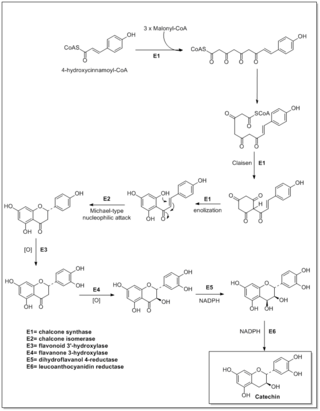
Flavonoids are synthesized by the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway in which the amino acid phenylalanine is used to produce 4-coumaroyl-CoA. This can be combined with malonyl-CoA to yield the true backbone of flavonoids, a group of compounds called chalcones, which contain two phenyl rings. Conjugate ring-closure of chalcones results in the familiar form of flavonoids, the three-ringed structure of a flavone. The metabolic pathway continues through a series of enzymatic modifications to yield flavanones → dihydroflavonols → anthocyanins. Along this pathway, many products can be formed, including the flavonols, flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins (tannins) and a host of other various polyphenolics.
In enzymology, a 6'-deoxychalcone synthase (EC 2.3.1.170) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acridone synthase (EC 2.3.1.159) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an anthocyanin 5-O-glucoside 6'''-O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an anthocyanin 6"-O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an anthranilate N-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a benzophenone synthase (EC 2.3.1.151) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a biphenyl synthase (EC 2.3.1.177) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a D-tryptophan N-malonyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.112) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavonol-3-O-beta-glucoside O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isoflavone-7-O-beta-glucoside 6"-O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pinosylvin synthase (EC 2.3.1.146) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trihydroxystilbene synthase (EC 2.3.1.95) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
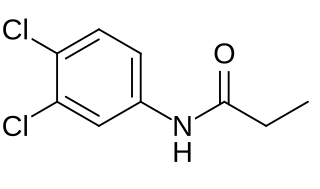
Propanil is a widely used contact herbicide. With an estimated use of about 8 million pounds in 2001, it is one of the more widely used herbicides in the United States. Propanil is said to be in use in approximately 400,000 acres of rice production each year.

Biochanin A is an O-methylated isoflavone. It is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as flavonoids. Biochanin A can be found in red clover in soy, in alfalfa sprouts, in peanuts, in chickpea and in other legumes.

3,4-Dichloroamphetamine (DCA), is an amphetamine derived drug invented by Eli Lilly in the 1960s, which has a number of pharmacological actions. It acts as a highly potent and selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) and binds to the serotonin transporter with high affinity, but also acts as a selective serotonergic neurotoxin in a similar manner to the related para-chloroamphetamine, though with slightly lower potency. It is also a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), as well as a very potent inhibitor of the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase which normally functions to transform noradrenaline into adrenaline in the body.
The biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes.
3,5,7-Trioxododecanoyl-CoA synthase (EC 2.3.1.206, TKS) is an enzyme with systematic name malonyl-CoA:hexanoyl-CoA malonyltransferase (3,5,7-trioxododecanoyl-CoA-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4-hydroxycoumarin synthase (EC 2.3.1.208, BIS2, BIS3) is an enzyme with systematic name malonyl-CoA:2-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA malonyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction




