
Acacia enterocarpa, commonly known as jumping jack wattle, is a shrub species that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia flexifolia, commonly known as bent-leaf wattle or small winter wattle, is a shrub species that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia notabilis, known colloquially as mallee golden wattle, Flinders wattle or stiff golden wattle, is a species of Acacia native to Australia.

Acacia continua, or the thorn wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Alatae. It native to New South Wales and South Australia.

Acacia acuaria is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Western Australia.
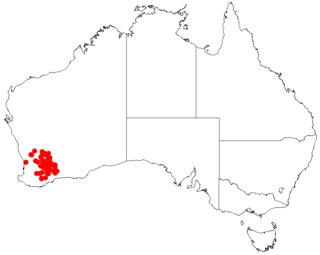
Acacia acutata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae where it is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia baxteri, commonly known as Baxter's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae, and is endemic to the south west of Western Australia.

Acacia bidentata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae and is native to Western Australia.

Acacia brachyclada is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae.

Acacia erinacea, also known as prickly wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to Western Australia.

Acacia gonophylla, also known as rasp-stemmed wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western parts of Australia.

Acacia leptopetala is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia pachypoda is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia scalena is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia havilandiorum, also known as Haviland's wattle or needle wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to areas in South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria.

Acacia nyssophylla, commonly known as pin bush, wait a while and spine bush, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a large area of central and south-western and southern Australia.

Acacia uncinella is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia warramaba is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia dictyocarpa is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.
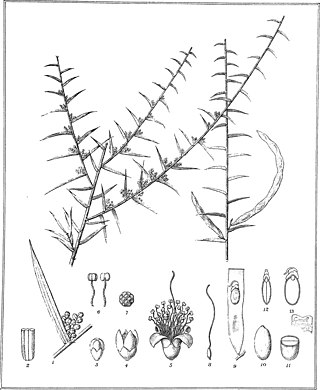
Acacia rhigiophylla, commonly known as dagger-leaf wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to southern Australia.




















