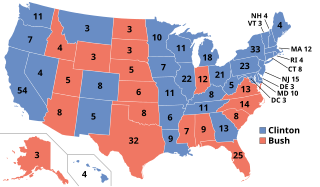
The 1992 United States presidential election was the 52nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1992. Democratic Governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent Republican President George H. W. Bush and independent businessman Ross Perot of Texas. The election marked the end of a period of Republican dominance in American presidential politics that began in 1968, and also marked the end of 12 years of Republican rule of the White House, as well as the end of the Greatest Generation's 32-year American rule and the beginning of the baby boomers' 28-year dominance until 2020. It was the last time the incumbent president failed to win a second term until 2020, when Donald Trump lost the election to Joe Biden; it was the first such occurrence since 1980.

The 1872 United States presidential election was the 22nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 5, 1872. Despite a split in the Republican Party, incumbent President Ulysses S. Grant defeated Democratic-endorsed Liberal Republican nominee Horace Greeley.

The 1884 United States presidential election was the 25th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1884. In the election, Governor Grover Cleveland of New York defeated Republican James G. Blaine of Maine. It was set apart by unpleasant mudslinging and shameful personal allegations that eclipsed substantive issues, such as civil administration change. Cleveland was the first Democrat elected President of the United States since James Buchanan in 1856, the first to hold office since Andrew Johnson left the White House in 1869, and the last to hold office until Woodrow Wilson, who began his first term in 1913. For this reason, 1884 is a significant election in U.S. political history, marking an interruption in the era when Republicans largely controlled the presidency between Reconstruction and the Great Depression.
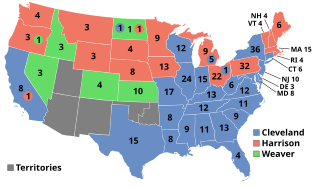
The 1892 United States presidential election was the 27th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1892. In a rematch of the closely contested 1888 presidential election, former Democratic President Grover Cleveland defeated incumbent Republican President Benjamin Harrison. Cleveland's victory made him the first and, to date, the only person in American history to be elected to a non-consecutive second presidential term. It was also the first of two times incumbents were defeated in consecutive elections—the second being Jimmy Carter's defeat of Gerald Ford in 1976, followed by Carter's subsequent loss to Ronald Reagan in 1980.

The 1896 United States presidential election was the 28th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1896. Former Governor William McKinley, the Republican nominee, defeated former Representative William Jennings Bryan, the Democratic nominee. The 1896 campaign, which took place during an economic depression known as the Panic of 1893, was a political realignment that ended the old Third Party System and began the Fourth Party System.

The 1900 United States presidential election was the 29th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 1900. In a re-match of the 1896 race, incumbent Republican President William McKinley defeated his Democratic challenger, William Jennings Bryan. McKinley's victory made him the first president to win a consecutive re-election since Ulysses S. Grant accomplished the same feat in 1872. Until 1956, this would be the last time in which an incumbent Republican president would win re-election after serving a full term in office. This election saw the fifth rematch in presidential history, something that would also not occur again until 1956. This was also the first rematch to produce the same winner both times.

The 1904 United States presidential election was the 30th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1904. Incumbent Republican President Theodore Roosevelt defeated the conservative Democratic nominee, Alton B. Parker. Roosevelt's victory made him the first president who ascended to the presidency upon the death of his predecessor to win a full term in his own right. This was also the second presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1860, 1920, 1940, 1944, and 2016.

The 1908 United States presidential election was the 31st quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1908. Republican Party nominee William Howard Taft defeated three-time Democratic nominee William Jennings Bryan.
The Liberal Party of New York is a political party in New York. Its platform supports a standard set of socially liberal policies, including abortion rights, increased spending on education, and universal health care.

The Conservative Party of New York State is an American political party founded in 1962 following conservative dissatisfaction with the Republican Party in New York. Running on the Conservative Party line, James L. Buckley won election to the U.S. Senate in 1970 and served for one term. Since 2010, the party has held "Row C" on New York ballots—the third-place ballot position, directly below the Democratic and Republican parties—because it received the third-highest number of votes of any political party in the 2010, 2014 and 2018 New York gubernatorial elections. The party is known for its strategy of attempting to influence the Republican Party in a more conservative direction.
The United Citizens Party (UCP) was first organized in 1969 in the U.S. state of South Carolina in response to the state Democratic Party's opposition to nominating black candidates. The party's objective was to elect blacks to the legislature and local offices in counties with black majority populations. The party ran candidates in 1970 and 1972; as a result in 1970 the first three black candidates were elected to the South Carolina House of Representatives since Reconstruction.

The American Labor Party (ALP) was a political party in the United States established in 1936 that was active almost exclusively in the state of New York. The organization was founded by labor leaders and former members of the Socialist Party of America who had established themselves as the Social Democratic Federation (SDF). The party was intended to parallel the role of the British Labour Party, serving as an umbrella organization to unite New York social democrats of the SDF with trade unionists who would otherwise support candidates of the Republican and Democratic parties.

The Independence Party is a political party in the U.S. state of New York. The party was founded in 1991 by Gordon Black, Tom Golisano, and Laureen Oliver and acquired ballot status in 1994. They lost their ballot status in 2020 under a change in the New York state election law that required at least 130,000 votes on the party line every two years. Although often associated with Ross Perot, as the party came to prominence in the wake of Perot's 1992 presidential campaign, it was created prior to Perot's run. In 2020, it affiliated with the Alliance Party, but disaffiliated in 2021. It used to have one elected member of the New York State Assembly, Fred Thiele, until Thiele switched his party affiliation to the Democratic Party in 2022. On December 9, 2022, New York governor Kathy Hochul signed S1851A, banning the use of the words "Independent" and "Independence" from use in political party names in New York state.

The results of elections in the state of New York have tended to be more Democratic-leaning than in most of the United States, with in recent decades a solid majority of Democratic voters, concentrated in New York City and some of its suburbs, including Westchester County, Rockland County and Long Island's Nassau county, and in the cities of Buffalo, Rochester, Syracuse, Albany, and Ithaca.

In New York State, to qualify for automatic ballot access, a party must qualify every two years by receiving the greater of 130,000 votes or 2% of the vote in the previous gubernatorial election or presidential election. In years with a gubernatorial election or presidential election a party must run a gubernatorial candidate or a presidential candidate to be eligible for automatic ballot access; if 130,000 voters vote for that candidate on their party line, they have qualified the party for the next two years until the following presidential or gubernatorial general election whichever one comes first. A party that is not qualified may run candidates by completing a petition process. Parties are also allowed to cross-endorse candidates, whose votes are accumulated under electoral fusion, but any parties must cross-endorse both the governor and lieutenant governor candidates for fusion to apply. Parties that are already qualified must issue a Wilson Pakula authorization if they cross-endorse someone not enrolled in that party; there are no restrictions on who can be nominated on a non-qualified ballot line, as these lines are determined by filing petitions.
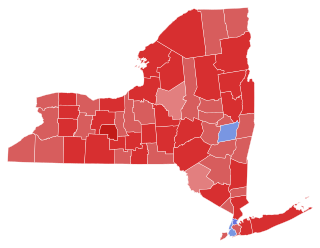
The 1946 New York state election was held on November 5, 1946, to elect the governor, the lieutenant governor, the state comptroller, the attorney general, a U.S. Senator, the chief judge and an associate judge of the New York Court of Appeals, as well as all members of the New York State Assembly and the New York State Senate.
A Wilson Pakula is an authorization given by a political party to a candidate for public office in the State of New York that allows the candidate not registered with that party to run as its candidate in a given election.

The 1896 United States presidential election in Louisiana took place on November 3, 1896. All contemporary 45 states were part of the 1896 United States presidential election. State voters chose eight electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.
From 1894 to 1900 the North Carolina Republican Party and the Populist Party collaborated via electoral fusion to compete against the North Carolina Democratic Party. This political coalition was dubbed Fusionism.

Elections are held in Syracuse, New York to election the city's mayor. Currently, these elections are regularly scheduled to be held once every four years, with the elections taking place in the off-year immediately after United States presidential election years.













