| 75th Oregon Legislative Assembly | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
 Opening ceremonies of the session | |||||
| Overview | |||||
| Legislative body | Oregon Legislative Assembly | ||||
| Jurisdiction | Oregon, United States | ||||
| Meeting place | Oregon State Capitol | ||||
| Term | 2009–2010 | ||||
| Oregon State Senate | |||||
| Members | 30 Senators | ||||
| Senate President | Peter Courtney | ||||
| Majority Leader | Richard Devlin | ||||
| Minority Leader | Ted Ferrioli | ||||
| Party control | Democratic Party | ||||
| Oregon House of Representatives | |||||
| Members | 60 Representatives | ||||
| Speaker of the House | Dave Hunt | ||||
| Majority Leader | Mary Nolan | ||||
| Minority Leader | Bruce Hanna | ||||
| Party control | Democratic Party | ||||


The 75th Oregon Legislative Assembly convened beginning on January 12, 2009, for its biennial regular session. All of the 60 seats in the House of Representatives and half of the 30 seats in the State Senate were up for election in 2008; the general election for those seats took place on November 4.
Contents
- Sessions
- Notable legislation
- 2009 regular session
- 2010 supplemental session
- Senate members
- Senate committees
- Joint Ways & Means committee
- House members
- House committees
- See also
- References
- External links
The results:
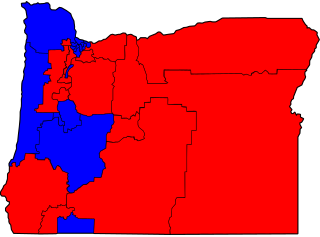
Senate: Democrats 18 seats, Republicans 12 seats
House: Democrats 36 seats, Republicans 24 seats
Democrats took control of the Senate in the 2004 elections, and of the House in the 2006 elections. The Senate had been controlled by Republicans since 1997 and the House since 1990.[ citation needed ] Many Republican legislators resigned or declined to run for reelection in 2008. Democrats lost one seat in the Senate, and gained five in the House.
The Republican House caucus released an agenda for the 2009 session; priorities included improving economic growth, bringing accountability to state government, improving the state's education system, extending health care and extending in-home care for seniors, enhancing public safety, and managing natural resources. [1] House Majority Leader Dave Hunt (D–Gladstone) responded to the agenda in July 2008, characterizing it as a departure from the failed policies of the George W. Bush administration, and stating that the problems Republicans seek to solve resulted from 14 years of Republican leadership. [2] The House Democrats also released an agenda for 2009. [3]
The legislature, in its 2009 regular session, worked to close a budget shortfall brought on by the economic recession. One critical factor in the legislature's work is the fact that Democrats hold three fifths of the seats in each chamber, theoretically providing the three-fifths supermajority support required by the Oregon Constitution for bills to increase revenue. [4]
In the effort to balance the budget, bills were passed to raise income taxes on corporations and wealthy individuals and households. This is expected to raise US$733 million in revenue over the next two years, which is meant to lessen the need to make spending cuts to state services and programs. [5] Opponents led an effort to force a statewide referendum on these increases, [5] which appeared as Measures 66 and 67 on the January 26, 2010 special election ballot. They were both passed by voters and will take effect February 25, 2010.
The 2009 Legislature passed two major new laws that had been unsuccessfully attempted for several prior years:
The Jobs & Transportation Act (the largest jobs bill in Oregon history) was passed with funding for the Sunrise Highway Corridor in Clackamas County, Newberg-Dundee Bypass, Woodburn/I-5 Interchange, Highway 62 extension in Medford, Beltline/I-5 Interchange in Eugene, and major new permanent annual road funding for all Oregon cities and counties. The Act also allocated $100 to ConnectOregon to improve air, rail, and marine infrastructure.
The Healthy Kids Act was passed to provide health insurance to 90,000 uninsured children and 30,000 low-income adults, which resulted in Oregon reducing the number of uninsured children by more than any other state.