
Acacia neriifolia, also known as the oleander wattle, silver wattle or pechy wattle, is a tree in the genus Acacia native to north eastern Australia. It is common in the Moonbi Ranges.

Acacia bakeri, known as the marblewood, white marblewood, Baker's wattle or scrub wattle, is one of the largest of all acacias, growing to 40 m (130 ft) tall. It is a long-lived climax rainforest tree from eastern Australia. Unlike most acacias, fire is not required for seed germination. This tree is considered vulnerable to extinction. Its former habitat is lowland subtropical rainforest, which has been mostly cleared in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Acacia flexifolia, commonly known as bent-leaf wattle or small winter wattle, is a shrub species that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia cognata, commonly known as bower wattle, river wattle or narrow-leaved bower wattle, is a tree or shrub species that is endemic to south eastern Australia.
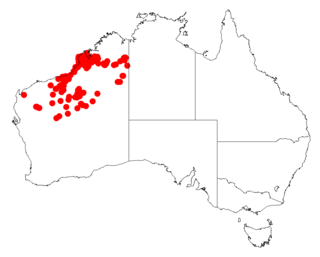
Acacia eriopoda, commonly known as the Broome pindan wattle and the narrow-leaf pindan wattle, is a species of wattle in the legume family that is native to northern Western Australia. It is also known as Yirrakulu to the Nyangumarta people.

Acacia jibberdingensis, also known as Jibberding wattle or willow-leafed wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia websteri is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia jennerae is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to arid parts of central Australia.

Acacia dawsonii commonly known as Dawson's wattle or poverty wattle or mitta wattle, is a flowering shrub in the family Fabaceae. It has yellow ball flowers, short stalks and is found along parts of the east coast of Australia.
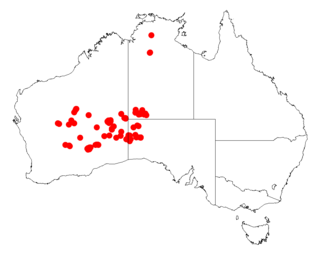
Acacia helmsiana, commonly known as Helm's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to arid areas of central and western Australia.
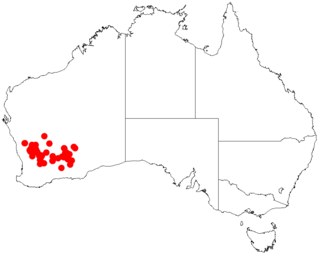
Acacia inceana is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia havilandiorum, also known as Haviland's wattle or needle wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to areas in South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria.
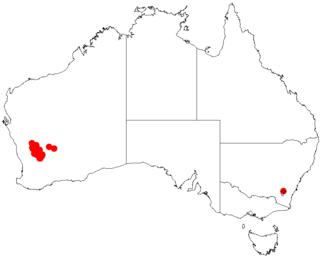
Acacia obtecta is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia.

Acacia trineura, known colloquially as three-nerve wattle or three nerved wattle or green wattle, is a species of Acacia native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia barringtonensis, commonly known as Barrington wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae endemic to New South Wales.
Acacia centrinervia, commonly known as hairy white wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of eastern Australia.

Acacia confluens, commonly known as wyrilda, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to central Australia.
Acacia forsythii, commonly known as Warrumbungle Range wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of eastern Australia.

Acacia jucunda, commonly known as yetman wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia and is considered to be endangered in New South Wales.

Acacia pilligaensis, commonly known as Pillaga wattle or pinbush wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.



















