
3Com 3c509 is a line of Ethernet IEEE 802.3 network cards for the ISA, EISA, MCA and PCMCIA computer buses. [1] It was designed by 3Com and put on the market in 1992, followed by the improved version 3c509B in 1994. [1] [2]

3Com 3c509 is a line of Ethernet IEEE 802.3 network cards for the ISA, EISA, MCA and PCMCIA computer buses. [1] It was designed by 3Com and put on the market in 1992, followed by the improved version 3c509B in 1994. [1] [2]
The 3Com 3c5x9 family of network controllers has various interface combinations of computer bus including ISA, EISA, MCA, and PCMCIA. For network connection, 10BASE-2, AUI and 10BASE-T are used.
Physical card configurations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
B = On ISA and PCMCIA, adapter numbers indicate that these adapters are part of the second generation of the Parallel Tasking EtherLink III technology. [1] |
The DIP-28 (U1) EPROM for network booting may be 8, 16, or 32 KB in size. [1] This means EPROMs of type 64, 128, and 256 kbit (2^10) are compatible, like the 27C256.
Boot ROM address is located between 0xC0000 - 0xDE000. [1]
The Etherlink III 3C509B-Combo is registered with the FCC ID DF63C509B. The main components on the card are Y1: crystal oscillator 20 MHz, U50: coaxial transceiver interface DP8392, U4: main controller 3Com 9513S (or 9545S etc.), U6: 8 kB 70 ns CMOS static RAM, U1: DIP-28 27C256 style EPROM for boot code, U3: 1024 bit 5V CMOS Serial EEPROM (configuration).
Detailed teardown |
|---|
Label: Etherlink III (C) 1994 3C509B-C ALL RIGHTS RESERVED ASSY 03-0021-001 REV-A FCC ID: DF63C509B Barcode: EA=0020AFDCC34C SN=6AHDCC34C MADE IN U.S.A. R = Resistor C = Capacitor L = Inductance Q = Transistor CR = Transistor FL = Transformer T = Transformer U = Integrated circuit J = Jumper or connector VR F FL70: Pulse transformer bel9509 A 0556-3873-03 * HIPOTTED Y1: 20 MHz crystal 20.000M 652DA U50: P9512BR DP8392CN Coaxial Transceiver Interface T50: Pulse transformer, pinout: 2x8 VALOR ST7033 x00: Pulse transformer VALOR PT0018 CHINA M 9449 C U4: Plastic package 33x33 pins Parallel Tasking TM 3Com 40-0130-002 9513S 22050553 AT&T 40-01302 Another chip with the same function: 40-0130-003 9545S 48324401 AT&T 40-01303 U6: 8192 x 8-bit 70 ns CMOS static RAM HY 6264A LJ-70 9509B KOREA Another chip with the same function: CY6264-70OSC (photo) U1: Boot ROM DIP-28 EPROM 8, 16, or 32 KB (27/28C256) for boot code. U3: 256 Bit/1K 5.0V CMOS Serial EEPROM B 52AH 93C46 M8 Q41: N-Channel Logic level Power MOSFET 60V, 11A, 107 mΩ (using ASSY 03-0021-004 due to obscured view) F3055L 96 45 (H)H VR41: 3-Terminal 0.5 A Negative Voltage Regulator (-5V) in D2PAK KA79 M05 ASSY 03-0021-004 REV-B has written on it: U.S. Patents: U.S. patent 5,307,459 |
Connector for the computer bus: ISA 16-bit
Connections for networking: 10BASE-T (8P8C), AUI (DA-15), 10BASE2 (BNC)
Some of the possible ISA I/O bases are 0x280, 0x300, 0x310, 0x320, 0x330, 0x340, 0x350. And IRQ 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12. The driver for OpenBSD, [3] NetBSD and FreeBSD is "ep"; [4] [5] for Linux it is "eth". [6] [7]
3c509B-C from 1996 specify the use of U.S. patent 5,307,459 with a priority date of 1992-07-28.
The patent describes a method where a data transfer counter triggers a threshold logic that generates an early indication or interrupt signal before the transfer is completed. The adapter also writes timing information into status registers such that a device driver can optimize for any latency. [8]

In computing, BIOS is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the booting process. The BIOS firmware comes pre-installed on an IBM PC or IBM PC compatible's system board and exists in some UEFI-based systems to maintain compatibility with operating systems that do not support UEFI native operation. The name originates from the Basic Input/Output System used in the CP/M operating system in 1975. The BIOS originally proprietary to the IBM PC has been reverse engineered by some companies looking to create compatible systems. The interface of that original system serves as a de facto standard.
Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) is the network layer protocol in the IPX/SPX protocol suite. IPX is derived from Xerox Network Systems' IDP. It also has the ability to act as a transport layer protocol.

Apple Attachment Unit Interface (AAUI) is a mechanical re-design by Apple of the standard Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) used to connect computer equipment to Ethernet. The AUI was popular in the era before the dominance of 10BASE-T networking that started in the early 1990s; the AAUI was an attempt to make the connector much smaller and more user friendly, though the proprietary nature of the interface was also criticized.

In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common.

In computing, an expansion card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer's motherboard to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard.

A Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) is a transceiver which converts signals on an Ethernet cable to and from Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) signals.

QEMU is a free and open-source emulator. It emulates a computer's processor through dynamic binary translation and provides a set of different hardware and device models for the machine, enabling it to run a variety of guest operating systems. It can interoperate with Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) to run virtual machines at near-native speed. QEMU can also do emulation for user-level processes, allowing applications compiled for one architecture to run on another.

The SPARCstation 20 or SS20 is a discontinued Sun Microsystems workstation introduced in March 1994 based on the SuperSPARC or hyperSPARC CPU. It is one of the last models in the SPARCstation family of Sun "pizza box" computers, which was superseded by the UltraSPARC design in 1995.

The SPARCstation 10 is a workstation computer made by Sun Microsystems. Announced in May 1992, it was Sun's first desktop multiprocessor. It was later replaced with the SPARCstation 20.

SPARCstation 5 or SS5 is a workstation introduced by Sun Microsystems in March 1994. It is based on the sun4m architecture, and is enclosed in a pizza-box chassis. Sun also offered a SPARCserver 5 without a framebuffer. A simplified, cheaper version of the SS5 was released in February 1995 as the SPARCstation 4. Sun also marketed these same machines under the "Netra" brand, without framebuffers or keyboards and preconfigured with all the requisite software to be used as web servers. An estimated 400,000+ SPARCstation 5s were sold.
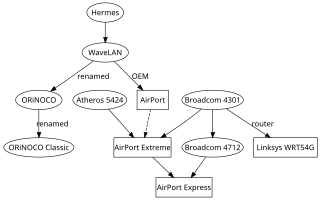
WaveLAN was a brand name for a family of wireless networking technology sold by NCR, AT&T, Lucent Technologies, and Agere Systems as well as being sold by other companies under OEM agreements. The WaveLAN name debuted on the market in 1990 and was in use until 2000, when Agere Systems renamed their products to ORiNOCO. WaveLAN laid the important foundation for the formation of IEEE 802.11 working group and the resultant creation of Wi-Fi.

The SPARCstation 2, or SS2 is a SPARC workstation computer sold by Sun Microsystems. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is implemented in a pizza box form factor.
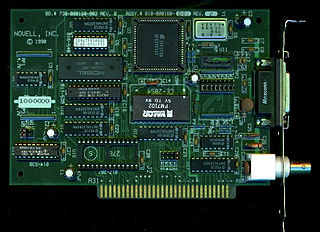
The NE1000 and NE2000 are members of an early line of low cost Ethernet network cards introduced by Novell in 1987. Their popularity had a significant impact on the pervasiveness of networks in computing. They are based on a reference design from National Semiconductor using their 8390 Ethernet chip.

The Apple Communication Slot, or Comm Slot, is an internal expansion data interface (slot) found in Apple Macintosh computers from the early to mid-1990s. It was designed as an inexpensive way to add communication expansion cards like network adapters or modems to Macs and Power Macs.
HP X-Terminals are a line of X terminals from Hewlett Packard introduced in the early- to mid-1990s, including the 700/X and 700/RX, Envizex and Entria, and the Envizex II and Entria II. They were often sold alongside PA-RISC-based HP 9000 Unix systems. The primary use case was connecting several graphical consoles to a single server or workstation to allow multiple users access the same (expensive) processing system from terminal systems. These X-Terminals all allowed high-resolution, color-graphics access to the main server from which they downloaded their operating system and necessary program files. All models featured limited expandability, in most cases additional I/O options for peripherals and memory for more programs or local storage. HP did not use its own PA-RISC platform for these systems, the first design used an Intel CISC processor, while all later systems used RISC platforms, first Intel i960 and later the popular MIPS.

AMD Lance Am7990 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet media access controller (MAC) controller were introduced in 1985. Its architecture is the basis for AMD's PCnet Family of highly integrated single-chip Ethernet controllers. The one exception is the Am79C940 MAC. The Am7990 chip was fabricated in NMOS technology and has no integrated Manchester encoder/decoder (ENDEC) nor does it have an integrated 10BASE-T transceiver.

The SPARCclassic is a workstation introduced by Sun Microsystems in November 1992. It is based on the sun4m architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis. It shares the code name Sunergy with the SPARCclassic X, SPARCstation LX, and SPARCstation ZX. It was replaced by the SPARCstation 4 in February 1994.

The SPARCstation IPC is a workstation sold by Sun Microsystems, introduced July 1990. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis.

The SPARCstation IPX is a workstation that was sold by Sun Microsystems, introduced July 1991. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis.

Accton Technology Corporation is a Taiwanese company in the electronics industry that primarily engages in the development and manufacture of networking and communication solutions, as an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or original design manufacturer (ODM) partner.