customs Code, other international agreements and by decisions of supranational bodies as Supreme Eurasian Economic Council, Intergovernmental Council and Eurasian Economic Commission.

Mikhail Vladimirovich Myasnikovich is a Belarusian politician who was Prime Minister of Belarus from 2010 to 2014. He was the Chairman of the Board of the Eurasian Economic Commission in 2020-24.