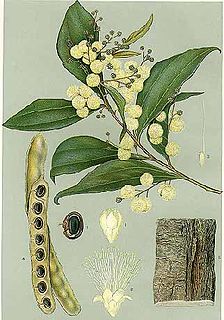
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia cognata, commonly known as bower wattle, river wattle or narrow-leaved bower wattle, is a tree or shrub species that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia obliquinervia, known colloquially as mountain hickory or mountain hickory wattle, is a species of Acacia that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia caesiella, commonly known as tableland wattle, bluebush wattle or blue bush, is a shrub or small tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia gloeotricha is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia georgensis, commonly known as Bega wattle or Dr George Mountain wattle, is a species of Acacia native to southeastern Australia. It was one of eleven species selected for the Save a Species Walk campaign in April 2016 when scientists walked 300 km to raise money for collection of seeds to be prepared and stored at the Australian PlantBank at the Australian Botanic Garden Mount Annan.

Acacia falciformis, also commonly known as broad-leaved hickory, hickory wattle, mountain hickory, large-leaf wattle, tanning wattle and black wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia
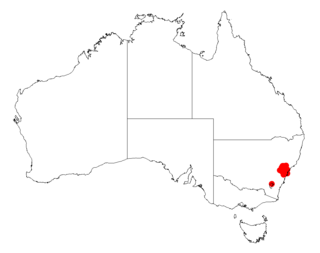
Acacia saliciformis is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia siculiformis, commonly known as dagger wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia torringtonensis is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia kybeanensis, commonly known as kybean wattle or kybeyan wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia kydrensis, commonly known as Kydra wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia blakei, commonly known as Blake's wattle or Wollomombi wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia cataractae is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia cretata is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia curranii, also known as curly-bark wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia. It is listed as vulnerable under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia gracilenta is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north Australia.

Acacia mariae, commonly known as golden-top wattle or crowned wattle, is a species of wattle native to central New South Wales.

Acacia sericoflorais a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia rhigiophylla, commonly known as dagger-leaf wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to southern Australia.



















