
Wake-on-LAN is an Ethernet or Token Ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened from sleep mode by a network message. It is based upon AMD's Magic Packet Technology, which was co-developed by AMD and Hewlett-Packard, following its proposal as a standard in 1995 – The standard saw quick adoption thereafter through IBM, Intel and others.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer: the layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium. The shapes and properties of the electrical connectors, the frequencies to transmit on, the line code to use and similar low-level parameters, are specified by the physical layer.

A network interface controller is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.

In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components on one or more integrated circuits that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. The chipset is usually found on the motherboard of computers. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance. Sometimes the term "chipset" is used to describe a system on chip (SoC) used in a mobile phone.

The DECstation was a brand of computers used by DEC, and refers to three distinct lines of computer systems—the first released in 1978 as a word processing system, and the latter two both released in 1989. These comprised a range of computer workstations based on the MIPS architecture and a range of PC compatibles. The MIPS-based workstations ran ULTRIX, a DEC-proprietary version of UNIX, and early releases of OSF/1.

On older personal computer motherboards, the southbridge is one of the two chips in the core logic chipset, handling many of a computer's input/output functions. The other component of the chipset is the northbridge, which generally handles onboard control tasks.

The SPARCstation 1 is the first of the SPARCstation series of SPARC-based computer workstations sold by Sun Microsystems. The design originated in 1987 by a Sun spin-off company, UniSun, which was soon re-acquired. The SPARCstation 1 has a distinctive slim enclosure and was first sold in April 1989, with Sun's support ending in 1995.

The NCR 53C9x is a family of application-specific integrated circuits (ASIC) produced by the former NCR Corporation and others for implementing the SCSI bus protocol in hardware and relieving the host system of the work required to sequence the SCSI bus. The 53C9x was a low-cost solution and was therefore widely adopted by OEMs in various motherboard and peripheral device designs. The original 53C90 lacked direct memory access (DMA) capability, an omission that was addressed in the 53C90A and subsequent versions.

A Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) is a transceiver which converts signals on an Ethernet cable to and from Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) signals.

The SPARCstation 20 or SS20 is a discontinued Sun Microsystems workstation introduced in March 1994 based on the SuperSPARC or hyperSPARC CPU. It is one of the last models in the SPARCstation family of Sun "pizza box" computers, which was superseded by the UltraSPARC design in 1995.

SPARCstation 5 or SS5 is a workstation introduced by Sun Microsystems in March 1994. It is based on the sun4m architecture, and is enclosed in a pizza-box chassis. Sun also offered a SPARCserver 5 without a framebuffer. A simplified, cheaper version of the SS5 was released in February 1995 as the SPARCstation 4. Sun also marketed these same machines under the "Netra" brand, without framebuffers or keyboards and preconfigured with all the requisite software to be used as web servers. An estimated 400,000+ SPARCstation 5s were sold.

DEC 3000 AXP was the name given to a series of computer workstations and servers, produced from 1992 to around 1995 by Digital Equipment Corporation. The DEC 3000 AXP series formed part of the first generation of computer systems based on the 64-bit Alpha AXP architecture. Supported operating systems for the DEC 3000 AXP series were DEC OSF/1 AXP and OpenVMS AXP.

The SPARCstation 2, or SS2 is a SPARC workstation computer sold by Sun Microsystems. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is implemented in a pizza box form factor.
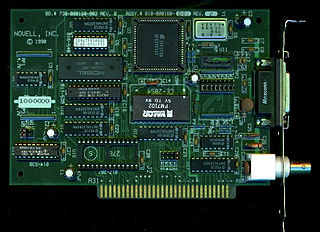
The NE1000 and NE2000 are members of an early line of low cost Ethernet network cards introduced by Novell in 1987. Their popularity had a significant impact on the pervasiveness of networks in computing. They are based on a reference design from National Semiconductor using their 8390 Ethernet chip.

The SPARCclassic is a workstation introduced by Sun Microsystems in November 1992. It is based on the sun4m architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis. It shares the code name Sunergy with the SPARCclassic X, SPARCstation LX, and SPARCstation ZX. It was replaced by the SPARCstation 4 in February 1994.
The SPARCstation LX is a workstation that was designed, manufactured, and sold by Sun Microsystems. Introduced in November 1992, it is based on the sun4m architecture and enclosed in a lunchbox chassis. It shares the code name Sunergy with the low-end range of SPARCclassic, SPARCclassic X, and SPARCstation ZX.

The SPARCstation IPC is a workstation sold by Sun Microsystems, introduced July 1990. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis.

The SPARCstation IPX is a workstation that was sold by Sun Microsystems, introduced July 1991. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis.

3Com 3c509 is a line of Ethernet IEEE 802.3 network cards for the ISA, EISA, MCA and PCMCIA computer buses. It was designed by 3Com and put on the market in 1992, followed by the improved version 3c509B in 1994.



















